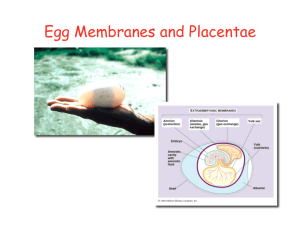
Embryonic Adaptations

EXTRAEMBRYONIC
ADAPTATIONS
1
Extraembryonic - structures that assist embryonic development, but that in most cases
(there is one exception) don ’ t form functional structures in the juvenile or adult.
Extraembryonic structures are generally left behind at hatching or birth, or they are reabsorbed shortly thereafter.
Extraembryonic structures may be acellular or cellular.
2
Acellular extraembryonic structures associated with the egg/zygote:
Secondary oocyte of hampster from which the cumulus cells have been removed by treatment with hyaluronidase.
http://www.mybitoftheplanet.com/2004/big_pictures/mar/spawn0503.html
3
Acellular extraembryonic structures associated with the avian egg/zygote:
4
Cellular extra-embryonic structures.
Extraembryonic structures are more complex in higher vertebrates amniotes (reptiles, birds, mammals)
5
Purposes of extraembryonic structures:
Acellular extraembryonic structures (vitelline/fertilization membrane, zona pellucida, jelly layers, albumin, shell, shell membranes)
1.
Aid in preventing polyspermy
2.
Create an axenic (bacteria free) environment for development.
3.
May deter predation
4.
Protect from mechanical damage
5.
Prevent dehydration (birds, reptiles)
6
Purposes of extraembryonic structures:
Cellular extraembryonic structures (amnion, chorion, yolk sac, allantois)
1.
Actively participate in gaseous transport (oxygen,
CO2) to and from embryo. (chorion, allantois)
2.
Actively participate in transport of nutrients to embryo. (birds & reptiles- yolk sac, mammals chorion, allantois [sometimes (e.g. pig embryos) the yolk sac during early development])
3.
Actively participate in storage or transport of metabolic waste. (birds & reptiles - allantois, mammals - chorion, allantois)
4.
Source of primordial germ cells (yolk sac mesoderm)
5.
Source of early blood stem cells (yolk sac extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm)
7
Origin of the somatopleure and splanchnopleure
8
Amnion - extraembryonic ectoderm + extraembryonic somatic mesoderm =
......................................................................extraembryonic somatopleure
Chorion - extraembryonic ectoderm + extraembryonic somatic mesoderm =
......................................................................extraembryonic somatopleure
Yolk sac - extraembryonic endoderm + extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm =
....................................................................extraembryonic splanchnopleure
Allanois -extraembryonic endoderm + extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm =
....................................................................extraembryonic splanchnopleure
Germ layer origin of the cellular extraembryonic membranes of amniotes.
9
Effect of increasing yolk volume on development
10
Formation of extraembryonic membranes in chickens (amniotes)
The head fold
11
12
13
transverse section transverse section
14
48-55 hr chicken embryo, sagittal view
15
The Allantois
2 1
3
Allantois
16
2
sagittal section sagittal section transverse section transverse section
17