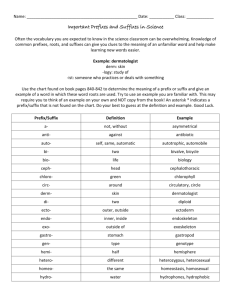
P&S PowerPoint
advertisement
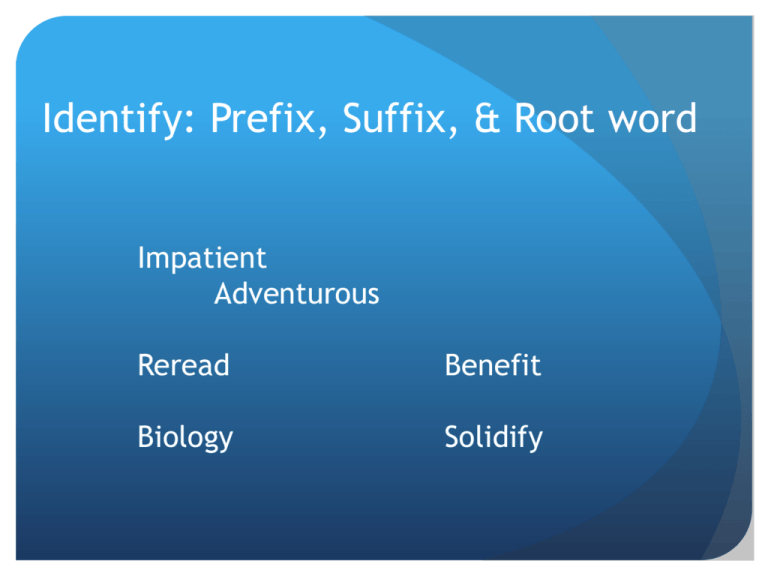
Identify: Prefix, Suffix, & Root word Impatient Adventurous Reread Benefit Biology Solidify Im patient [not]-patient Re read [again]-read Bio logy [life]-[the study of] Adventur ous adventure-[characterized by] Bene fit [good/well]- [condition] Solid ify [not gas or liquid]-[to make/to form into] Prefixes, Suffixes, & Root Words Root Words Most originate from Latin and Greek Serve as the basis for a new word, and often cannot stand alone love + -ly = lovely vs. bene + volent = benevolent “bene”= Latin for good Common Latin Roots Latin Root ambi aqua aud bene cent circum contra/counter dict duc/duct fac form fort fract ject jud Definition both water to hear good one hundred around against to say to lead to do; to make shape strength to break throw judge Examples ambiguous, ambidextrous aquarium, aquamarine audience, audition benefactor, benevolent century, percent circumference, circumstance contradict, encounter dictation, dictator conduct, induce factory, manufacture conform, reform fortitude, fortress fracture, fraction projection, rejection judicial, prejudice Common Greek Roots Greek Root Definition Examples anthropo man; human; anthropologist, philanthropy humanity auto self autobiography, automobile bio life biology, biography chron time chronological, chronic dyna power dynamic, dynamite dys bad; hard; dysfunctional, dyslexic unlucky gram thing written epigram, telegram graph writing graphic, phonograph hetero different heteronym, heterogeneous homo same homonym, homogenous hydr water hydration, dehydrate hypo below; hypothermia, hypothetical beneath logy study of biology, psychology meter/metr measure thermometer, perimeter micro small microbe, microscope Prefix A letter or group of letters that is added at the beginning of a word to change its meaning A Few Common Prefixes anti- = opposing, against -- ex. antibiotic pre- = before in time/place/order– ex. preface, prelude un- = not or reversal–- ex. unacceptable, unhappy, unplug re- = again – ex. repaint, redo, reread, repeat in-/il-/im- = not, without – ex. inappropriate, illegal, impossible de- = down, reduce – ex. descend, despair, deduct Suffix A group of letters placed at the end of a word to make a new word. A suffix can make a new word in one of two ways: Inflectional: the suffix can change a word from singular to plural or can change the tense: dog dogs or walk walked Derivational: creates new meaning, new word is “derived” from original word: teach teacher or care careful Common Inflectional Suffixes -s = plural – dog dogs -en = plural (irregular) – ox oxen -ing = present tense – sleep sleeping -ed = past tense – work worked -er = comparative – big bigger -est = superlative – big biggest Common Derivational Suffixes -er = changes to noun – teach teacher -ation = changes to noun – explore exploration -ness = changes to noun – sad sadness -ary = changes to adjective – imagine imaginary -y = changes to adjective – ease easy -ly = changes to adverb – helpful helpfully -ize = changes to verb – terror terrorize So, why do we need to know this? Breaking down words can help us understand word meanings Prefix, suffix, and root word knowledge can be as helpful as using context clues