Muon Capture - Precision Muon Physics
advertisement

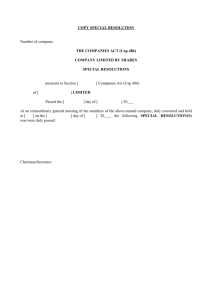
Precision Muon Physics Group K.D. Chitwood, P. Debevec, S. Clayton, D. Hertzog, P. Kammel, B. Kiburg, R. McNabb, F. Mulhauser, C. C. Polly, A. Sharp, D. Webber muon capture on proton - + p + n L to 1 % muon capture on deuteron - + d + n +n L to 1 % muon decay + e++e+ t+ to 1 ppm Nucleon form factors, chiral symmetry of QCD Cap experiment gP to < 7% (3%) Basic EW two nucleon reaction, calibrate v-d reactions D project Fermi Coupling Constant Lan experiment GF to < 1ppm Scientific case QCD is the theory of strong interactions • non Abelian Gauge theory, running coupling constant, • Precision tests at high energies • strong coupling, confinement at “everyday” energies Theoretical approaches to low energy domain • QCD inspired models • Lattice QCD Quark handedness conserved • Effective field theories (chiral perturbation theory) systematic expansion around chiral limit “spontaneous broken” symmetry governs dynamics mass generation accurate QCD prediction and QCD foundation for models model independent predictions of important reactions Cap - + p + n nucleon level elementary level u Ja d p n W W - Ja Ja = <d| ga (1- g5) |u> - QCD Ja = <n| Va - Aa |p> Va= gV(q2) ga + igM(q2)/2M sab qb Aa= gA(q2) ga g5 + gP(q2) qa/m g5 • fundamental and least known weak nucleon FF • solid theoretical prediction at 2-3% levelp • basic test ofpseudoscalar QCD symmetries • factor gP experimentsform not precise, controversial, 4 s discrepancy W to theory gpNN n p Fp T. Gorringe, H. Fearing, Induced pseudoscalar coupling of the proton weak interaction, nucl-th/0206039, Jun 2002 V. Bernard et al., Axial Structure of the Nucleon, Nucl. Part. Phys. 28 (2002), R1 Cap D project +dn+n+ n n d W - • fundamental EW 2-body reaction • high impact for fundamental astrophysics reactions • 10x precision improvement feasible by Cap techniques D pEFT: Class of axial current reactions related by single unknown parameter L1A • basic solar fusion reaction p + p d + e+ + • key reactions for solar neutrino detection and supernova neutrino +dp+p+e +d p+n+ • short distance, axial two body currents, ab-inito pEFT(NNLO) vs. SNPA vs. MEEFT d capture close terrestrial analogue n n d EFT L1A • soft enough ? d W W - p p MEC e+ e • precision measurement possible ? D Precision Measurement of Muon Capture on the Proton “Cap experiment” - + p + n www.npl.uiuc.edu/exp/mucapture/ Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute (PNPI), Gatchina,Russia Paul Scherrer Institut, PSI, Villigen, Switzerland University of California, Berkeley, UCB and LBNL, USA University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, USA Universite Catholique de Louvain, Belgium TU Munich,Garching, Germany Boston University, USA University of Kentucky, USA Cap @ PSI experimental challenges - p () + n p - e+e+ - = heavy electron (Rich) physics effects • Interpretation: where does capture occur ? LS Critical because of strong spin dependence of V-A interaction n+ LT p p F=0 • Background: Wall stops and diffusion Transfer to impurities p+Z Z +p • Rate and statistics (BR = • SR effect for + 10-3) F=1 Lortho pp J=1 n+ Lpara pp J=0 n+ Cap Cap experimental strategy I New idea: active target of ultra-pure H2 gas 10 bar “Lifetime” or “Disappearance” Method measure t+ and t- LS = 1/t- - 1/t+ , t to 10-5 Our experiment observes e+ and e– decay products. Muon capture reduces the μ– lifetime compared to the μ+ lifetime by 0.15% ! log(counts) ePC2 μ+ μ– 1010 events ePC1 TPC time High precision measurement of the lifetime difference: Ls = L( )' - L = (t ( )' ) - (t eSC) e Cap -1 - - -1 Cap experimental strategy II Physics 100% LH2 • Unambigous interpretation At low density (1% LH2) mostly capture from p(F=0) atomic state. p ppO 10% LH2 ppO 1 % LH2 p p ppP ppP • Clean muon stop definition: Wall stops and diffusion eliminated by 3-D muon tracking ppO ppP time (s) • In situ gas impurity control (cZ<10-8, cd<10-6) hydrogen chambers bakeable to 150 C, continuous purification TPC monitors impurities in-situ 10-8 sensitivity with gas chromatograph • +SR: calibrated with transverse field 70 G Statistics • 1010 statistics: Complementary analysis methods Cap Cap experimental setup Key ideas: active target of ultra-pure H2 gas 10 bar for muons, separate large tracking detector for electrons. Muon Detectors SC (t = 0) PC1 PC2 TPC μ Cap Electron Detectors ePC1 ePC2 eSC (Hodoscope) e Cap experimental setup: TPC The time projection chamber (TPC), is our active gas-filled target. It detects in muons and reaction products in 3D. stop rare impurity capture +Z Z’+n+ 2003 run Assembly: March → August Data-Taking: September → mid-October. commissioning / first physics Cap time spectra 2003 Cap status and plans Planned schedule Cap • technical proposal spring 2001, received “high priority status” Steve’s and Tom’s thesis • commissioning 2003 • final detector upgrades 2004 • data run 2003 4% precision • data run 2004 1% precision • …. Cap II or d project Contact me if you are interested ! Cap Experimental facility Location Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Switzerland Muon Source • PSI accelerator (ring cyclotron) generates 590 MeV proton beam • protons hit graphite target and produce pions • pions decay to muons Muon Beam Properties • Particles: μ+ or μ– • Momentum ~ 30-40 MeV/c • rate ~ 50 kHz