Mechanism of Action
advertisement

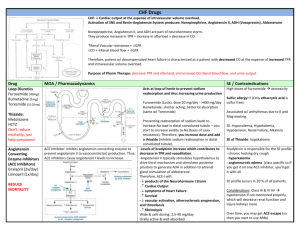
Dr. Florencia D. Munsayac HYPERTENSION "A state of abnormal arterial function and structure associated with endothelial dysfunction, vascular smooth muscle constriction or remodeling, increased impedance to left ventricular ejection and propensity for atherosclerosis." Diagnosis: repeated, reproducible measurements of elevated BP Consequences: damage to kidneys, heart & brain Etiology: A. Primary Hypertension 1. Abnormal cardiac & peripheral hemodynamics 2. Impaired pressure natriuresis 3. Baroreceptor resetting 4. Abnormalities in the renin-angioitensinaldosterone system 5. Abnormalities in other vasoregulatory systems a. Endothelin b. Atrial Natriuresis peptide (ANP) c. Endothelium-derived relaxation factor (EDRF) B. Secondary Hypertension 1. Renovascular hypertension 2. Renal parenchymal diseases a. Altered excretory function b. Altered renin-angiotensin-aldosterone activity 3. Endocrinologic causes a. Oral Contraceptives b. Mineralocorticosteroid excess syndrome c. Pheochromocytoma d. Miscellaneous causes (Acromegaly, Hyperparathyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Coarctation of the aorta) Major Factors Influencing Blood Pressure ABP = cardiac output x peripheral vascular resistance • • • • • • heart rate arteriolar volume contractility blood volume filling pressure venous tone Genetic influences + Environmental Factors Defects in renal NA+ homeostasis Functional Defects in vascular smooth muscle growth and structure vascular reactivity vascular wall thickness vasoconstriction Inadequate Na+ secretion Salt & water retention Plasma & ECF volume cardiac output total peripheral resistance (autoregulation) HYPERTENSION Circadian Rhythm and Blood Pressure Variability Daytime: BP is controlled by sympathetic activity Sleep: BP lowest sympathetic activity switch off renin level rise BP control under RAS Early Morning Waking: BP rise as much as 30 mmHg marked increased in sympathetic activity elevated levels of renin & angiotensin II Physiological Changes Associated With Early Morning BP Elevation Increase plasma cathecolamines & cortisol elevates myocardial oxygen demand Increase in platelet aggregability & vascular tone; reduce myocardial oxygen supply BP surge can cause rupture atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries Promotes clot formation due to activation of coagulation process Excess sympathetic activation results in release of adrenaline, an arrhythmic promoter Classification of Blood Pressure for Adults >/= 18 years: JNC 7 Pressure Category SBP (mmHg) DBP (mmHg) < 120 < 80 120 - 139 80 - 89 Stage 1 140 - 159 90 - 99 Stage 2 > / = 160 > / = 100 Normal Prehypertension Hypertension Management of Hypertension in Adults Aged > / = 18 Years Blood Pressure Classification Lifestyle Modification Initial Drug Therapy Without compelling indication Normal With compelling indication Encourage Prehypertension Yes No antihypertensive drug indicated Drug(s) for the compelling indications Stage 1HTN Yes Thiazide-type diuretics for most; may consider ACE inhibitor' ARB, betablocker, CCB, or combination Drug(s) for the compelling indications; other antihypertensive drugs (diuretics, ACE inhibitor, ARB, betablocker, CCB) as needed Stage 2 HTN Yes 2-drug combination for most (usually thiazide-type diuretic and ACE inhibitor or ARB or beta-blocker or CCB) Drug(s) for the compelling indications; other antihypertensive drugs (diuretics, ACE inhibitor, ARB, betablocker, CCB) as needed Classification of Antihypertensive Drugs A. Diuretics 1. Thiazides 2. Loop diuretics: Furosemide, Bumetanide 3. Potassium Sparing diuretics: Triamterene, Spirinolactone, Amiloride B. Sympathoplegic Agents 1. Centrally Acting Agents a. Acting on alpha adrenoceptor (First Generation) - methyldopa, clonidine, guanabenz, guanfacine b. Acting on imidazoline receptor (Second Generation) - moxonidine, rilmenidine 2. Ganglionic Blocking Agent - Trimetaphan 3. Adrenergic Neuron Blocking Agents - reserpin, guanethidine, guanadrel 4. Beta-adrenergic Antagonists - propranolol; metaprolol, atenolol, pindolol, acebutolol, bisoprolol 5. Alpha adrenergic Antagonists - prazocin, phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine 6. Mixed Antagonists (Alpha & Beta) - labetalol, carvedilol C. Vasodilators 1. Oral Vasodilators: hydralazine, minoxidil 2. Parenteral Vasodilators: nitroprusside, diazoxide, fenoldepam 3. Calcium Channel Blockers: Dihydropyridines nifedipine, amlodipine, felodipine. nimodipine, nicardipine, isradipine, licidipine; Phenylalkylamines --vcrapamil; Bcnzothiazcpincs - diltiazcm D. Inhibitors of Rcnin Aogiotcnsin System: 1. Angiotensin 11 Antagonists - saralasin, losartan, valsartan 2. ACE inhibitors - captopril, qiunapril, enalapril, pcrindopril, lisinopril Loop Diuretics furosemide, bumetamide and torsemide act primarily on the thick ascending loop of Henle which reabsorbs 20-30% of the filtered load of NaCl most potent diuretics in clinical use Very steep dose-response natriuresis curve, termed high-ceiling diuretics Furosemide Rapidly absorbed from the GIT Binds avidly to plasma proteins Rapidly eliminated from the body, by renal excretion (Proximal tubular secretion) Onset of action: 30-60 min after oral administration or 2-5 min after IV Duration of action: PO-6 hours, 2-5 min IV Thiazide Diuretics Low ceiling, flat dose response Slow onset of effect, long duration of action (6-12 hours) Reduce urine calcium Hydrochlorothiazide – sulfonamide derivative Indapamide – new thiazide like agent with a significant vasodilating effect Potassium sparing diuretics Spirinolactone – aldosterone antagonist in the collecting tubules has slow onset and offset of action (24-72 hours) - direct inhibitor of aldosterone at steroid receptor - Causes an increase in Na clearance & decrease in K excretion Amiloride and triamterene – inhibitors of tubular potassium secretion, with 12-24 hrs duration of action DIURETICS Mechanism of Antihypertensive Effects of Diuretics Decreased PVR Reduction in body sodium Decrease interstitial fluid volume Fell in smooth muscle sodium concentration Decrease in 1C calcium concentration Diuretics and Potassium-Sparing Agents Agent Daily Dosage (mg) Duration of Action (hour) 2.5 - 5.0 18 12.5 - 50 12 – 18 125 - 500 0.5 - 2 6 - 12 18 – 24 6.25 - 50 12 – 18 2.5 - 5.0 1-4 1-4 18 – 24 > 24 24 - 48 Thiazides Bendroflumethiazide (Neturcun) Benzthiazide (Aquata, Exna) Chlorthiazide (Diuril) Cyclothiazide (Anhydron) Hydrochlorothiazide (Esidrix, Hydrodiuril, Oretic) Hydroflumethiazide (Saluron) Methyclothiazide (Enduron) Polythiazide (Renese) Trichlormethiazide (Metahydrin Naqua) Related Sulfonamides Compounds Chlorthalidone (Hygroton) Indapamide (Lozol) Metolazone (Zaroxolyn, Diulo) Quinethazone (Hydromox) 12.5 - 50 2.5 0.5 - 10 24 - 100 24 - 72 24 24 18 - 24 0.5 - 5 25 - 100 40 - 480 5 - 40 4-6 12 4.6 12 5 - 10 24 - 100 50 - 100 24 8 - 12 12 Loop Diuretics Bumetanidc (Bumex) Ethacrynic acid (Edcecrin) Furosemide (Lasix) Torsemide (Demadex) Potassuim-Sparing Amiloride (Midamor) Spirinolactone (AIdactone) Triamterene (Dyrenium) Toxicity Potassium depletion (except K-sparing diuretics) Magnesium depletion Impair glucose tolerance Increase serum lipid concentration Increase uric acid concentration Action of Centrally - Acting Antihypertensive Agents Alphamethyldopa Guanfacine Guanabenz Alphaadrenoceptor Salivary Glands Dry mouth Clonidine Moxonidine Rilmenidine Imidazoline receptor Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Nucleus Coeruleus Sedation Inhibition of Sympathetic Nerve Activity Inhibition of norepinephrine release Decrease in vasoconstriction Vasodilation Lower Blood Pressure Methyldopa Mild to moderate hypertension Decrease PVR Extensive first pass metabolism Effect 4-6 hours up to 24 hours Side effects: sedation, lactation, positive coombs test Clonidine Decrease cardiac output, HR and relaxation of capacitance vessels, decrease PVR Decrease renal vascular resistance & maintenance of RBF 75% bioavailability Half-life 8-12 hours Lipid soluble, rapidly enters brain from circulation Toxicity: dry mouth, sedation, life threatening HTN crisis in sudden withdrawal Ganglionic-blocking Agents Drugs that block stimulation of postganglionic autonomic neurons by Ach No longer available because of intolerable toxicities Trimetaphan – prototype drug, given IV, short-acting, that block the nicotine receptor Adrenergic Neuron Blocking Agents Lower BP by preventing normal physiologic release of norepinephrine from postganglionic sympathetic neurons Guanethidine Bethanidine Guanadrel Debrisoquin reserpine Reserpine Effective & safe for mild to moderate HTN Enters BBB Causes depletion of central amines sedation, mental depression & parkinsonism symptoms Lowers BP by decreased CO and PVR Half-life 24-48 hours Guanethidine Treatment of severe HTN MOA is associated with reduce CO due to bradycardia & relaxation of capacitance vessels Half-life 5 days, bioavailability 3-50% 50% cleared by the kidneys Large volume of distribution Too polar to enter the CNS Has none of the central effects toxicity: postural hypotension, retrograde ejaculation BETA – ADRENOCEPTOR BLOCKING DRUGS Nonselective Nadolol Propranolol Timolol Sotalol Tetralol Pindolol Penbutolol Carteolol Alprenolol Dilevatol Oxyprenolol Selective Atenolol Esmolol Metoprolol Bevantolol Bisoprolol Betaxolol With alpha-blocking ability Acebutolol (Practolol) Celiprolol Labetalol Bucindolol Carvedilol Propranolol Well absorbed orally Extensive first pass metabolism Rapidly distributed, large volume of distribution Half-life 3-6 hours Dose: 80-480 mg/day Toxicity: result from blockade of cardiac, vascular & bronchial beta receptors GIT side effects Increase triglycerides & decrease HDL Mechanism of Action Beta-adrenoceptor blockers Decrease activation of B1 adrenoceptors on heart Decreased renin Decreased cardiac output Decreased angiotensin II Decreased Blood Volume Decrease PVR Decrease aldosterone Dec. Na+, H2O retention Decreased Blood Volume Decreased in Blood Pressure Alpha-adrenergic Antagonists Reduce arterial pressure by dilating both resistance and capacitance vessels Cause sympathetically mediated reflex increase in HR & plasma renin activity Long-term therapy: vasodilatation persists, but CO, HR & plasma renin activity return to normal Selective: prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin Non-selective: phentolamine, phenoxybenzamine Prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin Half-life 3-4 hrs (prazosin) Extensively metabolized but undergoes very little first-pass metabolism, half-life 12 hours, given OD (terazosin) Doxazosin has intermediate bioavailability, half-life 22 hours, given once a day Toxicity: first dose phenomenon, dizziness, palpitation, headache & lassitude, positive serum Antinuclear factor (prazosin) Mechanism of ActionVasodilators Inhibition of calcium influx into arterial smooth muscle cells relax smooth muscle of arterioles decreasing systemic vascular resistance decrease arterial pressure direct arterial dilation triggers baroreceptor, svmpathetic activation resulting in tachycardia, increase cardiac output, increase myocardial oxygen demand cause significant fluid retention work best in combination with other antihypertensive drugs (anti-adrenergic & diuretics) to overcome untoward effects Oral Vasodilators Hydralazine dilate arterioles but not veins effective in severe HTN well absorbed from GIT systemic bioavailability is low half-life 1 hour duration of action 12 hours toxicity: immunological reactions, druginduced lupus syndrome, serum sickness, hemolytic anemia, vasculitis & rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis Minoxidil Metabolized by hepatic sulfotransferase to the active molecule, minoxidil N-O sulfate Well absorbed Half-life 3-4 hours Duration of action 24 hours or longer Toxicity: fluid and salt retention, hypertrichosis Parenteral Vasodilators Nitroprusside Dilates both arterial and venous vessels Used in treating hypertensive emergencies, severe heart failure Rapidly lowers BP Given by IV infusion Effects disappear within 1-10 min after discontinuation Eliminated by the kidney Toxicity: metabolic acidosis, arrhythmia, hypotension, death, thiocyanate poisoning, delayed hypothyroidism, methemoglobinemia Diazoxide Arteriolar dilator – hyperpolarizes arterial muscle cells by activating ATP sensitive K channels, this cause relaxation of the vascular smooth muscle Used to treat hypertensive emergencies Toxicity: hypotension Fenoldepam Newer peripheral arteriolar dilator Acts primarily as an agonist to dopamine D1 receptors, resulting in dilatation of peripheral arteries and natriuresis Administered by IV infusion Half-life 10 mins Toxicity: reflex tachycardia, headache, flushing, increased intraocular pressure Calcium Channel Blockers Dilate peripheral arterioles Dihydropyridines more selective as vasodilator less cardiac depressant effects Verapamil greatest effect on heart, decrease heart rate and cardiac output Adverse Effects Nifedipine: 17 - 20% of patients - hypotension, headache, peripheral edema Verapamil: 17 - 20% of patients - cardiodepression (major), hypotension, peripheral edema (moderate), headache, constipation (minor) Diltiazem: 2 - 5% of patients - hypotension, peripheral edema, AV block, cardiodepression ANGIOTENSIN - CONVERTING ENZYME (ACE) INHIBITORS Mechanism of Action Reduction of circulating levels of Angiotensin II Decrease aldosterone secretion; blunts increased in sympathetic activity Direct inhibition of vascular hypertrophy Enhance endothelium dependent relaxation Inhibits the degradation of bradykinin – vasodilator, weak anti-aggregant peptide, enhances synthesis of vasodilatory prostaglandins Vasodilation Decrease peripheral vascular resistance Decrease blood pressure Various ACE inhibitors Drug Dosage (minmax) Administration Elimination Benazepril 5 - 40 o.d. Renal Captopril 12.5 - 150 t.i.d. Renal Cilazapril 5 - 10 o.d. Renal Enalapril 5 - 40 b.i.d. Renal Fosinopril 10 - 40 o.d. Renal & hepatic Lisinopril 5 - 40 o.d. Renal Moexipril 7,5 - 30 o.d. Renal Perindopril 1 - 16 o.d. Renal Qninapril 5 - 80 o.d. Renal Ramipril 1.25 - 20 o.d. Renal Tandolapril 1-4 b.d. Renal Spirapril 12.5 - 50 o.d. Hepatic Captopril Rapidly absorbed Bioavalability 70% with fasting, 3040% with food Half-life < 3 hours Metabolized to disulfide conjugates Eliminated in kidney HTN in DM – diminish proteinuria & stabilize renal function Toxicity Severe hypotension Acute renal failure Hyperkalemia Dry cough sometimes with wheezing & angioedema Contraindications 2nd & 3rd trimester of pregnancy Drug interaction Potassium supplements Potassium - sparing diuretics NSAIDs ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKING AGENTS bind selectively to AT1 receptors and displace angiotensin II blockers of the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor 1st drugs marketed: losartan, valsatran candesartan, eprosartan, irbesartan, & telmisartan - no effect on bradykinin metabolism more selective blockers of angiotensin effects SE: similar to ACE inhibitors but less cough and angioedema