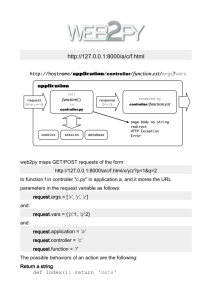
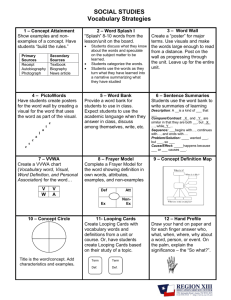
Extra Information ch 2
advertisement

Population Note Cards Age Distribution DEF - (Population pyramid) is two back-to-back bar graphs, one showing the number of males and one showing females in a particular population in fiveyear age groups. This is important because you can tell from the age distribution important characteristic of a country, whether high guest worker population, they just had a war or a deadly disease and more. Cairo Conference DEF – 1994 conference in Cairo that recommended stabilizing world population growth. EX - The plan calls for improved health care and family planning services for women, children and families throughout the world, and also emphasizes the importance of education for girls as a factor in the shift to smaller families. Carrying Capacity DEF - The largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can support. EX – Las Vegas, may have an ample amount of electrical power and inexpensive land, but in a place that receives just a few inches of rain a year, water should guide planting and limit growth. By this rule, the population of Las Vegas, like many other arid and semi-arid regions, has probably already surpassed is sustainable carrying capacity. Child Mortality Rate DEF - Number of deaths per thousand children within the first five years of life. Child mortality rate for the world in 2009 was 60 per 1,000 children under age 5. This was an improvement from 89 deaths per 1,000 children in 1990. Cornucopian Thinking DEF In the late 1980s, when many argued that stricter population controls needed to be placed on countries with high TFR in order to stimulate development, many economists argued that INCREASING POPULATIONS STIMULATE RATHER THAN HINDER ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT. Cornucopians believe that with increasing populations come increasing opportunities for innovation. EX - Esther Boserup was a cornucopian, who proposed the theory that farmers will adopt new and modern methods to keep up with demand caused by an increasing population. The Cornucopian theory was well espoused by the economist Julian L. Simon who was born on February 12, 1932 & died on February 8, 1998. Cornucopians believe that the problem in such instances arises out of poor distribution and inadequate planning in the current economic and political systems. J Curve DEF - This is when the projection population show exponential growth; sometimes shape as a J curve. This is important because if the population grows exponential our resource use will go up exponential and so will our use as well as a greater demand for food and more. The shape of a line graph of population graph when growth is exponential. S Curve DEF - traces the cyclical movement upwards and downwards in a graph. So named for its shape as the letter "s" Relates to growth and decline in the natural increase. Natalism DEF – Pro Natalist - Concerned with promoting population growth. EX – Pro natalist policies can be found in western Europe. DEF - Anti Natalist - Concerned with limiting population growth. EX – China has anti natalist policies. Demographic equation DEF - The formula that calculates population change. The increase (or decrease) in population is births minus deaths plus (or minus) net migration. This is important because it helps to determine which stage in the demographic transition model a country is in. EX - NIR = CBR – CDR Replacement Fertility DEF - The total fertility rate at which women would have only enough children to replace themselves and their partner. The replacement rate is the number of children each woman needs to have to maintain current population levels or what is known as zero population growth for her and her partner. EX – A family of only two children. Thomas Malthus DEF – British economist, who became the 1st critic to note that the world’s population was increasing faster than the food supplies needed to sustain it. He wrote An Essay on the Principle of Population as it Affects the Future Improvement of Society. Population increases at a geometric (exponential) rate, while food supplies grow at an arithmetic rate. Neo-Malthusians DEF –They support international programs for population limitation through birth control and family planning. Many Neo=Malthusians,advocate “Zero Population Growth” in which the number of births and immigrants are equally counteracted by the number of deaths and emigrants. EX - Paul Ehrlich, who wrote, Population Bomb in 1968, was a neo-Malthusian. Population Agglomeration DEF - any distribution of population other than the uniform distribution Agglomeration is a jumbled cluster or mass of varied parts. Population agglomerations can be found in East, South and South East Asia, as well as Western Europe. Contraception DEF - The voluntary control of fertility. EX – The Pill, sterilizaation, family planning. Demographic Transition DEF - High birth rates and death rates are followed by plunging death rates, producing a huge net population gain, this is followed by the convergence of birth rates and death rates at a low overall level. Epidemiological transition DEF – The focus on distinctive causes of death in each stage or the demographic transition. EX – In stage 1, pestilence and famine, are forms of epidemiological transition. The Black Plague. Demographic momentum DEF – Describes the concept that population will continue to grow even after fertility rates decline. This phenomenon occurs when a large segment of a population is young. Momentum in growth occurs because that generation will give birth to more people than the preceding generation and continue a trend of population growth. The momentum will continue to increase unless slowed by decreasing the birth rate or increasing the death rate.