QUESTIONS Virus and Bacteria
advertisement

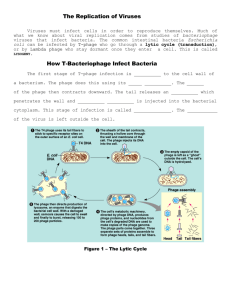
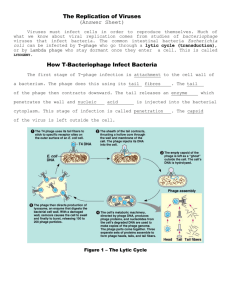
NAME_____________________________________DATE___________PERIOD________ UNIT 6 –VIRUSES AND BACTERIA QUEST- QUESTIONS VIRUSES- SIZE, SHAPE, AND STRUCTURE- Pages 40-43. 1. What is the definition of a virus? 2. Why do biologist consider viruses to be nonliving? 3. Where is the only place that viruses can multiply? 4. What is a host? 5. What is the definition of a parasite? Why is a virus considered a parasite? 6. What are the five possible shapes for viruses? 7. What is a bacteriophage? 8. What is the range of the smallest to the largest virus diameter? How many nanometers are in one meter? 9. How big is a virus compared to a bacteria? 10. What are the four ways that scientists name viruses? 11. What are the two basic parts of a virus? Use Figure 3 to draw a diagram of a virus. 12. How do surface proteins on a virus allow it to enter certain host cells? VIRUSES- MULTIPLICATION & HEALTH- Pages 44-45. 13. What are the five steps an ACTIVE VIRUS follows to multiply in a host cell? 1. ______________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________ 4. ______________________________________________________ 5. ______________________________________________________ STEPS: 1 2 3 4 5 14. Look at the steps of how a HIDDEN VIRUS multiplies below (also see Figure 4 on Page 45). What is the difference between an active and hidden virus? 15. What are common viral diseases in humans? 16. What are examples of viral diseases in other organisms besides humans? 17. How are viruses used for gene therapy? Provide an example of a genetic disorder that can be treated using this technique. BACTERIA- STRUCTURE, OBTAINING FOOD, REPRODUCTION- Pages 48-53. 18. What is the definition of bacteria? 19. Describe the function and location of each of the bacterial cell parts: CELL PART Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Genetic Material Flagellum FUNCTION LOCATION 20. Draw and provide an example of each of the cell shapes of bacteria: Cell Shape Drawing Example Spherical Rodlike Spiral 21. What is the range of bacterial cell sizes? How many micrometers are in one meter? 22. What are three ways that bacteria can obtain food? (Hint: Use Figure 8 on Page 51) 23. What is the definition of respiration? 24. What are the ideal conditions for a bacteria to reproduce? 25. What are the definitions of the following terms? a. Binary Fission: b. Asexual Reproduction: c. Sexual Reproduction: d. Conjugation: e. Endospore: BACTERIA- ROLE IN NATURE- Pages 54-57. 26. How do bacteria help produce oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere? 27. What foods are produced using bacteria? 28. What are the two methods to slow down food spoilage caused by bacteria? 29. What are decomposers and how do they recycle chemicals in dead organisms? 30. How do nitrogen fixing bacteria help plants (like peanut, pea, and soybeans) survive? 31. How are bacteria used to clean up the environment (bioremediation)? 32. How do bacteria in your body help keep you healthy? 33. How are bacteria used in the medical field? VIRUSES, BACTERIA, AND YOUR HEALTH- Pages 60-65. 34. What is an infectious disease? 35. How can infectious diseases spread? 36. What is a toxin? 37. What are the definitions of the following terms? a. Antibiotic: b. Antibiotic Resistance: 38. Complete the chart for the two Bacterial Diseases below: Bacterial Disease Lyme Disease Strep Throat Symptoms How it Spreads Treatment Prevention 39. How are viral infection treatments different from bacterial diseases? How are viral infections best treated? 40. Complete the chart for the two Viral Diseases below: Viral Disease Symptoms How it Spreads Treatment Prevention 41. What is a vaccine? Influenza (Flu) Chickenpox