Protist Detectives!
advertisement

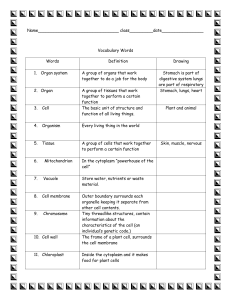
Name_________________________________________ Jan, 2012 Protist Detectives! Section______________________ Part 1: DEMO: What’s in the water? -label the cell membrane, cytoplasm, flagella (if seen), cilia (if seen) Specimen Notes: Part 2: The World of Protists What Makes Protists Special? Protists are _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Protists are _____________________________________________ many are ______________________________/ others are __________________________ some _______________________________________/ others ______________________________ Others are _____________________________________________ some are ________________________/ others __________________________ Scientists believe they provide __________________ of the oxygen in our current atmosphere What Do Protists Share in Common? They are all _________________________ (which means they have a ________________) They have a ______________________________________, but most have no cell wall Most are __________________, but some are ______________________ Protists are so diverse that they are more different than similar! Part 3: Color the Protists by NUMBER! Color each diagram using the color key below Typical Unicellular Pseudopod 6 4 Typical Unicellular Ciliate 5 1 Typical Unicellular Flagellate Typical Multicellular Flagellate 9 Cell parts in algae cell: 13 1 2 3 7 9 12 Key: Color the Squares to Match the Parts in the Diagrams 1. Cell Membrane 6. Pseudopod 10. Cilia 2.Cytoplasm 7. Chloroplast 3. Nucleus 8. Oral groove 12. Algae cell 4. Food vacuole 9. Flagella 13. Daughter colony (color green) 11. Eyespot (color RED) Part 4: Characteristics to look for… Number of cells: Multicelluar- Unicellular- (example___________________________________) (example_________________________________) Parts of the cell (organelles)? See chart on p. 74 of text for definitions of new terms Nucleus(examples from part 3 with a nucleus _____________________________________________________________________) Cytoplasm(examples from part 3 with cytoplasm _____________________________________________________________________) Cell Membrane(examples from part 3 with a cell membrane _______________________________________________________________) Chloroplast(examples from part 3 with chloroplasts __________________________________________________________________) Vacuole (use definition for large central vacuole)(examples from part 3 with a vacuole _____________________________________________________________________) How does it eat (get energy)? Definitions are provided Autotrophs- organisms that make their own food using sunlight (contain chloroplasts) (examples from part 3 that is an autotroph _________________________________________________________________) -Eyespot- an organelle that detects light and allows some protists to find light for energy (examples from part 3 that has an eyespot__________________________________________________________________) Heterotrophs- organisms that need to eat outside energy sources (can not make own food) (examples from part 3 that is a heterotroph ________________________________________________________________) -Oral Groove- an organelle that gathers food and take it into the cell (like a mouth) (examples of from part 3 with an oral groove _______________________________________________________________) Autotrophs that act like heterotrophs- organisms that can make food, but also eat food or have more “animal-like” qualities (____euglena________) (example from part 3 that is an autotroph that acts like a heterotroph How does it move? Describe the three types Flagella Cilia Pseudopods Part 5: Microscope Observational Research! Pseudopods Date of Observations: _________________________________________________________________ Movemen Name of Physical Appearance Action Observations t specimen Observations 1. Draw a picture 4. Check off the cell parts (organelles) you can identify in your drawing. ☐ cell membrane ☐ oral groove ☐ cytoplasm ☐ eyespot (red) ☐ nucleus ☐ pseudopods ☐ flagella ☐ cilia ☐ chloroplast (green) 2. Total magnification__________ 5. Describe the movements 3. Size? ___________um Describe (color, shape, texture, etc…) 6. How does it get its food? (sunlight or other sources, how do you know?) Ciliates 1. Draw a picture 4. Check off the cell parts (organelles) you can identify in your drawing. ☐ cell membrane ☐ oral groove ☐ cytoplasm ☐ eyespot (red) ☐ nucleus ☐ pseudopods ☐ flagella ☐ cilia ☐ chloroplast (green) 2. Total magnification__________ 5. Describe the movements 3. Size? ___________um Describe (color, shape, texture, etc…) 6. How does it get its food? (sunlight or other sources, how do you know?) Flagellates 1. Draw a picture 4. Check off the cell parts (organelles) you can identify in your drawing. ☐ cell membrane ☐ oral groove ☐ cytoplasm ☐ eyespot (red) ☐ nucleus ☐ pseudopods ☐ flagella ☐ cilia ☐ chloroplast (green) 2. Total magnification__________ 5. Describe the movements 3. Size? ___________um Describe (color, shape, texture, etc…) 6. How does it get its food? (sunlight or other sources, how do you know?) Part 6: Microscope Observational Research! 1. Directions: Uses “X” or “✔” to show what each protist has. Use pencil, we will go over this chart in class. Paramecium Stentor Blepharisma Euglena Arcella Volvox 2. In the space below, what do all the protists have in common? eyespot Oral groove pseudopods flagella cilia chloroplast cytoplasm Cell membrane DNA nucleus multicellular unicellular Amoeba