Vertebral Column
advertisement

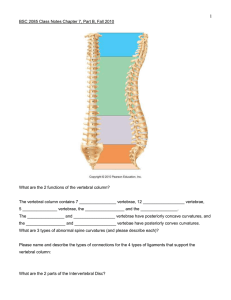
Vertebral Column and Thoracic Cage Notes Vertebral Column • 33 bones in infants • 26 bones in adults • 5 sections: – Cervical (7 bones) – Thoracic (12 bones) – Lumbar (5 bones) – Sacrum (5 fused bones) – Coccyx (4 fused bones) Vertebral Curvatures Primary – those present at birth: • thoracic • pelvic Secondary – develop after birth: • cervical – develops as baby holds head up • lumbar – develops as child begins to stand Features of Typical Vertebrae body – for support intervertebral arch – for articulation of next vertebrae sup. & inf. articulating processes – for articulation w/vert. above or below Features of Typical Vertebrae rib facet – for articulation w/ribs transverse processfor muscle attachment; project laterally spinous process - sharp projection for muscle attachment projects posteriorly lamina – 2 plates that fuse to become spinous process pedicle – projection from body vertebral foramen – opening for s.c. intervertebral disc – composed of cartilage for cushion Features of Atlas (C1) Atlas – supports skull • Fovea dentis – notch for dens • Facet for articulation w/occipital condyles • No body Features of Axis (C2) Axis – pivot point • Dens (odontoid process); fits into C1 for rotation of the skull Cervical Vertebrae (7) Features: • smallest • most dense • transverse foramina – for arteries to brain • bifid (forked) spinous process (C2-C5)- (for muscle attachment) • C7 – vertebra prominens (landmark) Thoracic Vertebrae (12) Features: • larger than cervical • long spinous process projects posteriorly and inferiorly • facets for ribs Lumbar Vertebrae (5) Features: • Largest, strongest bodies • Transverse process thinner & project laterally • Spinous process short, thick, nearly horizontal Sacrum & Coccyx Sacrum – triangular-shaped bone at base of vert. column •Consists of 5 fused vertebrae •Sacral foramen – for b.v. & nerves •Sacral canal – s.c. travels through •Sacral hiatus – where spinal cord exits Coccyx (tailbone) – consists of 4 fused vertebrae Thoracic Cage Includes ribs, thoracic vert., sternum & costal cartilage Support upper limbs, protect organs & aid in breathing Sternum – 3 parts: manubrium body xiphoid process Features of Sternum • Sternal angle – union of manubrium & body; at 2nd rib (anatomic landmark) • Clavicular notch – junction of clavicle & sternum • Sternal puncture – aspiration of red marrow for diagnosis Ribs – 12 pair 3 types: vertebrosternaltrue ribs (1st 7pair) vertebrochondral – false ribs (next 3 pr.) vertebral – floating (last 2 pair) Male vs. Female Pelvis Female Structure (All related to female pelvis functioning as a birth canal): • Iliac bones more flared • Angle of pubic arch greater • > distance b/t ischial spines • Sacral curvature shorter & wider • Bones lighter