06. Bones of the trunk

Bones of the trunk
Skeletal system • Your bones manufacture blood cells.
• Our bones are held by our muscles • The smallest bones are in our ears
Bones classified by shape: long, short, flat, irregular, round Bone enclosed in periosteum, which is continuous with tendons and ligaments blood vessels in periosteum Epiphysis- ends spongy bone contains red marrow compact bone, articular cartilage Diaphysis- middle compact bone medullary cavity- contains yellow marrow (fat) lined with endosteum (squamous epithelium)
Compact bone osteocytes within lacunae arranged in concentric circles called lamellae This surround a central canal; complex is called Haversian system Canaliculi connect osteocytes to central canal and to each other
Prenatal development skeleton is mostly cartilaginous Cartilage cells and then osteoblasts start to deposit minerals Cartilaginous disk (epiphyseal disk) remains in epiphysis Cells eventually stop dividing
Bursae & Tendon Sheaths
• Bursae: flat, fibrous sac w/synovial membrane lining • Tendon Sheaths: elongated bursae that wraps around tendons • 3 Factors in Joint Stability: – Muscle Tone – Ligaments – Fit of Articular Surface pg 219
pg 224
Joint Shapes
• Hinge: cylindrical end of 1 bone fits into trough shape of other – angular movement-1 plane (eg) elbow, ankle, interphalangal • Plane: articular surface in flat plane – Short gliding movement – (eg) intertarsal, articular processes of vertebrae
pg 225
Joint Shapes
• Condyloid: egg-shape articular surface + oval concavity – side-to-side, back+forth movement – (eg) metacarpophalangeal (knuckle) • Pivot: round end fits into ring of bone + ligament – rotation on long axis – (eg) prox. radius/ulna, atlas/dens
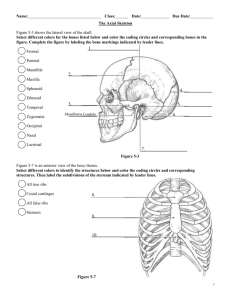
Thoracic cage ribs thoracic vertebrae sternum costal cartilages True ribs are directly attached to the sternum (first seven pairs) Three false ribs are joined to the 7 th Two pairs of floating ribs rib
Clavicles and scapulae Help brace shoulders Attachment sites for muscles
Bones of upper limb Humerus (upper arm) Radius; ulna Carpals, metacarpals, phalanges Bones of lower limb Femur Patella Tibia, fibula Tarsals, metatarslas, phalanges
Radius and Ulna
• Radius on Top • Ulna on Bottom
Carpals or (Wrist Bones)
Phalanges (Little Fingers)
Rib Cage
Sternum (Breastbone)
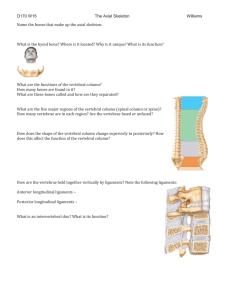
Characteristics - Ligaments • Ligaments hold the vertebral column in an upright position – The broad Anterior Longitudinal Ligament prevents hyperextension and is quite strong – The cord like Posterior Longitudinal Ligament prevents hyperflexion and is relatively weak
Characteristics - Ligaments • Ligaments also connect specific vertebra and support disc position – Supraspinos ligament – Ligamentum flavum – Interspinous ligament
Intervertebral Discs • Intervertebral discs are cushion like pads interposed between vertebra • The discs provide elasticity and compressibility • Compression flattens discs • Discs are thickest in the cervical and lumbar to provide flexibility
Characteristics - discs • Annulus fibrosus surrounds the outer margin – Collagen fibers • Nucleus pulposus is the semi fluid substance which shifts under body weight & pressure • Herniation of disc
Herniation of disk
General structure of vertebrae • Common pattern – Body or centrum – Vertebral arch • lamina • pedicle – Vertebral foramen – Spinous process • Muscles attach – Transverse process • Muscles attach
General structure of vertebrae • Interlocking pattern – Superior and inferior processes interlock – The inferior from above and the superior from the vertebrae below form a movable joint – The movement contributes to spinal rotation
Superior Articular Process
General structure • Pedicles have notches on their superior and inferior borders • Lateral openings are called intervertebral foramen – Spinal nerves from spinal cord exit through these foramina
Regional Characteristic: Cervical • Body is oval, but wide side to side C3 - C7 • Spinous process is short and bifid (split) except in C7 • Vertebral foramen is triangular • Transverse processes contain foramina for blood vessels leading to brain
Cervical Vertebrae C1 • Lateral masses articulates with the occipital condyles of the skull
Cervical Vertebrae C1
Body of the Vertebrae is missing
• Inferior articular surface articulates with C2 below
Cervical Vertebrae C2 • The axis has the odontoid process or dens is its unique feature • The dens is the missing body of the atlas which fuses with the atlas during embryonic development
Regional Characteristic: Cervical • Spinous processes project directly posteriorly • Superior facets directed superoposteriorly • Inferior facets directed inferoanteriorly • Flexion/extension, lateral flexion and rotation
Regional Characteristic: Thoracic • Body is larger than cervical; heart shaped • Spinous process is long and sharp • Vertebral foramen is circular • Transverse processes project posteriorly and bear facets for ribs
Regional Characteristic: Lumbar • Body is massive and kidney shaped • Spinous processes are short and blunt • Vertebral foramen is triangular • Transverse processes are perpendicular to spinous process but has no special features
Regional Characteristic: Lumbar • Spinous process projects posteriorly • Superior facets directed medially • Inferior facets directed laterally • Flexion/extension, some lateral flexion, rotation prevented
Sacral • Ala are fused remnants of transverse processes that articulate with hip bones to form the sacro iliac joints of the pelvis • Sacral promontory – Center of gravity is 1 cm posterior of this point • Transverse line are sites of vertebral fusion • Sacral foramina transmit blood vessels and nerves
Ala Sacral promontory
Sacral • On the posterior aspect median sacral crest are fused spinous processes • The vertebral canal continues inside the sacrum as the sacral canal • Sacral hiatus is at the inferior end of the sacral canal • Superior articular surface form a joint with the spinal column
Coccyx • Coccyx articulates with sacrum
Sternum • Located on the anterior midline of the thorax • Consists of three fused bones; manubrium, body, and xiphoid process • Manibrium articulates with clavicle & 2 ribs • Body with ribs 2 - 7 • Xiphoid attachment site for abdominal muscle
Thorax to Vertebral Column
Ribs
• Ribs are bowed flat bones • Long shaft • Tear drop shaped with a costal groove on inner surface • Head of rib has 2 facets to articulate with its vertebrae as well as the one above Ribs
• Tubercle of rib articulates with transverse process • Ligaments secure rib to transverse process • Note how the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae are angled posteriorly Ribs
Pelvis (Dancing Bone)
Femur (Largest Bone in the Body)