Chemistry project Davide
advertisement

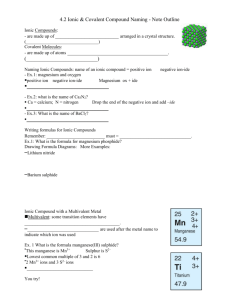
Davide Della Libera, Nadja Ganter, Andrea Susnik and Kelsey Lee Monovalent Compounds O Monovalent Compounds are compounds that have only one ionic charge, which means they have one valence electron to form a ionic bond with some other elements or compounds. We can also recognise them because in the periodic table, they are those which have only a + or – in their top right. For example: Bisulfate (hydrogen sulfate) HSO4- Multivalent Compounds are ionic compound metals with different numbers of electrons, having more than one valence. They are located in the large middle section of the periodic table (demonstrated to the bottom left). Because they are multivalent, they can be seen with up to 3 possible ionic charges that are positive, because they are metals. Ex. Fe2+ Fe3+ O Since a multivalent compound can form more than one stable icon, to determine whether a compound is multivalent or not we must look at the periodic table to see if the metal has more than one combining capacity. O You can also usually determine the combining capacity of the metal by looking at the formula if the compound by looking at the formula of the compound: by un-criss crossing the value (looking at the other element’s value) O When writing out a multivalent compound, clarify it’s capacity by it placing in brackets, in roman numerals. ex. Nickel (III), Manganese (IV). Polyatomic compounds O Polyatomic ions comprised of more than one atom, which share the electrons. O Examples for polyatomic ions: O Positive ions: Ammonium NH4+ O Negative ions: hydroxide OH- From Formula to Name O Write positive ions name either metal or ammonium O Check if metal is multivalent ion, if so indicate multivalent ions charge in roman numerals O Indentify negative ion and name it O Ex: Cr3 (Po4) 2 O chromate O Chromate (||) O Chromate (||) phosphate From name to formula O Identify each ion and its charge O Criss Cross charges O Put Symbole together and get rid of charge values. For Polyatomic ions, use brackets around the ion O Example: O Chromium (|||) (Cr3+) Sulphate (SO4-2) O Cr3+ SO42O Cr2 (SO4) 3 Hydrates O A solid compound that is surrounded by water molecules. O Copper sulfate pentahydrate How to name it!? O Steps to naming Hydrates O Name the compound as you would normally do so. O After the compound name, place the corresponding prefix(# of water molecules)in front of the word hydrate. Prefixes O Ex. O FeSO4 5H2O= Iron(II) sulphate pentahydrate O NiSO4 7H2O= Nickel sulphate heptahydrate O Co3(PO4)2 8H2O= Cobalt(II) phosphate octahydrate