Theories of Motivation
advertisement

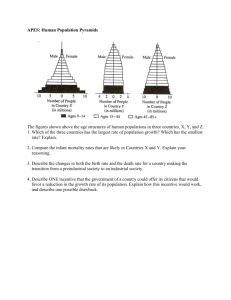
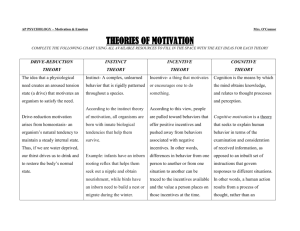
Theories of Motivation HOT ROC • Motivation • Injury: third-degree lateral sprain and tendon damage • What motivated Kerri to jump again after her first injury? • What are other examples of people who have accomplished the seemingly impossible? Motivation • Definition: an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal • What motivates you? • Outside & inner motivations • Types of motivation: • Drive-reduction • Incentive • cognitive Instinct Theory • Innate tendencies that determine behavior • Does not explain behavior, just labels it Drive-Reduction Theory • Needs- organism requirements • Physiological: food, oxygen, etc. • Psychological: self-esteem • Produce drive (internal condition) • When a baby is deprived it feels agitated and needs to relieve this tension through a random activity. • Homeostasis- the tendency of the body to return to a balanced state • All human motives are extensions of basic needs • Does it work? Incentive Theory • Our actions are directed towards a goal (incentive) • Reinforcers • Goals • Rewards • Praise • Recognition • Does it work? Cognitive Theory • Extrinsic Motivation • Activities that either reduce biological needs or help obtain external incentives • (Your parents want you to play football) • Intrinsic Motivation • Activities that are personally rewarding or because they fulfill our beliefs and expectations • (You love to play football) Motivation Activity Make an Ad • Purpose: • Apply theories of motivation • Strategy: • You are industrial psychologists who have been hired to create an ad for a new, innovative product Make an Ad • Pick a new product to design/invent: • Snack food • Perfume/cologne • Car • Nonalcoholic drink • Line of clothing • Communication device • Motivation theories: • Drive-reduction • Incentive • Cognitive • Necessary Components: • Name • Slogan • Image • Target population