H&P Summary

OSCE 1
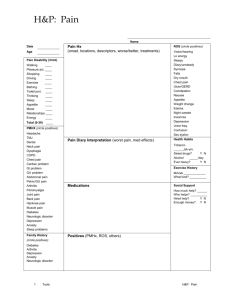
HPI
: LIQOR AAA
L Location of the symptom (forehead, wrist...)
I Intensity of the symptom (scale 1-10, 6/10)
Q Quality of the symptom (burning, pulsating pain...)
O Onset of the symptom + precipitating factors
R Radiation of the symptom (to left shoulder and arm)
A Associated symptoms (palpitations, shortness of breath)
A Alleviating factors (sitting with my chest on my knees)
A Aggravating factors (effort, smoking, large meals)
Social History
: DANTE’S RUMORS
(They can ruin a social life)
D – Drugs
A – Alcohol
R
U
- Recreation
- Upbringing
N – Nutrition M - Military
T – Tobacco O - Occupation
E – Exercise R - Religion
S – Sex S – Schooling
PMHx
-
Pam Hugs Foss
P Previous presence of the symptom (same chief complaint)
A Allergies (drugs, foods, chemicals, dust ...)
M Medicines (any drugs the patient used)
H Hospitalization for any illness in the past
U Urinary changes (esp if diabetic, elderly...)
G Gastrointestinal complains (diet changes, bowel movements...)
S Sleep pattern (waking up/going to sleep...)
F Family history (similar chief complaints/serious illness)
O OB/GYN history (LMP, abortions, para...)
S Sexual habits (active/preferences/STD...)
S Social life (job/house/smoking/alcohol.....)
Family History
–
Start at the roots (grandparents/parents), to the siblings, spouse and kids. Alive, Age, Health (Cause of Death,
Pathologies)
CAGE Questions
1.
Do you ever feel like you should Cut back?
2.
Do you ever feel Angry when people ask you about your alcohol consumption?
3.
Do you ever feel Guilty about your drinking?
4.
Do you ever need an Eye opener in the morning?
OSCE 2
Sexual History
– Series of questions o Partners
Are you currently in a relationship? o Practrices
Are you in an intimate relationship?
Are you sexually active?
Do you have sex w/ men, women, or both? o o o
How many sexual partners have you had in the past year?
Are you having sex with anyone other than your patner?
Past Hx
Ever been diagnosed w/ STI
Pregnancy Planning and Prevention of STI’s
What contraceptives do you use to prevent pregnancy or spread of disease?
Problems
Do you have concerns about your sexual function?
Problems w/ erection or ejaculation
Pain or discomfort during intercourse?
"Are you sexually active?”/"Have you ever been sexually active?"
Are your partners male, female, or both?"
"Are you having any sexual problems?"
"Are you satisfied with your sexual performance?" "Do you think your partner is?" If not, "What is unsatisfactory to you
(or your partner)?"
"Have you had any difficulty achieving orgasm?"
"How frequently does it occur that your partner desires sexual intercourse and you do not?"
"What activities and positions does your sex include?"
"Are there any questions pertaining to your sexual performance that you would like to discuss?"
"Most people experience some disappointment in their sexual function. Can you tell me what disappointments you might have?"
"Many people experience what others may consider unusual sexual thoughts or wish to perform sexual acts that others consider abnormal. We are often bothered by these thoughts. What has been your experience?"
"Do you have protected sex?"
"Have you ever had a sexually transmitted disease?"
"Have you been tested for HIV?" If yes, "What was the result?"
OSCE 3
ROS
–
Start General then go Head to Toe (just 2-3/area)
GENERAL: This is a statement of general, overall health. Also, the presence of fever, night sweats, and changes in weight.
SKIN: Change in color or texture, pruritus, eruptions, rash, sweating.
BLOOD: Excessive bleeding or bruising, unusual infections.
LYMPH: Enlarged nodes ("kernels") or glands.
NEURO: Convulsions, paresis (weakness), paralysis, sensory disturbances, involuntary movements.
PSYCH: Disturbed relationships, uncomfortable emotions, unreal or unusual thoughts.
HEENT: Headache, change in hair/vision, photophobia, diplopia, itching of eyes, changes in hearing, tinnitus, vertigo, drainage from ears, discharge from nose, epistaxis, bleeding from gums, soreness in mouth, tongue or throat, hoarseness
NECK: Stiffness, pain, swelling, enlargement.
BREASTS: Change in size, lumps or masses, tenderness, discharge, self-examination.
PULMONARY: Pleuritic chest pain, wheezing, cough, sputum production, character of sputum, hemoptysis.
HEART: Location and character of chest discomfort, rapid or irregular heart beat, shortness of breath, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, edema, cyanosis, syncope, intermittent claudication.
GI: Dysphagia, pyrosis, abdominal pain, food intolerance, nausea, emesis, hematemesis, jaundice, diarrhea, constipation, melena, hematochezia, colorize and flushability of stools
GU: Dysuria, hematuria, nocturia, oliguria, polyuria, urgency, frequency, hesitancy, dribbling.
BJE (Bones, Joints, Extremities): Extremity pain, muscle pain, back pain, joint pain, swelling of joints, edema, restriction of movement.
Upper Limb
– Inspection, Palpation, Active/Passive ROM
A. Shoulder i.Inspection
1. Symmetry, deformity, redness, swelling ii.Palpation
1. Palpate acromioclavicular joint
2. Palpate sternoclavicular joint
3. Palpate for tenderness, warmth, crepitus iii.Active Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension
2. Abduction/Adduction
3. Internal/External rotation iv. Passive Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension
2. Abduction/Adduction
3. Internal/External rotation
B. Elbow i.Inspection
1. Symmetry, deformity, redness, swelling ii.Active Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension
2. Pronation/Supination iii. Passive Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension
C. Wrist
i. Inspection
1. Symmetry, deformity, redness, swelling ii. Palpation iii .Active Range of Motion
1. Palmarflexion
2. Dorsiflexion iv. Passive Range of Motion
1. Palmarflexion
2. Dorsiflexion v. Tinel’s
D. Hand i. Inspection
1. Symmetry, deformity, redness, swelling
OSCE 4 ii. Palpation
1. Metacarpal bones
2. MCP joint
3. Phalanges iii. Active Range of Motion
1. Make fist
2. Spread fingers
Lower Limb –
Inspection, Palpation, Active/Passive ROM
A. Hip iv. Inspection is not useful and palpation is not easy and therefore not as applicable to this exam v. Active Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension vi. Passive Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension
2. Internal/External rotation
B. Knee vii. Inspection
1. Symmetry, deformity, redness, swelling viii. Palpation
1. Palpate for tenderness, warmth, crepitus
2. Check for joint effusion by ballottement ix. Active/Passive Range of Motion
1. Flexion/Extension x. Evaluate Knee Ligaments
1. Anterior/Posterior drawer test
2. Lachman test
3. MCL/LCL
C. Ankle/foot i. Inspection
1. Standing and sitting ii. Palpation
1. Medial/Lateral malleolus
2. Achilles tendon
3. Metatarsal bones
4. Toes iii. Active Range of Motion
1. Plantar flexion
2. Dorsiflexion
3. Inversion
4. Eversion iv. Passive Range of Motion
1. Plantar Flexion
2. Dorsiflexion
3. Inversion
4. Eversion v. Active Range of Motion – Phalanges
1. Flexion
2. Extension
CardioVascular –
Inspect, Palpate, Auscultation
A. Heart Exam
1. Inspection a. Jugular Venous Pulse (JVP) at 30° b. PMI
2. Palpation a. PMI (sitting up/leaning forward) b. Heave, Lift, Thrill
3. Auscultation SITTING UP with Diaphragm a. Listen in Aortic Area b. Listen in Pulmonic Area c. Listen in Tricuspid Area d. Listen in Mitral Area (APTM)
4. Auscultation SITTING UP with Bell a. Listen in APTM (All Physicians Take
Money)
5. Auscultation LEANING FORWARD with
Diaphragm a. Listen in Tricuspid Area b. Listen in Mitral Area
6. Auscultation SUPINE with Diaphragm a. Listen in APTM
7. Auscultation SUPINE with Bell a. Listen in APTM
8. Auscultation of Carotid Artery in the Neck (bell)
(Because you put a cowbell around the neck!)
B. Vascular Examination
1. Inspection a. Skin (temperature, hyperpigmentation, ulceration, varicose veins)
OSCE 5 b. Clubbing
2. Assess Capillary Refill (normal CR<2 sec)
3. Palpation of Pulses a. Radial Pulse (wrist) b. Brachial Pulse (arm) c. Dorsalis Pedis Pulse (top of foot) d. Posterior Tibial Pulse (medial ankle) e. Femoral Pulse (groin)
4. Palpation for Edema
Pulmonary Exam –
Inspect, Palpate, Percussion, Auscultation
A. Posterior Chest/Lung Exam c. 3 levels minimum
1. Inspection a. Palpation b. c. rib)
Feeling with hands
Respiratory expansion (10 th d. crossed)
Tactile fremitus (arms
2. Percussion a. Side-to-side (comparing bilaterally) b. crossed)
Apices to base (arms c. d.
3 levels minimum
Laterally, mid axillary
3. Auscultation a.
(comparing)
Listen bilaterally b. crossed)
Apices to base (arms d. Laterally, mid axillary
B. Anterior Chest/Lung Exam
1. Inspection a. Trachea position
2. Palpation a. b.
Trachea mobility
Tactile fremitus
3. Percussion a. Side to side (comparing bilaterally) b. c.
Apices to base
3 levels minimum
4. Auscultation a. Listen bilaterally
(comparing) b. c. d.
Apices to base
3 levels minimum
Laterally, mid axillary
ABDOMEN EXAM
– Inspect, Ascultate, Percuss, Palpate
1. Perform exam with patient in supine position with legs flexed and arms at side or on chest
2. Draping
3. Inspection a. Symmetry,
Fullness, Masses, Skin, Scars
4.
Inquire about pain
– “with one finger , please point to the area that is painful”
5. Auscultation (from RIGHT side) a. Listen in all four quadrants with diaphragm b. Listen for renal bruits with bell
6. Percussion a. tenderness last
Area of b. quadrants c. checking size
7. Palpation a. tenderness last b. in all four quadrants c. in all four quadrants d. e. f.
Tenderness
Percuss all four
Percuss liver –
Area of
Light palpation
Deep palpation
Palpate liver
Palpate spleen
Rebound
OSCE 6
8. Palpation of CVA tenderness while sitting
9. Additional Tests a. b.
Dullness
Fluid Wave
Shifting c. d. e. f.
Murphy’s sign
Obturator test
Psoas test
Heel Tap
EYE EXAM
– Inspect, Visual Acuity, Confrontational Visual Fields, Pupillary
Light Reflex, Extraocular Movements, Accomodation, Fundus Exam
A. Inspection – external, structures, pupil sizes
1. Notice pupil size, redness, tearing/discharge, and/or lesions
2. Eyelid sagging (ptosis)
3. Eye position (note any strabismus – exotropia, exotropia, hypertropia)
B. Test visual acuity – with eye chart; one-eye-at-a-time
Make sure eye card is about 14 inches from the face, elbow at side, arm at 90
2. Make sure you tell the patient to read the smallest line that they can read
3. Test one eye at a time with the opposite eye covered
4. Have patient wear their glasses/contacts for exam
C. Confrontational visual fields
1. Test one eye at a time with opposite eye covered
2. Examiner should mirror patient by covering opposite eye
3. Test with hands in upper, middle and lower visual fields
4. Hands should visible to examiner
5. Use 1, 2, or 3 fingers held horizontal to the ground
D. Pupillary light reaction – direction and consensual
1. Turn out overhead light (crank door or turn on gooseneck lamp for some light)
2. Test each eye twice from the side
3. On first test, notice constriction of direct pupil
4. On second test, observe constriction of consensual pupil
E. Extraocular movements
1. Have patient follow examiner’s finger with eyes ONLY in six cardinal movements (patient must keep head still)
Lateral CN3 CN3 Medial
CN6 right eye CN3
CN3 CN4
Medial CN3 CN3 Lateral
CN3 left eye CN6
CN4 CN3
F. Pupillary Accommodation
1. Observe papillary constriction and eye convergence while patient watched examiner’s finger move toward their nose (do not touch nose)
G. Exam of fundus with ophthalmoscope
1. Examine eyes with overhead lights off (again, crack door or use gooseneck lamp)
2. Adjust light source on hand (brightest light with small to medium diameter)
3. Patient right eye, your right eye, instrument in your right hand
4. Left hand at your side or on patient’s right shoulder
5. Ask patient to look at item in the distance in front of them
6. Start 15” lateral away from patient’s line of view
7. Look through instrument and shine light on eye
8. Look for red reflex
9. Move slowly into front of patient and look directly into eye
OSCE 7
10. Appreciate optic disk (with optic cup at its center) nasally
11. Appreciate retinal vessels
12. Appreciate macula (with fovea at its center) temporally
13. Use opposite hands for left eye
HEENT
A. Head Exam
1. Inspection
– symmetry, trauma
2. Palpation of the scalp for masses
B. Ear Exam
1. Inspection – external
2. Inspection
– internal with otoscope
3. Palpation
4. Acuity
– Whispered word, Rinne,
Weber
C. Nose Exam
1. Inspection
– external
2. Inspection – internal with light source
3. Palpation of sinuses
D. Mouth Exam
2. Inspection with tongue blade and light
3. Palpation with gloved hand
E. Neck Exam
1. Inspection
– jugular distention, carotid waveform, mass
2. Palpation – mass, lymph nodes, thyroid
3. Auscultation
– carotid bruits, thyroid bruits
NEUROLOGICAL EXAM
A. Mental Status Exam
1. Level of consciousness (AVPU)
2.
3.
Orientation to person, place and time
Assess speech (no ifs, ands or buts )
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Knowledge of current events (President)
Assess judgment (find letter near mailbox)
Short term memory recall (3 objects)
Assess calculation ability (serial 7’s)
Assess abstraction (“People who live in glass houses should not throw stones”)
Recall 3 objects
B. Cranial Nerve Exam
1. Patient identifies a scent
2. Optic, visual acuity (handheld eye chart; one-eye-at-a-time )
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Eye movement, pupillary response to penlight
Eye movement, pupillary response to penlight
Sensory of face (eyes closed, using cotton), jaw strength
Eye movement, pupillary response to penlight
Facial motor (wrinkle forehead, show teeth, eyelid closure)
Auditory acuity (whispering)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
OSCE 8
9.
10.
11.
12.
Say “ah”, gag reflex
Say “ah”, gag reflex
Turn neck against force or shrug shoulders
Strength of tongue against cheeks, protrude tongue
C. Motor Exam
1.
2.
3.
Test upper extremity strength proximally
Test upper extremity strength distally
Test lower extremity strength proximally
4.
5.
Test lower extremity strength distally
Be familiar with grading of strength (0-5/5)
D. Cerebellar Exam
Rapid alternating movements
Finger-nose-finger test
Assess gait
Assess tandem gait (heel-to-toe walking)
Walking on heels
Walking on toes
7. Romber’s Test (feet together, eyes closed, arms extended with palms up – look for swating, pronator drift)
E. Reflexes
1. Deep tendon reflexes – be familiar with the grading 0-4/4 a. b. c.
Biceps (C5,6)
Brachioradialis (on lateral foremarm)
Triceps (C7,8) d. e.
2.
Knee (L2,3,4)
Ankle (S1)
Babinski’s sign or reflex
F. Sensory Exam
1. Light touch in upper extremities
2. Light touch in LOWER extremities
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Pin-prick in UPPER extremities
Pin-prick in LOWER extremities
Vibration sensation in UPPER extremities
Vibration in LOWER extremities
Proprioception in UPPER extremities (use tuning fork)
8.
9.
10.
Proprioception in LOWER extremities (use tuning fork)
Stereognosis (eyes closed; identifying object)
Graphesthesia (eyes closed; identify number drawn in hand)