Buddhism
advertisement

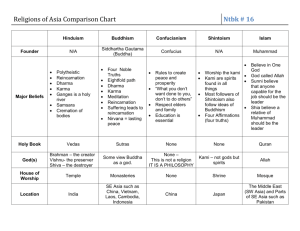
An ancient religion and philosophy based on the teachings of Buddha. • Realized that this world is full of suffering and was in search of lasting happiness. At the age of 29 he left the luxuries of the palace, retired to the forest and followed a life of meditation. • Attained enlightenment under the Bodhi tree in Bodh Gaya, India. • Spent rest of his life, teaching others to realize what he himself had discovered. Philosophy Buddhism inherits principles of dharma, karma, ahimsa, rebirth and nirvana (moksha) from Hinduism. • Dukha-Satya - Truth of suffering. Life is suffering. • Marga-Satya - Truth of path. The eight fold path. • Nirodha-Satya - Truth of cessation. Suffering can be ended if its causes, desire and ignorance are removed. • Samudaya-Satya - Truth of the cause. Suffering is caused by desire (Tanha) and ignorance (Avijja). The Eight-Fold Path Right Meditation Right Knowledge Right Speech Right Mindfulness Right Effort Right Resolve Right Conduct Right Livelihood • Dharma is understood as the practice (paripatti) of the truth. To take refuge in the Dharma is to take refuge in Buddha. • Karma is intentional action, physical, verbal or mental. Good karma brings happiness, bad brings suffering. • Avijja and Tanha is ignorance or not knowing the true nature of things and craving are the two root causes of Karma. • Cycle of Rebirth – We are born and reborn in six realms of exhistence based on one’s previous Karma. • Nirvana (Enlightenment) – To go beyond the cycle and achieving blissful state is Nirvana. Budhist Scriptures are called the Tripitaka or the “Three Baskets” •Suttapitaka – Budha’s sermons •Vinayapitaka – Monastic rules •Abhidhammapitaka – Early philosophical treatises Three Main Schools of Buddhism • Theravada or Hinayana – Sri Lanka, Thailand, Burma, Cambodia • Mahayana – China, Japan, Vietnam, Korea • Vajrayana – Tibet, Mongolia, Japan • Variety of practices aid in the journey to enlightenment. As Buddhism spread from India across many parts of Asia, it absorbed many local religious beliefs and traditions. Therefore practices differ widely in various parts of the world. • Five Rules to abstain from: killing, stealing, sexual misconduct lying, taking intoxicants such as alcoholic drinks • Meditation: Various types of meditation in various traditions • Chanting: Hymns of homage to Buddha, refuge in Buddha, Dhamma and Sangha etc.