Introduction & Orientation to the Human Body
advertisement

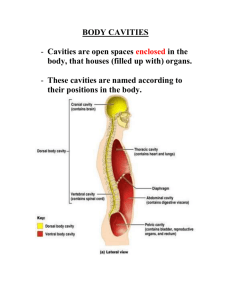
Introduction & Orientation to the Human Body Anatomy Field of study that describes the structure, location, and relationships of body parts. Branches of Anatomy Gross Anatomy- Study of body structures that are visible without a microscope. Regional Anatomy- Focuses on specific area of the body, such as the head, neck, or trunk. Microanatomy- Examines structures on a microscopic level. Histology- Microanatomy that studies tissues. Physiology The study of the mechanisms that enable the body to function. Study of functions of the human body. Levels of Organization Chemical Level- Simplest (O,H,C,K). Cellular Level- Combination of molecules (cell) basic unit of structure and function. Tissue Level- Combination of cells that perform a function. (Four types exist in the human body) Organ Level- Two or more types of tissues combined to perform a general function(heart ,liver) System Level- Two or more organs and associated structures that perform a more general function. Complete Organism- Composed of many systems dependant on each other to perform their function. Body Regions 1. Cephalic or Head 2. Cervical or Neck Body Regions Trunk 1. Thorax 2. Abdomen 3. Pelvis Directional Terminology Superior: Towards the head end or upper portion of the body. Inferior: Towards the bottom portion of the body. Ventral: The front of the body. Dorsal: The back of the body. Medial: Toward the middle or center of the body Lateral: Away from the center of the body. Directions Cont…. Cephalad: The head. Caudal: The tail (lower spine coccyx vertebrae). Proximal: Toward the base(trunk) of the body. Distal: Away from the base (trunk) of the body. Superficial: The surface of the body. Deep: The inside of the body. Body Cavities Dorsal Cavity- Is located on the posterior or back side and contains the cranial and vertebral cavities. Cranial cavity the space that contains the brain and vertebral (spinal) cavity (spinal cord). Body Cavities Ventral- Anterior or front side, contains the thoracic and abdominalpelvic cavity. Thoracic- Divided into 3 smaller cavities. Pleural- two cavities which enclose the lungs. Pericardial- small space between the two membranes around the heart. Mediastinum- contains, trachea, esophagus, vessels. Body Cavities Abdominal-pelvic: Contains the peritoneal cavity which is divided into two separate cavities, the Abdominal and Pelvic. Abdominal- contains the stomach, small intestines, liver, and most of the large intestines. Pelvic- contains the urinary bladder, the rest of the large intestines, internal reproductive organs. Diaphragm- Flat muscular sheet that separates the thoracic and abdominalpelvic cavities. Body Cavities Body Planes Sagittal: Extends parallel to the long axis of the body and divides the body into right and left portions. Frontal/Coronal: Extends parallel to axis but divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) planes. Transverse/Horizontal: Extends perpendicular to the sagittal and frontal planes. Abdomino-pelvic Quadrants Right Upper Right Lower Left Upper Left Lower Regions Anatomical Landmarks (QUIZ) Frontal Orbital Buccal Cervical Abdominal Pelvic Inguinal Femoral Pedal Olecranal Patellar Digital Antebrachial Brachial Axillary Acromial Popliteal Sural Calcaneal Plantar