Epithelial Tissue
advertisement

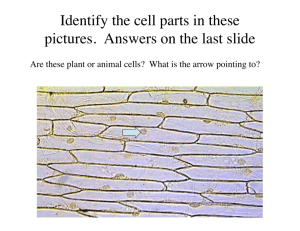
Epithelial Tissue Chapter 4.1 (Human Anatomy) Histology is the branch of anatomy that studies the structure of animal tissue on a microscopic level. What is a tissue? ►A group of cells that all perform the same specific function ►Example: cardiac, muscle, or nerves 4 Types of Tissues ►1) Epithelial Tissue – covers body surfaces and organs, lines body cavities ►2) Connective Tissue – binds and supports body parts ►3) Muscular Tissue – contracts producing movement ►4) Nervous Tissue – responds to stimuli and transmits nerve impulses Epithelial Tissue ►Tightly packed cells ►Readily divides (mitosis) producing new cells to replace old or damaged cells ►Lacks blood vessels ►Exists on the skin and on the surface of organs, blood vessels, and body cavities ►Function: - Externally – protects body from drying out, injury, and bacterial invasion - Internally – protects, sweeps up impurities, secretes mucus, absorbs ► Covers cavities surfaces and lines Has a free surface Other surface attached to underlying tissue by the basement membrane Nucleus Free Surface Nucleus Basement membrane Basement membrane Free Surface Cytoplasm ► Simple Epithelial Tissue – composed of a single layer of cells ► Stratified Epithelial Tissue – composed of 2 or more layers of cell Types of Epithelial Tissues 1] Squamous Epithelium: simple and stratified 2] Cuboidal Epithelium 3] Columnar Epithelium 4] Pseudostratified Epithelium 5] Transitional Epithelium Squamous Epithelium ►2 types of squamous epithelium: * Simple Squamous Epithelium * Stratified Squamous Epithelium ► SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM: – Single layer of flattened cells – Function: secretion, absorption, and filtration – Location: lines the lungs, blood vessels and heart Nucleus Cytoplasm Simple Squamous Epithelium ►STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM – Many layers of flattened cells – Function: protection – Location: outer layer of skin, lining the various orifices of the body Stratified Squamous Epitlelium Cuboidal Epithelium ► Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: - single layer of cubeshaped cells attached to a basement membrane ► Stratified Cubiodal Epithelum: two or more layers of cube-shaped cells Location Glands Function secretion Kidney tubules Secretion & absorption Nucleus Free Surface Basement membrane Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple Columnar Epithelium ►Composed of cells that are longer than wider ►Nucleus found in the lower half of the cell Location Digestive organ Uterine tubes Function Absorption Propel egg to uterus Free Surface Nucleus Basement membrane Pseudostratified Epithelium ► Cells appear to be layered due to irregularly placed nuclei but each cell touches the basement membrane ► May contain cilia – aids in movement of particles ► Function: protection, secretion, movement of mucus and sex cells ► Location: respiratory tract, reproductive tract Cilia Nucleus Basement membrane Pseudostratified Epithelium Transitional Epithelium ► Tissue that changes in response to tension ► Found in organs that need to stretch ► Location: urinary bladder, ureters, urethra Free Surface Nucleus Basement membrane Transitional Epithelium