The Diencephalon
advertisement

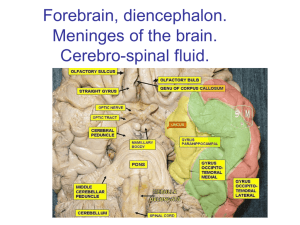
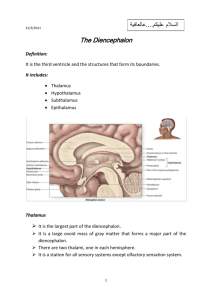
The Diencephalon Two is company, but three is a crowd The Diencephalon • The diencephalon is the section of the brain that contains the thalamus, hypothalamus and the epithalamus • It is a complex part of the brain due to the many different structures that are working at the same time The Diencephalon • The diencephalon is responsible for the interpretation of sensory information with motor output • Most of the information that is processed and acted upon happens at a subconscious level • This includes information to and from cranial nerves, regulation of emotions and various nervous and autonomic funitons The Diencephalon • The diencephalon is located superior to the brainstem • It is directly attached to the midbrain • The thalamus is divided into two different lobes that are located on the right and left half of the brain • The hypothalamus is central and does not contain multiple divisions The Epithalamus • The epithalamus is the dorsal posterior of the diencephalon superior to the third ventricle • This section of the diencephalon contains a large section of the choroid plexus • It extends through the interventricular foramen and into the lateral ventricles The Epithalamus • The epithalamus contains the pineal gland • The pineal gland is an endocrine structure that secretes hormones • The main hormone that is secretes is melatonin • Melatonin is important in the regulation of day and night cycles Video • http://www.cbsnews.com/news /parents-use-melatonin-to-getkids-to-sleep-is-it-safe/ • Keep in mind for 10 years from now… The Thalamus • The thalamus is a two lobed structure that lies at the top of the diencephalon • The two sections of the thalamus are the right thalamus and the left thalamus • The third ventricle separates the left thalamus and the right thalamus The Thalamus • Each thalamus has groups of thalamic nuclei • These nuclei are divided into several groups • These groups include the anterior, medial, ventral, posterior and lateral groups The Thalamus • The thalamus acts as a basic filter, that passes on the important sensory information that is needed in the higher parts of the brain • It also coordinates the activities of the basal nuclei and the cerebral cortex • It also is important for coordinating with the hypothalamus to control emotional states The Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus is located inferior and slightly ventral to the thalamus • It is small and is sandwiched between several different structures including the mammillary bodies, the infundibulum and the tuberal area The Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus has an important relationship to the pituitary gland • The pituitary gland is often called the master gland due to its relationship with other glands in the body • The pituitary can increase or decrease the production and function of the other glands The Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus oversees many aspects of regulating the body • When it needs to, it will communicate with the pituitary gland • Then the pituitary will send hormone signals to the rest of the body through the blood stream The Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus has many actions including… • Subconscious control of skeletal muscles • Coordination of nervous and endocrine systems • Production and regulation of emotions and behavior drives • Coordination between voluntary and autonomic functions • Regulation of body temperature • Control of circadian rhythms Video • https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=sG9wqZ7Dtx4 • http://abcnews.go.com/Health/r are-condition-drives-indiana-girleat-lightbulb/story?id=14750367