Demographic Trends Affecting Cities
advertisement

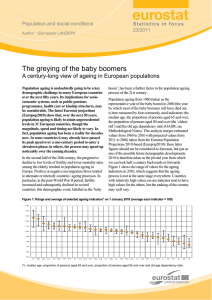
Demographic Trends Affecting Cities Population Change Outline Trends Implications for cities Checklist for cities Information resources Trends Minnesota continues to grow 1 million more people by 2030; 2 million more by 2060 Midwest neighbors and other cold weather states seeing population declines Trends Minnesota population growth through 2060 Projected Population (Millions) 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.5 6.5 7.1 4.9 5.0 4.0 5.9 6.3 6.8 3.8 4.1 4.4 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 1970 1980 1990 State Demographer projection 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 2060 Trends 2000-2005 population growth 7 of 13 metro counties in fastest 100 growing of the nation 40% of state’s population lives in metro suburbs; 57% of 2000-05 growth 34% of state’s population lives in greater MN; only 13% of 2000-05 growth Trends Suburbs and collar counties account for less than half of population but 77% of growth 100% 13.2% 90% 80% 7.1% 34.0% 70% 60% 20.8% 6.6% 5.4% 50% 40% 30% 39.4% 57.3% 20% 10% 14.6% 1.6% 0% Share of 2005 Population Share of Change 200005 Met Council and State Demographer estimates. Rest of State Six Regional Centers Collar Suburbs Core Cities Trends Regional trends projected through 2030: Twin Cities will grow by 800,000 32% more people will live in central lakes region—mostly older adults Central lakes region only region to see significant growth in residents under 19 North and northwest regions will grow by 14%, reversing long trend of no growth In south and southwest regions, the only population growth will be among residents over 65 Implications for Cities Cities with no growth or population loss School closures Business closures; job losses Declining tax base Less investment in infrastructure No new services Pressure to find new ways to deliver services Difficulty filling elected and appointed positions Implications for Cities Cities expecting growth: New demand for services and infrastructure New kinds of service needs depending on changing population (e.g. more older residents, more ethnic diversity) Finding fair distribution of burden for paying for growth among new and old residents Implications for Cities Density issues Trends of people moving to low-density areas (e.g. lakes areas) Cost of service delivery can be higher in lowdensity areas Urban-style development in formerly lowdensity areas increases pressure for expanding infrastructure and services Implications for Cities City employment City employment affected by whether region is stable, growing, or shrinking in population Declining areas will face difficulties filling vacancies Growing cities will face competition from private sector to find new employees Aging and ethnic diversity trend complicate employment issues Checklist for Cities What is role of city in region What are factors in people’s location decisions How do we enter partnerships with other entities to provide services Checklist for Cities What are population projections How will role of city affect growth trend Can we change the future How will need and demand for services change Can we partner with other entities to meet those demands What are future housing needs; what type of housing will residents want Checklist for Cities What will be impact on property values and tax base How does size and composition of our workforce compare to future needs What is retirement pattern of current workers What is our workforce plan to recruit and retain staff Resources Office of State Demographer www.demography.state.mn.us League of Minnesota Cities www.lmc.org