Vliv akutního hladovění a diabetes mellitus 2. typu na inzulínovou
advertisement

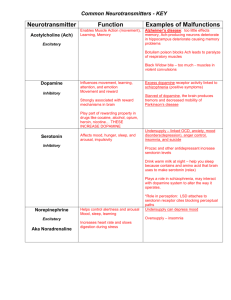
Neurotransmitters František Duška Overview • General physiology of synaptic transmission • Chemical division of neurotransmitters ▫ Amino acid excitatory: Glu, Asp inhibitory: GABA, Gly ▫ Monoamines: Catecholamines: NA, D Serotonin, (melatonin) ▫ Acetylcholine ▫ Peptides ▫ Others: purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Definice: neurotransmitter, neuromodulator Synapsis Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials Definitions of terms • neurotransmitter: ▫ a componud secreted into synaptic cleft and bound to postsynaptic receptors ▫ removal from synaptic cleft by spercific biochemical mechanism • neuromodulator: ▫ a compound secreted by neurons into environment and spread by diffusion (or CSF) ▫ modulates behavior of other neurons Postsynaptic membrane • Resting ponential = - 70 mV ▫ negative IC, positive EC ▫ spontaneous depolarization treshold = -55 mV • Excitatory neurotransmitters EPSP: ▫ open Ca2+, Na+ channels (influx) ▫ depolarize = decrease membrane negativity • Inhibitory neurotransmitters IPSP ▫ open K+ channels (efflux) or Cl- channels (influx) ▫ hyperpolarize = increase negativity Summatin of postsynaptic potentials • Neurone: integrates inputs (EPSPs, IPSPs) into output: 0 or 1 (action potential or not) Summatin of postsynaptic potentials -synthesis -postsynaptic receptor (receptors) -mechanism of removal from synaptic cleft -clinical and pharmacological significance Chemical groups of neurotransmitters Amino acid • excitatory: Glu, Asp • inhibitory: GABA, Gly Monoamines • Catecholamines: NA, D • Serotonin, (melatonin) Acetylcholine Peptides Others • NPY, ADH, neurotensin … • purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Glutamate • Most cammon excitatory neurotransmitter • Synthesis: ▫ from 2-OG (GDH or transaminase) ▫ deamination of glutamine (glutaminase) • postsynaptic receptors: ▫ NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartát): ▫ AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate) ▫ cainate Glutamate • Clinical significance: ▫ antagonisté NMDA: ketamin (disociativní anestezie), fencyklidin („angel dust“) ▫ excitotoxicita ▫ synaptická plasticita, role v učení and paměti Aspartate • Excitatory neurotransmitter, mostly of spinal cord • Synthesis ▫ derived from OAA (citric acid cycle) • Postsynaptic receptor ▫ NMDA – lower affinity than Glu • Removal from synaptic cleft: re-uptake GABA = γ-aminobutyric acid • inhibitory neurotransmitter of the brain Synthesis: GABA shunt GABA: postsynaptic receptors • GABAA: chloridový channel ▫ agonisté: benzodiazepiny, barbituráty ▫ antagonisté: flumazenil • GABAB: metabotropní rec.G-prototevření K+ channel ▫ agonista: baclofen Glycine • Inhibitory neurotransmitter of spinal cord • Synthesis: ▫ from serine • Receptor ▫ chloride channel: IPSP ▫ (co-agonist on NMDA receptors) • Antagonist = strychnine ▫ „seizure poison“ Chemical groups of neurotransmitters Amino acid • excitatory: Glu, Asp • inhibitory: GABA, Gly Monoamines • Catecholamines: NA, D • Serotonin, (melatonin) Acetylcholine Peptides Others • NPY, ADH, neurotensin … • purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Catecholamines: Synthesis C H2 1. H C H C C COOH2 NH3+ HO COO- NH3+ Phenylalanin Tyrosin 2. H C C COOH2 NH3+ HO HO 3,4 DihydrOxyPhenylAlanin (DOPA) 3. H C HO H2 C 5. H C HO OH NH HO Adrenalin CH3 HO H2 C OH NH3+ Noradrenalin 4. C H2 HO HO Dopamin H2 C + NH3+ CO2 Catecholamines - Degradation • Reuptake followed by IC degradation: MAO H C COOHO 77 78 OH CH3O COMT • Final metabolite: vanilmandelic acid Dopamine • Receptors are metabotropic: ▫ D1: Gs proteincAMP ion. channel phosph. EPSP ▫ D2: Gi protein: phosphodiesterase activation IPSP Dopaminergic systems System Anatomy Function Significance Mesocortical tegmentumfron t. cortex Motivation, mood, will Schizophreny Mesolimbic tegmentum nc. accumbens dtto Schizophreny, addiction Nigrostriatal s.nigrastriatum Motoric system M.Parkinson Tuberoinfundibul ar Inhibits prolactin nc. arcuatus eminent. mediana secretion Adverse eff. of antipsychotics Dopamine – Clinical significance • Antipsychotics: ▫ phenothiazines = D-receptor blockers ▫ AE = parkinsonism, hyperprolactinemia • Cocaine, amfetamines: ▫ dopamine re-uptake blockers • Parkinson disease: ▫ loss of dopaminergic neurons in s. nigra. Treatment: L-DOPA Noradrenaline • postsynaptic receptors: ▫ metabotropic: α1, 1 … ▫ ! presynaptic, inhibitory receptors also exist: α2 • Adrenergic systems: ▫ locus coeruleus, lateral tegmentum ▫ arousal, stress, mood Serotonin • = 5-hydroxytryptamin • Anatomy: limbic systém, retikular formation • Function: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ anger/aggression, mood, sleep appetite/satiety/vomitting body temperature sexual behavior Serotonin • Degradation MAO: 5-hydroxyindolacetate Melatonine • Pineal gland • Biorythms • Hormone/neuromodulator Chemical groups of neurotransmitters Amino acid • excitatory: Glu, Asp • inhibitory: GABA, Gly Monoamines • Catecholamines: NA, D • Serotonin, (melatonin) Acetylcholine Peptides Others • NPY, ADH, neurotensin … • purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Acetylcholine • CNS: pontomesencefalotegmental complex ▫ autonomic NS: preganglionic mediator of both symp. and p-symp., postganglionic mediator of p-symp ▫ peripheral NS: neuromuscular junction • Synthesis: AcCoA + choline: CH3 + H3C C O C C N CH3 H2 H2 CH 3 O • Degradation: Acetylcholine eserase Acetylcholine: postsyn. receptors • Nicotinic = inotropic ▫ Na+ channels, neuromuscular junction • Muscarinic = metabotropic ▫ M1 = Gq-prot. = K+ current: CNS (cognit. function), autonomic ganglia ▫ M2= Gi-prot = K+current: CNS, heart ▫ M3= Gq: eye, glands ▫ etc. Acetylcholine –Clinical significance • Lecithin = phosphatidylcholine as nootropic agent • Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors: ▫ physostigmine (passes through HEB): arousal from general anesthesia ▫ neostigmine (does not pass): p-sympatomimetic, myastenia gravis • M-receptor blockade = atropin ▫ parasympatolytics • N-receptor blockade = curare (arrow poison) Chemical groups of neurotransmitters Amino acid • excitatory: Glu, Asp • inhibitory: GABA, Gly Monoamines • Catecholamines: NA, D • Serotonin, (melatonin) Acetylcholine Peptides Others • NPY, ADH, neurotensin … • purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Peptides • Appr. 50 known • Hypothalamus • Synthesis: ▫ prepropeptidER, signal sequence cleavage propeptide in vesicles further processing peptide neurotransmitter (1 or more) • Removal from synaptic cleft: ▫ Degradation, but not re-uptake Peptides: Peptides: examples • Opioids: endorfines, enkefalins ▫ limbic system, inhibits l. coeruleus ▫ axo-axonal synapsis • NP-Y ▫ mediates the influence of leptin on food intake • Neurotensine: ▫ regulates LH and prolactin secretion • substance P… Chemical groups of neurotransmitters Amino acid • excitatory: Glu, Asp • inhibitory: GABA, Gly Monoamines • Catecholamines: NA, D • Serotonin, (melatonin) Acetylcholine Peptides Others • NPY, ADH, neurotensin … • purines, gases, endogenous cannabinoids Others • Endocannabinoid system: ▫ retrograde neurotransmission: anandamide synthesized in the postsynaptic neurone diffuses to presynaptic neurone bound to CB1 and CB2 rec. (G-prot.) influence presynaptic neuron behavior ▫ regulates cognitive function, food intake ▫ THC as illicit drug Closing remark • Neurotransmitters cannot cross hematoencefalic barrier • Chemically identical compounds have many functions aoutside the brain. • These have not been discussed!! ▫ catecholamines in regulating blood pressure and blood flow ▫ serotonin: immunity ▫ pituitary peptides…. etc…