File

SIGNALING IN THE
NERVOUS SYSTEM
N I C K U P R I G H T
OBJECTIVES
• Review membrane potentials
• Examine the initiation and propagation of an action potential
• Understand what affects conduction of signals
• Explore the fundamentals of the synapse and the different forms of signaling
• Discuss the various neurotransmitters and their roles in the nervous system
DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
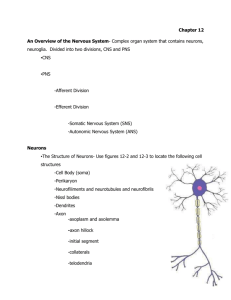
Dendrites
THE NEURON
Soma
Axon
Myelin
Sheath
Axon
Terminals
Nucleus
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
Resting potential = -70 mV
Sodium/Potassium Pump
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL ACTIVITY
• Na + =+60 mV
• K + = -90 mV
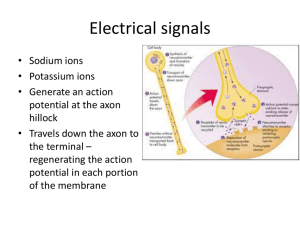
ACTION POTENTIAL
• All or nothing
• Driven by relative permeability
• Refractory periods
• Absolute
• Relative
MYELINATION = FASTER CONDUCTION
• Myelin – high electrical resistance and low capacitance (Insulator)
• Schwann Cells (PNS)
• Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
NONMYELINATED AXONS
• Smaller diameter
• Uniform distribution of Na + and K + voltage-sensitive channels
• Impulse crawls slowly down axon
TYPES OF FIBERS
• A fibers
• Large and myelinated
• Conduct rapidly and carry various monitor or sensory impulses
• B fibers
• Smaller and myelinated
• Conduct less rapidly and carry autonomic functions
• C fibers
• Smallest and non-myelinated
• Conduct slowest and serve pain conduction and autonomic functions
MYELIN-RELATED DISEASES
• Multiple Sclerosis
• Auto-immune
• Demyelination in CNS
• Guillain-Barré Syndrome
• Auto-immune
• Demyelination in PNS
SUMMARY
• Two Types
• Electrical
• Chemical
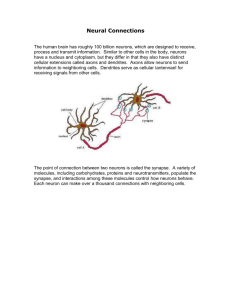
THE SYNAPSE
ELECTRICAL SYNAPSE
CHEMICAL SYNAPSE
NEUROTRANSMITTER RELEASE
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
• Two types
• Direct (utilizes ligand-gated ion channel)
• Transmitter acts directly on postsynaptic ion channel
• Fast
• Acts on single postsynaptic target
• Excitatory or inhibitory
• Indirect (utilizes metabotropic receptor)
• Mediated by secondmessenger pathways
• Slow
• Acts on a wide range of postsynaptic targets
• Excitatory or inhibitory
POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIALS
• Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs)
• Binding of transmitter to receptor that results in opening of channels
• Na + or Ca 2+ channels
• Produces depolarization
• Tend to be axodendritic
• Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs)
• Caused by increased permeability to Cl or K +
• Produces hyperpolarization
• Tend to be axosomatic
PRESYNAPTIC INHIBITION
REVIEW
• Which form of active transport assists in maintaining the resting potential of a neuron at -70 mV?
• The Na + /K + Pump
• Add-on: What is the ratio of ions that are distributed by the pump?
• 3 Na + : 2 K +
• Which ion is released at the axon terminals and signals vesicles to release their contents?
• Calcium
• What auto-immune disorder is characterized by demyelination of PNS neurons and a sudden onset of symmetrical weakness and, occasionally, total paralysis?
• Guillain-Barré Syndrome
• What cells form the myelin sheath of neurons in the central nervous system? Of the PNS system?
• Oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann Cells in PNS
• What is the name for the duration after an action potential when no further action potential can be generated?
• Absolute Refractory Period
ACETYLCHOLINE
• Excitatory transmission in neuromuscular junction
• Motor axons terminate at a section of the muscle membrane termed the motor end-plate
• Removed from the synapse via acetylcholinesterase
• Nicotine and nerve gas
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS
GLUTAMATE
• Major excitatory neurotransmitter
• Two primary ionotropic receptors
• NMDA
• AMPA
• Long-term potentiation
• Enhanced transmission at synapses that follow repeated high-frequency stimulation
• Domoic acid (shellfish)
• MSG and Chinese food
• Stroke and excitotoxicity
ERIC KANDEL AND APLYSIA
• Strong model for studying learning and memory
• Only ~20,000 neurons
• Stimulus activates neural circuit with sensory and motor neurons
• Habituation and sensitization
• Ultimately, learning may lead to changes in structure and function of the synapse
• Greater efficacy and more transmitter released
CATECHOLAMINES
• Includes
• Dopamine
• Norepinephrine
• Epinephrine
• Formed from hydroxylation and decarboxylation of phenylalanine
DOPAMINE
• Synthesis: L-tyrosine L-DOPA Dopamine
• Dopaminergic neurons concentrated in four brainstem nuclei
• Hypothalamus
• Substantia nigra
• Parkinson’s disease
• Reward Pathway
• Inhibitory effect
• Act on receptors D
1
• Schizophrenia to D
5
• Amphetamine, cocaine, LSD
NOREPINEPHRINE
• Synthesis: L-tyrosine L-DOPA Dopamine NE
• PNS located in sympathetic ganglia; also released into bloodstream by adrenal glands
• Plays roles in sleep, movement, mood, and sensory processing
• Sleep-wake cycle
• Fight-or-flight response
• Alertness and arousal
• Drugs that affect NE levels include cocaine, amphetamine, and propanolol (hypertension)
SEROTONIN
• Synthesis: Tryptophan
5-HTP 5-HT
• Also called 5hydroxytryptamine
• Distributed throughout the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus
• Projections to hypothalamus play role in sleep-wake cycle and food intake
• SSRIs commonly used to treat depression
• Amphetamine, cocaine, and LSD
GABA
• Synthesis: Glutamic Acid
GABA
• Enzyme is GAD
• Major inhibitory neurotransmitter
• GABA is a frequent neurotransmitter in interneurons of the CNS and controls output of excitatory neurons by negative feedback
• Present in large amounts of gray matter in the brain and spinal cord
• Plays roles in memory, anxiety, and alertness
• Alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines
ENDORPHINS & ENKEPHALINS
• Endorphins function specifically with analgesia, sedation, pain, and mood
• Exercise
• Enkephalins bind to opiate receptors (GPCRs)
• Inhibit calcium channels to reduce transmitter release and activate potassium channels to hyperpolarize the neuron
• Opiod peptides are closely involved in control of pain
• Opiod receptor antagonists induce hyperalgesia
(heightened sensitivity to pain)
SUMMARY
REFERENCES
• http://kin450-neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/Synaptic+Transmission
• http://www.mun.ca/biology/desmid/brian/BIOL2060/BIOL2060-13/CB13.html
• http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/Anatomy%20%26%20Physiology/2010/2010%20Exam%20
Reviews/Exam%203%20Review/chemical%20synapse%20fig.11.18.jpg
• http://www.mun.ca/biology/desmid/brian/BIOL2060/BIOL2060-14/14_14A.jpg
• http://images-its.chemistdirect.co.uk/Viagra-sildenafil-100mg-Tablets-
12030.jpg%3Fo%3DP@DOy82DJNsHcombQv7R9Th27VUj%26V%3DsFHq
• http://faculty.pasadena.edu/dkwon/chap%208_files/images/image71.png
• http://nba.uth.tmc.edu/Assets/images/content/faculty-page/waxham_fig01.jpg
• http://scientopia.org/blogs/scicurious/files/2010/11/neuromuscular-junction.jpg
• http://img2.tfd.com/mk/M/X2604-M-44.png
• http://mybrainnotes.com/dopamine-norepinephrine-epinephrine.gif
• http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/28/L-phenylalanine.png
• http://www.zuniv.net/physiology/book/images/fp3-10.jpg
• http://share.pdfonline.com/5d8c6af1dc454ec99790998056fe8a5b/EXCITABLE%20CELLS%20AND
%20ACTION%20POTENTIAL-17%20OCAK%202013,%2010,30.htm
• http://www.frca.co.uk/article.aspx?articleid=228
• http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v13/n1/fig_tab/nrn3138_F1.html
• http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biology-iv/nervous-coordination/transmissionmessages.php
• http://bio1152.nicerweb.com/Locked/media/ch48/gradients.html