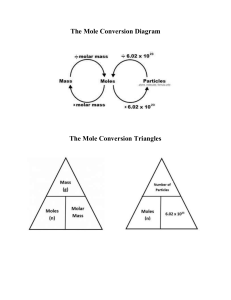
1- The mole fraction of He in gaseous solution prepared from (4 g of He) (6.5 g Ar) (10 g Ne) is ………… A) 0.7336 B) 0.09822 C) 0.2987 D) 1.6584 Answer = A 2-- A triple point: A) point where all three phases are unstable B) The point in phase diagram where solid , liquid and gas phases of substitution coexist at equilibrium C) three dimensional phase diagram D) Three places in phase where the solid, liquid and gas can coexist. Answer = B 3- Which one of the following is most soluble in hexane (C6H14)? A) CH3OH B) CH3CH2CH2OH D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH C) CH3CH2OH E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH Answer = E 4- Rank the following liquids in order of increasing boiling point (from lowest to highest): (He , NH3 , Ar , N2 ) A) He < NH3 < Ar < N2 C) He < N2 < Ar < NH3 B) He < NH3 < N2 < Ar D) He < Ar < N2 < NH3 Answer = C 5- In given first order reaction (A→ product), the initial concentration of A is 0.4 M, what is the concentration of A after 25 sec if the half – life of the reaction is 3 sec? A) 1.24 * 10 -3 Answer = A B) 2.66 * 10 -2 C) 0.05 D) 1.25 * 10 -2 6-- A catalyst can increase the rate of a reaction __________. A) By changing the value of the frequency factor (A) B) By lowering the overall activation energy of the reaction C) By lowering the activation energy of the reverse reaction D) By providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy E) All of these are ways that a catalyst might act to increase the rate of reaction. Answer = D 7- As ample of Potassium chlorate (15 g) is dissolved in 201 g of water at 70 °C, the solution id cooled to 30 °C and no precipitated is observed, and this solution is: A) Saturated B) Supersaturated C) unsaturated D) Hydrated Answer = C 8- Arrange the following compound according in increasing melting point: KCl , He , H2O , HF A) Kcl > HF > H2O > He B) H2O > HF > KCl > H C)) HF > H2O > KCl > He D) KCl > H2O > HF > He Answer = A 9- Formation of solutions where the process is endothermic can be spontaneous provided that __________. A) They are accompanied by another process that is exothermic B) They are accompanied by an increase in order C) They are accompanied by an increase in disorder D) The solvent is a gas and the solute is a solid E) The solvent is water and the solute is a gas Answer = C 10-- A first order reaction has rate constant of 0.33 min -1, it takes …….. Min for the reactant concentration to decrease from 0.13 to 0.088 M: A) 1.18 min Answer = A B) 2.2 min C) 2.04 min D) 6.18 min 11- What is the molarity of 16 g urea (60 g/mole) that dissolved in 39 g water (density = 1.3 g/ml) A) 6.3 B) 8.88 C) 9.1 D) 0.03 Answer = B 12- Which of the following aqueous solutions will have the highest boiling point? A) 0.10 m Na2SO4 B) 0.20 m glucose D) 0.10 m NaCl C) 0.25 m sucrose E) 0.10 m SrSO4 Answer = A 13- The ideal value of i (van't Hoff factor) for (NH4)3PO4 A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Answer = D 14- Which one of the following is most soluble in water? A) CH3OH B) CH3CH2CH2OH D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH C) CH3CH2OH E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH Answer = A 15- Calculate the freezing point (0 °C) of 0.055 m aqueous solution of NaNO3, the molal freezing point dispersion constant of water is = 1.86 °C/m: A) - 0.2046 B) – 0.1023 C) 0.2046 D) 1.023 Answer = B 16- Which one of the following compounds has only London force? A) NaCl B) HF C) H2O D) N2 E) CH3Cl Answer = D 17- Given that ∆H vap for water is 40.7 KJ/mol , and the normal boiling point of water is 100 C , calculate the vapor pressure (in mmHg) of water at 47 C ( R = 8.314 J/mol.K): A) 86.5 Answer = A B) 31.2 C) 18.7 D) 52.8 E) 25.4 18- The freezing point of ethanol (C2H5OH) is (- 114.6 °C) , the Molal freezing point depression constant for ethanol is 2 °C/m, what is the freezing point of solution prepared by dissolving 50 g of glycerin in 200 g of ethanol (molar mass of glycerin = 92 g/mole): A) 120 °C B) – 120 °C D) – 115 °C C) 114.5 °C Answer = B 19- A first order reaction is 35 % complete at the end of 35 minutes, what is the length of the half – life of this reaction? A) 41 min B) 39 min C) 30 min D) 56 min E) 70 min Answer = D 20- When solutions of strong electrolytes in water are formed, the ions are surrounded by water molecules. These interactions are best described as a case of ____. A) Hydration B) super saturation D) Dehydration C) crystallization E) solvation Answer = A 21 – Which one of the following compounds is most likely to be solid at room temperature? A) HF B) NH3 C) Na2S D) CO E) H2O Answer = C 22- The osmotic pressure of a solution formed by dissolving 25.0 mg of aspirin (C9H8O4) in 0.250 L of water at 25 °C is __________ atm. A) 13.6 B) 1.14 × 10 –3 C) 0.0136 D) 2.45 Answer 23- Which one of the following has the highest boiling point? A) 0.1 m Na2SO4 C) 0.1 m NaCl Answer = A B) 0.2 m glucose D) 0.1 m SrSO4 E) 1.38 24 – The catalyzed pathway in the mechanism of reaction has ……. Activation energy and these caused a …………. reaction rate: A) Higher, lower B) Lower, higher D) Lower, lower C) Higher, higher E) Lower, steady Answer = B 25- Which produces the greatest number of ions when one mole dissolves in water? A) NaCl B) NH4NO3 C) NH4Cl D) Na2SO4 E) sucrose Answer: D 26- Consider the following rate law equation (Rate = K [A] 2 [B]), which one of the following is not true about the reaction having this expressing? 1234- the reaction is overall third order The reaction is first order in B The reaction is second order in A Doubling the concentration of A doubles the rate Answer = D 27- A supersaturated solution __________. A) is one with more than one solute B) is one that has been heated C) Is one with a higher concentration than the solubility D) Must be in contact with undissolved solid E) Exists only in theory and cannot actually be prepared Answer = C 28- At 20°C, a 2.32 M aqueous solution of ammonium chloride has a density of 1.0344 g/mL. What is the molality of ammonium chloride in the solution? The formula weight of NH4Cl is 53.50 g/mol. A) 2.55 B) 0.0449 C) 2.32 D) 0.446 E) 12.00 Answer: A 29- The rate constant for this reaction HNO3 + NH3 → NH4NO3 is (14.5 M -1. S -1), if the concentration of nitric acid (HNO3) = 0.05 M and the concentration of ammonia (NH) = 0.1 M and both reactants are first order, what will the rate of this reaction be? A) 0.073 M/S B) 0.005 M/S C) 0.725 M/S D) 1.45 M/S Answer = A 30- The rate constant for a second-order reaction is 0.13 –M--1 s –1. If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.26 mol/L, it takes __________ s for the concentration to decrease to 0.13 mol/L. A) 0.017 B) 0.50 C) 1.0 E) 4.4 × 10 –3 D) 30 Answer = D 31- Which one of the following compounds has dipole – dipole intermolecular force? A) HF B) SO2 C) CO2 D) CF4 E) He Answer = B 32- A liquid has an enthalpy of vaporization of 155 KJ/mole. At 274 K, it has vapor pressure of 103 mmHg, what is the normal boiling point of this liquid? A) 315 K B) 325 K C) 289 K D) 282 K E) 293 K Answer = D 33- The concentration of urea (60 g/mole) in solution prepare by dissolving 16 g urea in 39 g water is ……… molal: A) 6.9 B) 8 C) 10 D) 8.6 Answer = A 34- Hydration is a specific example of the phenomenon known generally as __________. A) Salutation B) disordering C) solvation D) condensation E) dilution Answer = C 35- A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.6 g of nicotine (non-electrolyte) in water to make 12 ml of solution. The osmatic pressure of the solution is 7.55 atm at 25 °C, the molecular weight of nicotine is ………. g/mole: A) 160 Answer = B B) 162 C) 170 D) 151 36- The process of the solute particles that surrounded solvent particles is known as…… A) Solvation B) Crystallization C) Hydration D) agglomeration Answer = A 37- A 0.100 m solution of which one of the following solutes will have the lowest vapor pressure? A) KClO4 B) Ca (ClO4)2 C) Al (ClO4 )3 D) sucrose E) NaCl Answer: C 38- The reaction A → product is second order reaction , A solution originally at 0.6 M is found to be 0.075 M after 83 min , the half-life reaction is ………… min: A) 11.85 B) 31 C) 83 D) 27.66 E) 47.43 Answer = A 39- For this hypothetical reaction (A + B → C + D), the rate law is (K [A] [B] 2), If the concentration of A is increased by a factor of 3, and the concentration is doubled B, the rate law will be: A) 4 times B) 12 times C) 6 times D) 8 times Answer = B 40- 0.1 m of solution, of which one of the following solute have the lowest vapor pressure? A) KClO4 B) Ca(ClO4)2 C) Al (ClO4)3 D) NaCl Answer = C 41- The concentration of urea in a solution that prepared by dissolving 16 g of urea in 39 g of water is ……….. % by mass (molar mass of urea = 60 g/mole) A) 29 B) 50 C) 16 Answer = A 42- In a saturated solution of a salt in water, __________. A) The rate of crystallization > the rate of dissolution B) The rate of dissolution > the rate of crystallization D) 55 C) Seed crystal addition may cause massive crystallization D) The rate of crystallization = the rate of dissolution E) Addition of more water causes massive crystallization Answer = D 43- Which one of the following substances would be the most soluble in CCl4? A) CH3CH2OH B) H2O C) NH3 D) C10H22 E) NaCl Answer: D 44- As the concentration of a solute in a solution increases, the freezing point of the solution __________ and the vapor pressure of the solution __________. A) Increases, increases B) increases, decreases D) Decreases, decreases C) decreases, increases E) decreases, is unaffected Answer: D 45- The rate law for the following reaction is rate = K [H2] [F2], If the rate is (3.15 * 10 –4 M/S) when [H2] = 0.084 M and [F2] = 0.25 M, calculate the rate when [H2] = 0.039 M and [F2] = 0.01 M: A) 5.85 * 10 –6 M/S B) 7.22 * 10 –4 M/S C) 5.79 * 10 –5 M/S D) 1.29 * 10 –5 M/S Answer = A 46- The combustion of ethylene proceeds by the reaction C2H4 (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) When the rate of disappearance of O2 is 0.23 M—1 s, the rate of disappearance of C2H4 is __________ M –1 s. A) 0.15 B) 0.077 C) 0.69 D) 0.35 E) 0.46 Answer = B 47- A 0.1 m of solution, which one of the following solutes will have the lowest boiling point? A) CH3OH Answer = A B) Ca(ClO4)2 C) Al(ClO4)3 D) KClO4 48- A solution is prepared by dissolving 23.7 g of CaCl2 in 375 g of water , the density of resulting solution = 1.05 g/ml , the concentration of Cl--- in this solution is ……… M and the molality of CaCl2 in this solution …….. Molal: A) 1.12 , 0.568 B) 0.596 , 1.12 C) 0.569 , 0.584 D) 1.22 , 0.56 Answer = A 49- The kinetics of the reaction below were studied and it was determined that the reaction rate did not change when the concentration of B was tripled. The reaction is __________ order in B. A+B→P A) Zero B) first C) second D) third E) one-half Answer: A 50- The reaction below is first order in [H2O2]: 2H2O2 (l) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g), A solution originally at 0.600 M H2O2 is found to be 0.075 M after 54 min. The half-life for this reaction is __________ min. A) 6.8 B) 18 C) 14 D) 28 E) 54 Answer: B 51- The concentration of sodium chloride (NaCl) in aqueous solution that is 2.23 M and that has density = 1.01 g/ml is …….. % by mass A) 15 B) 20 C) 17.3 D) 12.9 E) 11.5 Answer = D 52- Which of the following substances is more likely to dissolve in CH3OH? A) CCl4 B) Kr C) N2 D) CH3CH2OH E) H2 Answer = D 53- The magnitudes of Kf and of Kb depend on the identity of the __________. A) Solute B) solvent D) Solvent and on temperature C) solution E) solute and solvent Answer = B 54- An aqueous solution of soluble compound (non-electrolyte) is prepared by dissolving 33.2 g of the compound in sufficient water to form 250 ml of solution. The solution has n osmatic pressure of 1.2 atm at 25 °C, what is the molar mass of the compound? A) 2706 B) 2500 C) 350 D) 2840 Answer = A 55- The solubility of Ar in water at 25 °C is 1.6 * 10 -3 M When the pressure of Ar above the solution is 1 atm , the solubility of Ar at pressure equal to 2.5 atm is…… M: A) 1.6 * 10 –3 B) 4 * 10 –3 C) 2.5 * 10 –4 Answer = B 56- The first order of reaction is 75 % complete in 60 min, the rate constant of the reaction is …. A) 0.0346 min –1 B) 0.0693 min—1 C) 0.0231 min--1 D) 0.0132 min –1 Answer = C 57-- Which one of the following will lower the activation energy for chemical reaction abcde- increasing the pressure rising the temperature of the reaction increasing the concentration of the reaction removing products as the reaction proceeds adding catalyst for this reaction Answer = E 58- How much heat is released when 40 g of steam at 250 °C that cools to water at 30 °C (Cs heat of H2O (L) = 4.18 J/g.°C , Cs heat of H2O (g) = 2.03 J/g.°C and Heat of vaporization = 2.26 KJ/g): A) 32.9 KJ B) 122 KJ C) 24 KJ D) 67 KJ Answer = D 59-- Solution is prepared by dissolving 2.60 g of a strong electrolyte (formula weight = 101 g/mol) in enough water to make 1.00 L of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.25 atm at 25.0 °C. What is the van't Hoff factor (i) for the unknown solute? A) 1.9 Answer = A B) 2.5 C) 2.01 D) 5.19 60- Calculate the molality of 21.2 % by mass of aqueous solution of H 3PO4 (m.m = 98 g/mole) A) 2.75 B) 4.45 needed to solve this problem C) 2.59 D) Density of solution is Answer = A 61- The vapor pressure of pure water at 25 °C is 23.8 torr, what is the vapor pressure in torr of water above solution prepared by dissolving 18 g of gleusoces (180 g/mole) in 95 g water? A) 25 B) 23.8 C) 23.4 D) 26 Answer = C 62- A solution contains 11% by mass of sodium chloride. This means that _______. A) There are 11 g of sodium chloride in in 1.0 mL of this solution B) 100 g of the solution contains 11 g of sodium chloride C) 100 mL of the solution contains 11 g of sodium chloride D) The density of the solution is 11 g/mL E) The molality of the solution is 11 Answer: B 63-- Which one of the following would be expected to have the highest vapor pressure at room temperature? Ethanol (78 °C) methanol (65 °C) Water (100 °C) Acetone (56 °C) Answer = C 64-- The half-life of zero order reaction of the reaction type (A → product) is 198 s, if the initial concentration of A is 4 M, how many seconds would be required for the concentration of A to drop to 0.5 M? A) 792 s Answer = C B) 1386 s C) 347 s D) 396 s E) 99 s 65-- What is the molarity of Sodium chloride (NaCl) in solution that s 13 % by mass NaCl has density = 1.10 g/ml (m.m NaCl = 58.4 g/mole)? A) 2.448 B) 2.85 C) 3.6 D) 4.25 Answer = A 66-- A solution Contain 10 g of unknown liquid and 90 g of water has freezing point of (-3.33 C), given (Kf = 1.86 C/m) for water , the molar mass of this liquid is ….. A) 62.06 B) 63 C) 18.6 D) 95 Answer = A 67-- According to the figure that shown below, what is the substance at 25 C and 1 atm: A) Liquid B) Solid C) Gas D) Supercritical Fluid Answer = A 68-- The mechanism for formation product X is: A+B→C+D (slow) B+D→X (Fast) The intermediate for this reaction is: A) B Answer = C B) X C) D D) A 69-- The graph shown the relationship between concentration and time for the following chemical reaction (2 A → C) The slope of this line is: A) K B) 1/K C) Ln [Ao] D) ---k Answer = D 70- Which of the following should be the highest critical temperature: A) CBr4 B) CCl4 C) CF4 D) CH4 E) H2 Answer = A 71- Which one of the following compound is most volatile? A) CBr4 B) CCl4 C) CF4 D) CH4 E) C6H14 Answer = D 72-- The strongest intermolecular force in (CH3)2NH: A) Hydrogen bond B) ion – dipole C) Dipole – dipole D) London force Answer = A 73- The half-life period of second order reaction is 10 min, what is the percentage of the reaction will be complete in 150 min? A) 12.5 % B) 6.25 % C) 25 % D) 3.13 % E) 50 % Answer = B 74- A second-order reaction has a half-life of 18 s when the initial concentration of reactant is 0.71 M. The rate constant for this reaction is __________ A) 12.78 Answer = C B) 13 C) 0.0782 D) 0.09 75- At elevated Temperature (N2O5) discomposed to (NO2 and O2) according to this equation: 2 N2O5 → 4 NO2 + O2 When the rate of formation of NO2 is (5.5 * 10 -4 M/S), the rate of decomposition of (N2O5) is: A) -2.75 * 10 –4 B) 2.75 * 10 –4 C) 5.5 * 10 –4 D) – 5.5 * 10 –4 Answer = A 76- For first order reaction, a plot of …………… versus ……………. A) ln [A] Vs t B) ln [A] Vs 1/t C) 1/ [A] Vs t D) [A] Vs t Answer = B 77- In energy diagram, the maximum point on the curve called: A) Activation Energy C) Enthalpy B) Activated Complex D) Product Answer = Activated Complex 78- For elementary reaction (NO3 + CO → NO2 + CO2), the molecularity for this reaction is ….. And the rate law is ……….. Answer = Moleculartiy = 2 = coefficient → Rate Law = K * [NO3] * [CO] 79- A solution is prepared is dissolving by 15 g of NH3 in 250 g of water , the density of this solution is 0.974 g/ml , the mole fraction of NH 3 in the solution is …. A) 0.0597 B) 0.024 C) 0.0471 D) 0.069 Answer = A 80- What is the freezing point of solution is prepared by dissolving 11.3 g of (Ca(NO3)2) (molar mass = 164 g/mole) in 115 g of water ? The molal freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86 C/m: A) 33.4 Answer = B B) – 3.34 C) 3.34 D) 3.58 81- The largest value of henry constant for liquid solvent H 2O, will be obtained with ……… gas as solute and the temperature of ……………. °C: A) C2H4 (45 °C) C) HCl (49 °C) B) Ar (11 °C) D) CO2 (32 °C) Answer = C 82- Calculate the vapor pressure in mmHg of aqueous solution containing 60 g of urea (m.m = 60 g/mole) in 180 g of water (m.m = 18 g/mole), the vapor pressure of water is 290 mmHg: A) 368.1 B) 263.6 C) 258.9 D) 789.2 Answer = B 83- The following data were measured for the reaction of nitric oxide with hydrogen a) Determine the rate law for this reaction. (b) Calculate the rate constant. (c) Calculate the rate when [NO] = 0.050 M and [H2] = 0.150 M Answer: a) Rate law = K ∗ [H2] ∗ [NO]2 b) For K value → Exp. 1 → 1.23 ∗ 10−3 = K ∗ [0.1] ∗ [0.1]2 → K = 1.23 c) Rate law = 1.23 ∗ [0.05]2 ∗ [0.15]1 → 4.6 ∗ 10−4 M s 84- The rate constant for a reaction is 1x 10 -9 S -1 at 320 K and 3 x 10 Calculate the Activation energy: A) 153.775 KJ Answer = A B) 157.88 KJ C) 147.98 KJ -8 s -1 at 340 K. D) 748.8 KJ 85- The kinetic of reaction below were studied and it was determined that the reaction rate increased by factor 9 when the concentration of B was tripled, the reaction is ……. order in B: (A + B → Product) A) First B) Second C) Third D) one – half Answer = B الوسيلة الوحيدة للنجاح هي االستمرار بقوة !!!!!... حتى النهاية Eng.Razan Alkisswany