sci-ch-7-lesson-4 - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
advertisement

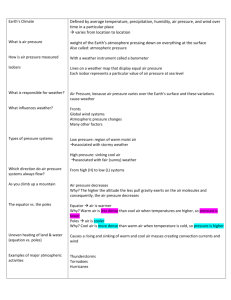
Science Notes – Chapter 7 Lesson 4: Climate (pg. 190-195) Vocabulary: 1. climate- the average weather patter of a region over time 2. climate regions- A region of land can have certain patters of temperature, humidity, precipitation and wind 3. latitude- lines that run east and west across a map. Latitude is a measure of how far a place is from the equator (0 degrees) 3. current- a flow of a gas or a liquid 4. altitude- how high a place is above sea level Climate and Climate Regions: Climate is not the same everywhere, and is not the same as weather o For example: the climate of Arizona is warm and dry all year with rarely any snow or rain. Climate Regions ex: Polar Regions have cold climates with little precipitation and Tropical Regions are warm and rainy. What determines climate? 1. Latitude Climate near the equator are often warm and rainy The climate between the equator and poles is mild The climate near the poles is cold all year 2. Global winds These winds move air between the equator and the poles Warm air near equator rises and moves towards poles Cold air near the poles sinks and moves towards the equator 3. Ocean currents Some ocean currents move warm water from the equator to the poles Others move cold water from the poles towards the equator 4. Distance from water Land and water warm up and cool down at different speeds. Water gets hotter more slowly and cools more slowly than land Climates near lakes and oceans are different than climates farther inland Climates near water have more clouds and rain, have cooler summers, and warmer winters How do mountains affect climate? Air is colder at higher altitudes Altitude changes as you move up the mountains Climate at bottom is hotter than on top By the time air mass gets over the mountain, the air is dry = one side of mountain has a wet climate, the other side has a dry climate * Please be sure to re-read the chapter, and study the quick-checks! *