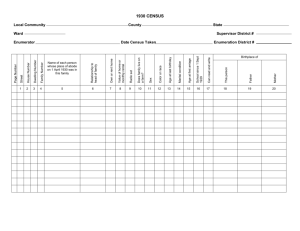
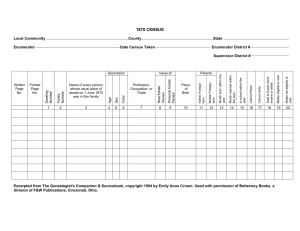
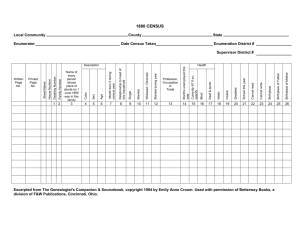
Census Data Management using Tablets for 2018 Algerian Census
advertisement

الجمهورية الجزائرية الديمقراطية الشعبية Ministère des Finances “Census Data Management using Tablets for the 2018 Algerian Census” DR. TARIK BOUREZGUE DIRECTOR, OFFICE FOR NATIONAL STATISTICS, ALGERIA ADDIS ABBEBA, OCTOBER 2015 PRESENTATION OUTLINE I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM II- STATISTICS PROCESS and STATISTICAL SYSTEM III- ICT USE: CURRENT STATUS IV- ICT USE: THE WAY FORWARD V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT CONCLUSION I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM HISTORY 1962: Creation of a Planning Institution with a Statistics Department. September 1962: Establishment of COCOES: coordination, control and statistical confidentiality. 1964: Creation of the National Committee in charge of First Population Census. 1971: Creation of the Commission for Census and Survey Statistics (CNRES). Mai 1971: Decree on Regulations, Coordination and Statistical obligations. 1982: Creation of The Office for National Statistics ( ONS). 1982: Dissolution of CNRES and transfer of its structures, resources and activities to ONS. 1994: Algerian Statistical Law (Legislative decree N°94-01, January 15th, 1994). 1995: ONS statutes reorganization (Executive decree N°95-159, June 3rd, 1995). I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM ALGERIAN STATISTICAL LAW GENERAL PRINCIPLES ORGANIZATION OF THE STATISTICAL SYSTEM STATISTICS CONFIDENTIALITY STATISTICS DISSEMINATION I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM ALGERIAN STATISTICAL LAW GENERAL PRINCIPLES Faculty for everyone to produce, process, analyze and disseminate statistical Information. Compliance with methodological and ethical standards of statistical practices. Coordination and standardization statistics. Any statistical information prepared by state services or have benefited from Statistics Registration is in the public domain. I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM ALGERIAN STATISTICAL LAW - ORGANIZATION OF THE STATISTICAL SYSTEM BODIES COORDINATION AND PRODUCTION The National Statistics Council (CNS) The Central Institution of Statistics (ONS) Private and Public Bodies of Statistics INSTRUMENTS AND STANDARD PROCEDURES The Statistics Identification Number (NIS) Statistics Registration (for Statistics Surveys) The National Statistics Program Codes and Classifications I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM ALGERIAN STATISTICAL LAW - STATISTICAL CONFIDENTIALITY Protection of individual information. Staff sworn to Professional Secrecy. The National Statistical Council may propose the classification of certain information as sensitive after review of reasons and referral of an institution. I- ALGERIAN STATISTICAL SYSTEM ALGERIAN STATISTICAL LAW - STATISTICAL DISSEMINATION Any publication of statistical data must be accompanied by elements necessary for an assessment of their validity and reliability. The publication of statistical data from non-registered surveys must be marked “Data from non-registered survey”. Any statistical publication derived from registered surveys should be recorded subject to Legal Deposit. II- STATISTICS PROCESS and STATISTICAL SYSTEM Surveys + Administrative Sources SNIS Structural statistics operations: The General Census of Population and Housing Labor Survey Income and Consumption Survey Economic Census The General Census of Agriculture The Municipal Survey SNIS: National Statistical information System III- ICT USE: CURRENT STATUS 2011 : - Use of the optical scanning technology for the exploitation of Economic Census questionnaires. - Use of CAPI in interviews of behavior of household consumption national survey. Since 2014 : Testing of use of PDA in CPI data collection. Since 2012 : Switching over of all publications to the website in order to move progressively towards a paperless environment. IV- ICT USE: THE WAY FORWARD 2015- 2019: Constitution of Institutional Memory Project through the use of digitization technologies. African Information Highway Project through the establishment of a Data Portal in collaboration with the African Bank for Development. RGPH (Population and Housing Census) 2018: use of ICT in mapping supervision and PDA in data collection. IV- DIGITAL SPACE: THE WAY FORWARD V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT For RGPH 2018: -50,000 agents will be recruited and trained as enumerators ; -13,000 agents will be recruited and trained as controllers; -The municipal delegates . V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT The enumerator Each enumerator will be equipped with a tablet for data entry and a paper district notebook that is provided by the municipal delegate. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT The controller Each controller is also equipped with a Notebook tablet (for an overall vision of the questionnaire) to: -verify the quality of work of the five enumerators, under his supervision, -have a status of the collection in the field and daily statistics on households surveyed and enumerator performance. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Authentication of enumerators and controllers: -Login lists (username and password) will be defined following the use of mobile chips’ PINs affected by the mobile operator. -The login could be defined as the concatenation of the wilaya, municipality and district codes (given at the conclusion of cartographic updates). V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Procedure for the enumerator: i. The enumerator connects to the census application via a 3G chip connected to the regional server, and this, through the login assigned by the mobile operator. ii. The enumerator should have the opportunity to fill in a new questionnaire, as well as to correct a questionnaire that has not been validated by his controller. (Only the enumerator has the ability to modify the questionnaire.) Household questionnaires are filled in a chronological order of questions and consistency checks. iii. The filled in questionnaire will be automatically put on a validation wait state. At the end of the interview, the enumerator performs a transfer operation as follows: i. A direct transfer to the secure database located at the regional data center, where 3G coverage is available. ii. In case of absence of mobile connection, an encrypted asynchronous backup is made to a SD card located at the tablet level (in a transfer queue state). Once connected, data is transferred automatically. iii. If the interview is not completed for force majeure reasons, the partial backup is saved directly onto the database. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Procedure for the controller: i. - The controller in turn connects via his login on the server in its region, through the supervision and monitoring application: He consults and verifies questionnaires awaiting validation in order to spot anomalies found on the basis of data that was collected from the questionnaire. A correct questionnaire moves to a validated state, otherwise it will be on update waiting status by the enumerator (back to household). ii. The controller also accesses the supervision and monitoring application to assess the progress of data collection of its enumerators in the field, their yields and the share of absent households, etc. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Flow of Information Chart V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Technical requirements A relational database management system such as SQL Server is needed to administer and manage the RGPH database to guarantee quality, continuity and confidentiality of information. A global database at the central site to store and retrieve real-time data entirety. An implementation of database levels at regional collection sites. Software installed at regional levels for supervision, control and monitoring of the implementation on the field. Entry applications for entering data collected on tablets as well as the transcript of paper questionnaires. (As per international recommendations, 10% of the questionnaires will be on paper as to take charge of the specific cases on the field.) Establishment of specialized interconnection links between the central site (headquarters) and various regional sites. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Information flow estimates 50 000 enumerators spread over the four regional annexes: - 17 819 enumerators for the central region. - 12 437 enumerators for the western region. - 16 749 enumerators for the eastern region. 2 995 enumerators for the southern region. 150 questionnaires per enumerator during the period of execution (average of 10 daily). 50 Ko per questionnaire and 15 days of census data collection on the field. - 890 950 Ko total for the central region. - 621 850 Ko total for the western region. - 837 450 Ko total for the eastern region. - 149 750 Ko total for the southern region. V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Challenges Consideration should be given to how and where the data are held on devices. Storage and Transport. Concerns about tablet screen brightness and breaking. Concerns about battery autonomy of tablets: (at least six hour autonomous and battery boosters for tablets.) Selection and training of enumerators and controllers. Maintaining data security. Immediate feedback on data quality. Adequate preparation: (Sufficient time must be allocated to designing and pretesting of the electronic questionnaire and to overall testing and debugging of the software, particularly for questionnaires in multiple languages and in a non-Latin script, as it is the case for Arabic in Algeria.). V- CENSUS ALGERIA 2018: USE OF ICT Perspectives We will be looking into: Implementing ICT into our surveys (household and business) as an integral part of our testing of the mobile census solution. Looking into Cloud Computing, software as a service, platform as a service, and infrastructure as a service, as a possibility. Explore the possibilities and the challenges to, post census, implement a population register and explore the option of internet based surveys/census. CONCLUSION New technology is not a magic potion, but it can help ONS achieve its mission more efficiently and effectively. “…In an uncharted world of boundless data, information designers are our new navigators. They are computer scientists, statisticians, graphic designers, producers and cartographers who map entire oceans of data and turn them into innovative visual displays, like rich graphs and charts, that help both companies and consumers cut through the clutter. These gurus of visual analytics are making interactive data synonymous with attractive data”. Source: The NY Times, “When the data struts its stuff”, April 2011. Questions, comments or suggestions bourezgue@ons.dz; or ons@ons.dz / stat@ons.dz . IN LOOKING FORWARD TO SEEING YOU ON OUR WEBSITE, www.ons.dz , THANKS!