PowerPoint
advertisement

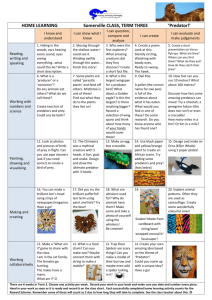
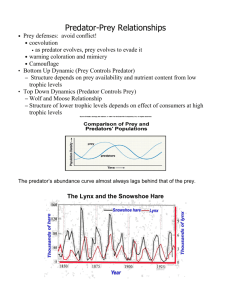
Communities & Biodiversity Communities Multicelled organism Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere Communities An interacting group of various species in a common location. For example, a forest of trees and undergrowth plants, inhabited by animals and rooted in soil containing bacteria and fungi, constitutes a biological community. Communities Structure arises from… Physical & chemical conditions of habitat Availability of food & resources (type, amount, etc.) History of habitat & species Traits that help species survive in habitat Interactions among species Physical disturbances Communities Niche— “profession” of a species that sets it apart from other species. Fundamental niche— Would happen even in absence of competitors or other limiting factors. Realized niche—Actual position taking into account competition & limiting factors; can change over time. Species Interactions Commensalism One species helped, other species not affected Bird & tree Barnacles & whales Remoras & sharks Species Ineractions Mutualism Both species benefit Ants & aphids Pollen & insects Sea anemones & fish Bacteria & larger organisms Horses & cecal bacteria Termites & hindgut bacteria Species Interactions Parasitism One species benefits, other is harmed Endoparasite—live inside the host Roundworms Malaria (Plasmodium) Ectoparasite—live on the host Lice Ticks Brood parasite—manipulate other animals to raise young Cuckoos Cowbirds Cuckoo bees & wasps Species Interactions Parasitism (cont.) Drain nutrients from host Using resources that host needs Weakened hosts more easily preyed upon Weakened hosts may not be able to forage Hosts may die Species Interactions Predation One species kills and feeds on another species Balanced relationship As prey increases or decreases, so does predator Predator-Prey Relationship Predation a strong factor in natural selection Some modifications in prey make them less likely to be preyed upon Predators also undergo selection to overcome prey’s defenses Prey Defenses Camouflage Blend into surroundings Avoid being seen (predator & prey) Prey Defenses Chemical Defense Bad-tasting—Monarch butterfly Toxic—Poison dart frog, scorpionfish Venomous—Coral snake Irritant—Skunk, bombardier beetle Often have bright coloration or specific behavior as a warning Prey Defenses Mimicry Closely resemble dangerous or unpalatable species Predator avoids due to perceived danger Prey Defenses Physical Defense Shell, armor—turtles, armadillos Spines, spikes—porcupines, hedgehogs, lizards Horns, antlers—rhinocerous, deer Prey Defenses Startle/Surprise Defenses Look fearsome or larger False eye spots—moths, caterpillars Neck frills—lizards, birds “Fluffing” hair or feathers—birds, mammals Vocal displays—hissing cockroach, cats, growling dogs Predator Armament Camouflage (tiger, leopard) Lures (anglerfish, snapping turtle) Heat sensors (pythons, vipers) Pack behavior (wolves, lions) Community Stability Communities usually reach stability Can be upset by new additions or subtractions Keystone species—species that has disproportionately large effect relative to its abundance Predators Sea star experiment Sea stars prey on several species Remove sea stars Mussels take over, crowd out other species Sea otters & sea urchins Community Stability Keystone species (cont.) Engineers Change the environment through actions Grizzly bears—transfer oceanic nutrients (salmon) to forest ecosystem Up to half of salmon captured ends up on forest floor Beavers—transform stream to pond or swamp Elephants—destroy trees, make room for grass Community Stability Introduced species Can upset balance May not have natural predators May not have competition Rabbits in Australia 24 introduced in 1859 for hunting By 1869 could kill 2,000,000 without affecting population Currently over 100 million Eat native plants, leads to large erosion Community Stability Introduced species (cont.) Zebra mussels Native to Russia & Caspian Sea First detected in Great Lakes in 1988 Suspect were attached to ship ballast, anchors, chains Invaded waterways Kill & outcompete native mussels Damage boats, harbors, power plants