Geography of Development
advertisement

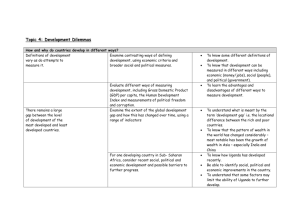
Basic Terms Rostow’s Modernization Model Dependency Theory World Systems Microcredit Other issues www.therightplanet.com Let’s let Hans Rosling get us started http://www.ted.com/talks/hans_rosling_and_the_magic_washing_machine.html Basic Terms • Informal Economy • MDCs and LDCs • GNP, GDP and GNI • PPP and Big Mac Index • HDI and Better Life Index • Neocolonialism • NIDL • EPZs and SEZs • Maquiladoras • NGOs • MNCs • Parallel States • Globalization? • Define and give some examples Basic Terms • Informal Economy • MDCs and LDCs http://www.oxfamblogs.org/fp2p/?p=285 • GNP, GDP and GNI • PPP and Big Mac Index • HDI and Better Life Index • Neocolonialism • EPZs and SEZs • Maquiladoras • NGOs • Parallel States http://www.forbes.com/fdc/welcome_mjx.shtml Basic Terms • Informal Economy • MDCs and LDCs • Colonialism & Neocolonialism http://jong-preanger.deviantart.com/art/neocolonialism-183882158 • EPZs and SEZs • Maquiladoras • NGOs • Parallel States • GNP, GDP and GNI • PPP and Big Mac Index • HDI and Better Life Index The Motherland by Brouguereau – 1883 - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neocolonialism What is the NIDL? • New International Division of Labor • Outcome of globalization where labor moves across international borders • Industrialized countries outputs have dropped, while LDCs has grown • Improved transportation and growth of transnational corporations has fed the NIDL Rostow’s Modernization Model Sometimes called the Ladder of Development http://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/unit-6-vocabulary/deck/5285919 Rostow’s Modernization Model • Stage One – TRADITIONAL – Subsistence – Static Society – Resist Technological Change • Stage Two – PRECONDITIONS TO TAKEOFF – Progressive leadership moves country forward – More openness and diversity • Stage Three – TAKEOFF – Industrial Revolution – Sustained Growth – Urbanization increases – Technology increases • Stage Four – DRIVE TO MATURITY – Diffusion of Technology – Specialization – International trade expands – modernization – population increases • Stage Five – HIGH CONSUMPTION – high incomes – widespread production of many goods/services – Most work in service sector Rostow’s Modernization Model • Liberalist Model • What did the world look like when Rostow wrote this in 1960? • For hint – see map pages 250-251 • What else does this model remind us of: • 1. Organic Theory • 2. 5 Economic Sectors • 3. Demographic Transition Criticisms of Rostow • Eurocentric and Americentric • Doesn’t account for regional differences within a country • Doesn’t account for cultural differences within a country • Doesn’t account for one-commodity economies • Neo-colonialism • Major bias that all economies will grow the same way developed countries grew • Rostow believed all countries would grow in an orderly fashion like Japan and Europe and the US did • Use exercise to further understand Rostow Dependency Theory – pp. 306-08 • Structuralist Model • Political and economic relationships between countries and regions control and limit development possibilities • Example – colonialism created… • Dependent relationships between mother country and the occupied country • These relationships sustain prosperity of the core country and poverty of the periphery country • Gives rise to NEOCOLONIALISM in the 1970s, 80s and on to the present Dependency even in the Core? http://www.ritholtz.com/blog/2012/05/the-illusion-of-choice/ Global Carbon Footprint http://i.imgur.com/CVNUeml.jpg World Systems Theory – pp. 308-09 • Structuralist Model • Immanuel Wallerstein • See handout • Does NOT assume all countries will change the same way • I call this the “Life sucks and then you die theory” • The good news is that each sector is not necessarily static – can move from one sector to another • 3 sectors that we have discussed before – These are relationships between countries – all three types need each other • CORE • SEMIPERIPHERY • PERIPHERY • But, who always wins? EPZs, SEZs and Maquiladoras • EPZs and SEZs • Maquiladoras • NGOs • Parallel States • World Cities MNCs • Multinational Corporations • Decisions made here affect stockholders, regions and states • Also make decisions that make them actors on the global stage • Examples Gender Inequality Index http://www.hiidunia.com/2012/03/what-contribution-does-feminist-economics-make-to-the-understanding-of-gender-equality/ Millennium Development Goals http://ec.europa.eu/europeaid/what/millenium-development-goals/index_en.htm Right to Work States • States in which employees do not have to join unions as part of their jobs • PRO – employee has the right to be in a union or not be in a union. All employees do not have to pay union dues if they do not want to • CON – employers choose these states because they can pay lower wages and not guarantee work, pay levels or certain benefits to employees http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Right-to-work_law NGOs • NGOs • Global Actor World or Global Cities and Primate Cities– pp. 295-97 • World Cities • These cities function at the global scale – meaning, reaching beyond state borders and functioning as service centers for the global economy • Examples are… • New York City, London and Tokyo • See map for more information • Primate Cities • Disproportionately large and exceptionally expressive of the national culture and center of the country’s economy. • Many former colonies have primate cities • Examples are Paris, Mexico City, Athens, Cairo, Lima, Seoul Countries without a primate city Can you say, effects of colonialism? according to wikipedia. Microcredit What about development terms like PPP, HDI and such? What does this say? Parallel States • Parallel States • World Cities