Chapter 5
Attitudes Can Shape Your Life
Learning Objectives
After studying Chapter 5, you will be able to:
Understand
the impact of employee attitudes on the
success of individuals as well as organizations.
List
and explain the ways people acquire attitudes.
Describe
attitudes that employers value.
Learn
how to change your attitudes and help others
change their attitudes.
Understand
what adjustments organizations are
making to develop positive employee attitudes.
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–2
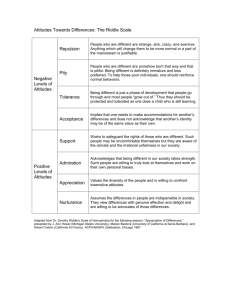
The Importance of Attitudes
• Attitude Defined:
– A thought, accepted as true, that leads one to
think, feel or act positively or negatively toward
a person, idea or event
– An emotional readiness to behave in a
particular way
– You learn them and can change them
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–3
FIGURE 5.1
The Relationship Among Core Values, Attitudes,
and Behaviors
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–4
Core Values Revisited
• Core Values
– Are unique values that an individual consistently
ranks higher than other values
– Are the building blocks of personality
– Provide answers to questions:
• What are the highest priorities in my life?
• Of these priorities, which do I value most
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–5
The Powerful Influence of Attitudes
• People with positive attitudes are more likely
to achieve personal and professional goals
• People with negative attitudes find it difficult
to achieve contentment or satisfaction in life
How do attitudes have an
impact in the workplace?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–6
The Information Age Mandates
Attitude Change
• Quick, accurate information and advanced
technology is not enough to retain customers
– Empathizers provide the balance between “high
tech” and “high touch” as we move from the
information age to the conceptual age
– Competitive advantage is now based on superior
customer service
What attitudes are important for strong
customer service personnel to have?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–7
How Attitudes Are Formed
• Socialization
– Process through which people are integrated
into a society by exposure to actions and
opinions of others
• Media Influences
How does the presentation of
messages in the news by the
media affect our attitudes?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–8
How Attitudes Are Formed
• Peer Groups
– Have a powerful influence on attitude during
adolescence, possibly stronger than adults
• Reference Groups
– Share a common interest that can influence
behavior, provide a point of comparison and
serve as a source of information
In what reference groups
do/could you belong?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–9
How Attitudes Are Formed
• Rewards and Punishment
– Attitudes are developed to minimize
punishment and maximize rewards
• Role Model Identification
– Someone that you admire or are likely to
emulate such as managers in organizations
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–10
How Attitudes Are Formed
Cultural Influences
• The sum total of knowledge, beliefs, values, and
customs that we use to adapt to our environment
What attitudes have you adopted from your:
-national culture?
-ethnic culture?
-regional culture?
-state culture?
-school culture?
-work culture?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–11
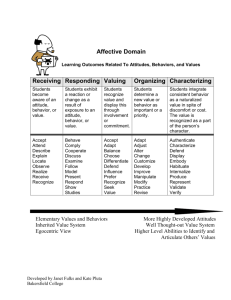
Attitudes Valued by Employers
Basic Interpersonal
Skills
Self-Motivation
Team Spirit
Valued
Attitudes
Openness to
Change
Appreciation of
Coworker Diversity
Personal
honesty
Health
Consciousness
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–12
How to Change Your Attitude
• Attitudes are hard but not impossible to
change; they foster achieving positive
results by helping a person:
– Choose happiness
– Embrace optimism
– Think independently
– Keep an open mind
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–13
How to Change Your Attitude
• Choose Happiness
– Happiness is the state of mind that
permits us to live life enthusiastically
– Perceptions of the situation are critical
Happy people
– more sociable
– flexible
– creative
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
Unhappy people
– self-focused
– socially withdrawn
– antagonistic
5–14
How to Change Your Attitude
• Embrace Optimism
– Optimistic thoughts give rise to good moods,
which help develop positive attitudes
– Avoid pessimism which leads to cynicism
Is “reality” all relative?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–15
How to Change Your Attitude
• Think for Yourself
– Avoid “group think” by not intermixing personal
and professional relationships
– Evaluate situations based on your values
• Keep an Open Mind
– Know that attitudes can persist in the face of
overwhelming evidence to the contrary
– Grow more flexible by exposing yourself to new
experiences and information
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–16
FIGURE 5.2
Serenity Prayer
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–17
Helping Others Change Attitudes
• Change attitudes by:
– Changing conditions that precede the behavior
– Changing the positive or negative
consequences that follow when the person
exhibits the behavior
Do you believe it’s possible to change
others’ attitudes? If so, under what
conditions?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–18
Organizations’ Efforts Toward
Improving Employees’ Attitudes
• Employees’ attitudes and performance
cannot be separated
• Workers’ attitudes are positively affected by:
– Respect and recognition
– Interesting work
– Skill development
Does pay affect attitude?
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–19
KEY TERMS
attitudes
empathizer
socialization
peer group
reference group
role model
culture
cynicism
© 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5–20