lect5cut
advertisement

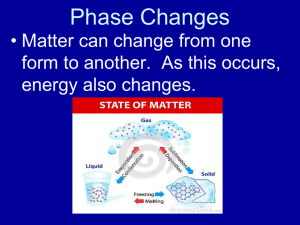
Temperature Relations (Ch. 5) Endothermic Animals Endothermic Animals • HS = Hm + Hcd + Hcv + Hr - He • Use behavior + metabolism (Hm) too Endothermic Animals • Thermal neutral zone: range temperature where metabolic rate stable – Varies by species Humans? Endothermic Animals • Humans tropical: all over planet! Aquatic Endothermic Animals • Cold water problem – Convective heat loss: 20x faster than air (still water) to 100x faster (moving water) • Solutions? (3) “Stop the lecture, you’re killing me!” Aquatic Endothermic Animals • Solutions: • 1) breathe air (avoid gill surface exposure) • 2) insulate! Blubber (whales), waterproof feathers (penguins), air-trapping fur (sea otters) Otter fur: up to 1 million /sq. in. “Stop the lecture, you’re killing me!” Aquatic Endothermic Animals • Solutions: • 3) limit heat loss from appendages by countercurrent heat exchangers Exceptional fishes • Some fishes regulate temp. swimming muscles • Ex, bluefin tuna (fast!) Exceptional fishes • Countercurrent heat exchange keeps muscle temp. constant – Artery blood cooler in this case… Surviving Extreme Temperatures • Reducing Metabolic Rate – Hummingbirds: enter torpor (reduce metabolic rate & lower body temp.) Months? Surviving Extreme Temperatures • Reducing Metabolic Rate (for months) – Hibernation - Winter (temperate climates) – Ex, black bear Avoid summer? Surviving Extreme Temperatures • Reducing Metabolic Rate (for months) – Estivation - Summer (deserts) – Ex, lungfishes – Bury in mud to survive dry season Water Relations (Ch. 6) Why Water Matters • Life aquatic (you: 60% water!) • Solute concentration affects enzymes • Water useful: temp. regulation – HS = Hm + Hcd + Hcv + Hr - He Water Content Air • Terrestrial: Most water loss evaporation (concentration gradient) – How express air water content? Water Content Air • Relative Humidity: Water Vapor Density Saturation Water Vapor Density (x 100%) – Water vapor density = gm water vapor per unit volume (meter cubed) – Saturation water vapor density = water vapor air potentially holds • Changes with temperature…..(how?) Water Content Air • Note kPa: pressure unit (kiloPascals) • Pascal: metric unit pressure (1 Newton per sq. meter) Vapor pressure…. Water Content Air • Water Vapor Pressure (WVP): Partial pressure water vapor. • Saturation Water Vapor Pressure (SWVP): Pressure water vapor at saturation • Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD): SWVP – WVP: drying power air Water Movement: Soil to Plant • Water: flows down water potential gradient Water potential? Water Movement: Soil to Plant • Water: flows down water potential gradient. • Water potential (Psi): capacity water to perform work (water’s free energy content) • “Tendency water to move from one place to another” – Pure Water Psi = 0 MegaPascals (MPa) Mega = one million (106) Psi • Units: megaPascals (MPa) • Psi values negative! Why? Mega = one million (106) Water Movement: Soil to Plant • Psi values negative! Why? • Water potential lowered by: – Dissolved substances (solute potential) – Attraction water to charged surfaces (matric potential) – Pull of evaporation (tension) on water in plants (negative pressure potential) • Water potential raised by: – Pressure (positive pressure potential) Water Movement: Soil to Plant • Psiplant = Psisolute + Psimatric + Psipressure • Psisoil = Psisolute + Psimatric • Solute potential: salts. Psisolute important saline soils • Matric potential (#1 all soils): attraction water to clays (tiny mineral materials) in soil Water Movement: Soil to Plant • Concept! If Psiplant < Psisoil, water flows to plant Water Regulation on Land Water Regulation on Land • Terrestrial organism challenges: – Evaporative loss (air dry) – Access replacement water Recall Energy Balance Equation: HS = Hm + Hcd + Hcv + Hr - He Now: one for water… Water Regulation: Plants • Wip= Wr + Wa - Wt - Ws • • • • Wip= Plant internal water Wr = Roots (+) Wa = Air (+: humid spots) Wt = Transpiration (evaporation from tissues) • Ws = Secretions (nectar) Next: roots Water Acquisition: Plants • How get water? • Wip= Wr + Wa - Wt - Ws – Dry sites: more roots! Plant from W. Canada grasslands Water Regulation on Land: Animals • Wia = Wd + Wf + Wa - We - Ws • • • • • • Wia= Animal internal water Wd = Drinking (+) Wf = Food (+) Wa = Absorbed from air (+) We = Evaporation (-) Ws = Secretions (-) Focus: how get water Water Acquisition by Animals • Wia = Wd + Wf + Wa - We - Ws • Most land animals: get water by eating & drinking (“preformed water”) Some watering hole photos... Water Acquisition by Animals • Water gained via metabolism (metabolic water) • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • Water made by aerobic respiration. Who am I? Water Acquisition by Animals • Wia = Wf - We – Ws Water Acquisition by Animals • Special adaptations: behavior • Namib desert (S. Africa) Lizard flashback Fog from Atlantic Water Acquisition by Animals • Onymacris beetle