Chapter-7-and-acid
advertisement

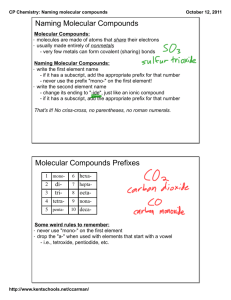
Chapter 7 and Acid Review Ironic isn’t it What’s in a name ironically Molecular Stuff Acidic Overload Mixed Bag Bagging it 200 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 Ironic isn’t it 200 • State the Law of Conservation of Matter. – During a chemical reaction matter is neither created or destroyed therefore the mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products Ironic isn’t it 400 • Discuss what elements are involved in an Ionic Bond and what happens to the electrons. – Metal (+) to a non-metal(-). The electrons are taken from the metal by the non-metal because it is much more electronegative (able to attract and hold electrons) Ironic isn’t it 600 • Name at least 3 properties of Ionic Compounds – Strong attraction between ions therefor solid at room temperature, High melting and boiling points, brittle…. Ironic isn’t it 800 • Discuss the difference between a Binary I and Binary II Compound – Binary I compound- the metal comes from the s block plus Ag, Zn and Al. These metals can only have one possible + charge – Binary II compound- these metals come from the d and lower p blocks, the metal can have more than one + charge. Ironic isn’t it 1000 • How do you name a Binary I and Binary II compound? – Binary one – (+) ion keeps its name, (-) monoatomic ion ends in ide. Polyatomics keep their name – Binary II – roman numerals indicate the (+) ion’s charge, (-) monoatomic ion ends in ide. Polyatomics keep their name What’s in a name 200 • Name these compounds Li2O, MgS, CaCO3, KNO3, Sr(OH)2 Na3PO4. – Lithium oxide – Magnesium sulfide – Calcium carbonate – Potassium nitrate – Strontium hydroxide – Sodium phosphate What’s in a name 400 • Name these compounds. Ni(NO3)2, MnCl4, PbS, SnO, FeCl3, Cu2O – Nickel II nitrate – Manganese IV chloride – Lead II sulfide – Tin II oxide – Iron III choride – Copper I oxide What’s in a name 600 • Name these compounds. Na2O, Cu3PO4, K3N, Fe3(PO4)2 – Sodium oxide – Copper I phosphate – Potassium nitride – Iron II phosphate What’s in a name 800 • Write the formula for sodium nitride, lithium nitrate, magnesium hydroxide, calcium sulfate – Na3N – LiNO3 – Mg(OH)2 – CaSO4 What’s in a name 1000 • Write the formulas for Copper II phosphide, copper I phosphate, Iron III oxide, Tin IV sulfate – Cu3P2 – Cu3PO4 – Fe2O3 – Sn(SO4)2 Molecular Stuff 200 • What type of elements are involved in molecular bonds? What happens to the bonding electrons, why? – Non-metal to a non-metal – Bond electrons are shared due to similar electronegativity's Molecular Stuff 400 • Write the formula for dinitrogen pentaoxide, carbon tetra iodide, Sulfur tri iodide, pentaphosphorous decaoxide – N2O5 – CI4 – SI3 – P5O10 Molecular Stuff 600 • Name the following real and imaginary molecular substances. P2N3, C3N4, NO – Diphosphorous trinitride – Tricarbon tetranitride – Nitrogen monoxide Molecular Stuff 800 • Draw the following molecules. Indicate if they are polar or non-polar. CH4, H2O – Non polar – Polar Molecular Stuff 1000 • Mixed practice, name or write. CO2, FeCl3, KI, BF3, CUO, ZnCl2, Sulfur dioxide, Lead IV oxide, zinc nitrate – – – – – – – – – Carbon dioxide Iron III chloride Potassium iodide Boron tri fluoride Copper II oxide Zinc chloride SO2 PbO2 Zn(NO3)2 Acidic Overload 200 • What is the definition of an acid? – Molecular compound that can dissociate and donate a hydrogen ion (H+) Acidic Overload 400 • Acids are named for their _________. • Give the naming rule for monoatomic and polyatomic anions of acids – Anion (negative ion) – Mono atomic gets named “Hydo_____ic” – Polyatomic gets named “_________ic” Acidic Overload 600 • How can you tell the difference between an organic and inorganic acid? – Organic acids have carbon, inorganic acids do not have carbon Acidic Overload 800 • Name these acids; HCl, H2S, H2SO4 – Hydrochloric acid – Hydrosulfuric acid – Sulfuric acid Acidic Overload 1000 • Write the formulas for nitric acid, hydrophosphoric acid, carbonic acid, hydroiodic acid – HNO3 – H3P – H2CO3 – HI Mixed Bag 200 • Name the compounds LiI, FeCl2 – Lithium iodide – Iron II chloride Mixed Bag 400 • How would you name CI5? Write the formula for sodium oxide – Carbon penta Iodide – Na2O Mixed Bag 600 • Write the formula for carbonic acid. For hydrobromic acid – H2CO3 – HBr Mixed Bag 800 • Name the compounds MgSO4, CrPO4, Ba(OH)2, AgI, HNO3, H2S – Magnesium sulfate – Chromium III phosphate – Barium hydroxide – Silver iodide – Nitric Acid – Hydrosulfuric acid Mixed Bag 1000 • Write the formulas for phosphoric acid, copper I carbonate, phosphorous trichloride, tetraphosphorous trisulfide, dinitrogen pentaoxide, hydrosulfuric acid – – – – – – H3PO4 Cu2CO3 PCl3 P4S3 N2O5 H 2S Bagging it 200 • Name the charges that each group on the periodic table will form as ions – – – – – – – – Alkali 1+ Alkaline 2+ Boron 3+ Carbon skip Nitrogen 3Oxygen 2Halogens 1Noble gases –no ions formed Bagging it 400 • Name the compounds K2S, PCl5 – Potassium sulfide – Phosphorous pentachloride Bagging it 600 • Discuss how acid rain is formed and how Michigans Limestone (CaCO3) protects our water pH – Acid rain forms when SOx and NOx combine with water vapor in the atmosphere – CaCO3 is a basic it creates a neutralization reaction when combined with acid rain Bagging it 800 • Write the formulas for Nickel II sulfate, cobalt II nitrate, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitride, potassium oxide, hydrosulfuric acid – – – – – – NiSO4 Co(NO3)2 (NH4)2SO4 (NH4)3N K2O H2S Bagging it 1000 • What do you call covalently bonded compounds with a charge? – Polyatomic ions Chapter 7&8 200 • In a circle, what physics concept is thought of as linear speed? – tangential speed Chapter 7&8 400 • What is confused with centrifugal force in rotational motion? – inertia Chapter 7&8 600 • Work in a circle is called? – torque Chapter 7&8 800 • The constant of Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation is? – 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 Chapter 7&8 1000 • Dan has a mass of 83.2 kg and Nate has a mass of 57.3 kg. What is the gravitational force between them if they are sitting .800 m apart? – 5.00 x 10-7 N Final Jeopardy • State Newton’s Third Law – For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.