Topic: Colligative Properties
advertisement

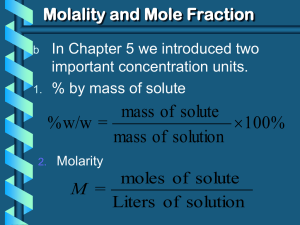
Topic: Colligative Properties Adding a non-volatile (doesn’t readily evaporate) solute affects… • • • • Conductivity (electrolytes) Freezing point Boiling point Vapor pressure Freezing Point Depression • Adding solute will lower the freezing point • Which one will lower the freezing point more? – NaCl or MgCl2 – Na+1 (aq) + Cl-1(aq) Mg+2 (aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) – 1 mol + 1 mol = 2 moles 1 mol + 2 mol = 3 moles Vapor Pressure Decreased • Solute particles at the surface get in the way of some solvent molecules evaporating Boiling Point Elevation • Adding solute will raise the boiling point • Which one will raise the boiling point more? – Sugar (C12H22O11) – C12H22O11 (aq) – 1 mol or salt (NaCl) Na+1 (aq) + Cl-1(aq) 1 mol + 1mol = 2 moles Boiling Point Freezing Point Vapor Pressure Depends on the # of moles dissolved in the solution and NOT on the type of particles The higher the concentration of solute in solvent, the more MP, BP, and VP are affect Which solution containing 1 mole of solute dissolved in 1000 g of water has the lowest freezing point? 1) C2H5OH(aq) 2) NaCl(aq) 3) KOH(aq) 4) CaCl2(aq) Be careful! What if the question asked which solution has the highest freezing point? C6H12O6 • Covalent • Dissolves as molecules C6H12O6(s) C6H12O6(aq) • 1 mole of sugar yields 1 mole of molecules NaCl • Ionic • Dissolves as ions • NaCl(s) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • 1 mole of salt yields 2 moles of ions. Get more particles from salt than sugar. MgCl2 • Ionic • Dissolves as ions • MgCl2(s) Mg2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) • 1 mole of salt yields 3 moles of ions