Notes - Mr. Barnes' Classroom
advertisement

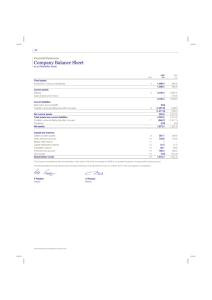
Accounting 11 Why study Accounting? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4kIWqD K4j5Q Top 10 Reasons why … • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zUD2MF YJf38 Unit 1: Financial Position The Purpose of Accounting • to provide financial information for decision making. Every accounting system must: • Record the day-to-day financial activities of the business • Summarize and report information in financial statements for analysis and decision making. Unit 1: Financial Position Purpose: helps determine whether you should grant a loan or not Total value of Items owned - Total owed to = Personal Net Creditors worth Creditors – are people or businesses that extended credit when goods and services were purchased or who loaned money used to purchase possessions. Personal Net Worth – is the difference between the cost of items owned and the debts owed. Calculating Financial Position Items owned by Lara Chari Cash Government Bonds Clothing Furniture Equipment Automobile Debts owed to creditors by Lara Chari $ 4 000 5 000 3 000 15 000 10 000 20 000 $57 000 Credit Card Debt Bank Loan Total value of Items owned - Total owed to Creditors $57 000 - $12 000 = = $ 2 000 10 000 $12 000 Personal Net worth $45 000 Accounting Terminology • Assets: are items of value owned by a business or person • Liabilities: are the debts of a business or a person. • Personal equity: is a person’s net worth. (a positive net worth is good…the greater the value, the more likely you will get a loan) Assets • • items of value owned by a person or business Something a person or business owns. Categories: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cash - currency, cheques, money orders, bank deposits. Accounts Receivable - total amount due from customers. Government Bonds Furniture Office Equipment Automobiles - cars, trucks Land Buildings How does a business acquire these assets? 1. Borrowing Creditor - a person/business to whom money or goods is owed. 2. Investment by the owner(s) Debtor - a person/business who owes money or goods. Borrowing = Debt = Liabilities • Liabilities - the debts of a business or person. - something a business or person owes. • Categories: 1. Loans 2. Accounts Payable - amounts owing to creditors for purchases of goods and services. 3. Mortgage - a long-term debt where the building or land is used as collateral for the debt. Investment by the owner(s) = Owner’s Equity • Owner’s Equity - claim of the owner against the asset of the business. • Personal Equity (Net Worth) - the difference between the cost of items owned and debts owed. Questions 1-4 Page (12-13) • Apply your knowledge Balance Sheet Equation - The financial position of a person or a business can be stated in the form of a balance sheet equation: (basis for much of the accounting theory you will learn) Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity A = L + OE $57 000 = $12 000 + $45 000 $57 000 = $57 000 Example: Balance Sheet – Template in Workbook See Figure 1.1 – Page 4 – Personal balance sheet Balance Sheet - Excel Template Business Entity Principle • Requires that each business be considered a separate entity, and that the financial data for the business be kept separate from the owner’s personal financial data. Company Balance Sheet • is a formal report or statement that shows the financial position of the business at a certain date. A = L + • Left side must equal the Right side • See Figure 1.2 OE More Accounting Terminology • Accounts Receivable: refers to the total amount due from debtors. (customers) “ASSET” • Accounts payable: refers to the total amount owed to creditors for the purchase of “Liability goods and services by the business ” • Mortgage Payable: time to repay is longer (typically larger in amount) “Liability ” Balance Sheet Preparation • Step 1: Prepare Statement Heading – Who, What, When? • Step 2: List Assets • Step 3: List Liabilities • Step 4: Show Owner’s Equity - See Diagrams on Pages 7-8. Facts to Remember 1) Totals of the left and right side must be written on the same line. 2) No abbreviations. 3) No corrections. 4) Dollar sign should be aligned and placed: - beside the first figure in each column - beside the final total on both sides of the statement. See Examples Page 10 Order of Items on Balance Sheet • Assets (two types) 1) Last a short time 2) Last a long time - listed in order of their liquidity - listed in order of their useful life to the business, with the longest lasting listed first. • Liabilities – are listed according to the date they are due to be paid, that it, their maturity date. – From shortest to longest term. • Ex: Accounts Payable (30 days), Bank Loan (1-5 years), Mortgage Payable (within 25 years) Cost Principle • when an asset is obtained, its value is recorded at the actual cost to the business. (does not rise…even if it is thought that the value of the asset has increased) Accounting Information is Used to Make Decisions: Creditors Government Owners Accounting Information Management Investors Common Recording Practices • 1) Ruled Accounting Paper – dollar signs, commas, spaces, and decimals are not used. • 2) Single Line – Addition or Subtraction. • 3) Double Line – Final Totals • 4) Opposite of #1 • 5) No Abbreviations. (unless in official name) • 6) Accounting records must be neat & legible! GAAP – Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (standard accounting rules and guidelines) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) The Purpose of Accounting The Business Entity Concept The Cost Principle Liquidity Order Maturity Date Rule (details given for each one on page 20 in your textbook) Apply your knowledge! • Page 13-14 (#5-8)