Cinematic Techniques
advertisement

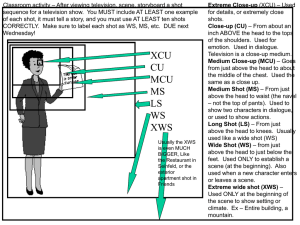
CINEMATIC TECHNIQUES AND THEIR EFFECTS TYPES OF SHOTS Type of Shot Description Effect Establishing Shot Often a long shot or a series of shots that sets the scene Establish Setting and show Transitions Long Shot A shot for a distance that shows a person’s whole body Isolation and Vulnerability Medium Shot Most common shot. Shows people from the waste up. Grounds the story and makes the audience feel like they are “with” the character. Close-up Image takes up 80% of the frame Shows importance or highlights details Extreme Close-up Takes up the whole frame and is part of a whole (foot) Show the importance of what is being shown. Two Shot A scene between 2 people that shows both characters equally Shows the relationship between the two characters and how they interact. TYPES OF ANGLES Angle Description Effect Eye Level A shot taken from a normal or natural height that is at the character’s eye level (Straight on) Shot taken from above the subject, makes the object/character look small The camera films from below the subject, makes the object/character look big Natural Angle, Helps the audience connect with the characters High Angle Low Angle Weak, powerless, and trapped Strong, powerful, and threatening TYPES OF LIGHTING Type of Lighting High Key Description The scene is flooded with light Low Key The scene is flooded with darkness or shadows Bottom or Side Lighting Direct lighting comes from below or the side Front or Back Lighting Soft lighting on the actor’s face or from behind Effect Bright, angelic, open, and honest Suspense, suspicion Dangerous or Evil (Object being shown) Innocence, goodness, halo effect TYPES OF SOUND Type of Sound Description Effect Diegetic Sound that could logically be Shows the relationships, heard by the characters actions, and characteristics I.E. Dialogue, musicians of the characters playing at a concert, etc Non-Diegetic Sound that cannot be heard Helps create the mood, by the characters but is foreshadowing, etc. for the designed for the audience’s audience. reaction only I.E. The background music in Jaws, etc. TYPES OF CAMERA MOVEMENT Type of Movement Description Effect Pan A stationary camera moves from side to side on a horizontal axis To give the audience more information about the scene and its progression Tilt A stationary camera moves up or down on a vertical axis To give the audience the feeling of “checking out” a character or object Zoom – In The camera focuses in on a specific object Reveals a personal or revealing moment about the character or shows importance Zoom – Out The camera gives the feeling of moving away from a character or object Distances or separates the audience from a character or object. Boom/Crane The camera is hanging over the action taking overhead shots Helps give the audience more detail in the setting or makes them more of an observer. Dolly The camera moves along with the action (Truck, car, helicopter, etc.) Makes the audience feel like they are right there with the characters. EDITING TECHNIQUES Type of Editing Techniques Description Flashback The scene jobs back to something that has happened in the past Shot-Reverse-Shot Fade or Dissolve Effect Gives the audience more information about the characters or the scene, clarifies, or explains A shot of one subject, Shows the relationship then another, then back between characters, their to the first. Often used in reactions to events, etc. conversation shots. The image slowly leaves Shows the end of the the film. scene or shows a connection between 2 images. HOW DOES STYLE/LITERARY TERMS APPLY TO CINEMA Style Device (Literary Term) Cinematic Technique Tone: The speaker’s attitude conveyed through the author’s choice of words or detail. Mood: The atmosphere of most common emotion in a literary work Lighting and Sound Diction: Word Choice Diegetic Sound (Dialogue) Imagery: Word or phrases that appeal t the senses that represent people, actions, objects, feelings, or ideas Setting, costumes, or symbolism (Shot types) Organization: The narrative structure of the piece – how a text begins and ends, is sequenced, paced or arranged. Storyboarding or editing of the screen Syntax: the arrangement of words and the order of grammatical elements in a sentence. Editing Techniques Point of View: The perspective from which a narrative Type of shots and Camera Movement is told.