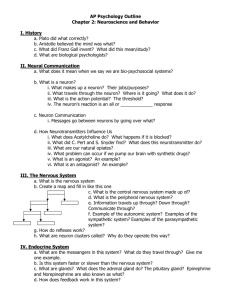
Ascending Tracts Types of Tracts Subdivisions 1st order neuron 2nd
advertisement

Ascending Tracts Types of Tracts Ascending tracts o o o o o Conveys sensory afferent impulses Ist order neuron Always pseudounipolar Location of cell bodies Enter spinal nerve Dorsal root ganglia Enter cranial nerve Respective cranial nuclei Medulla 2nd order neuron Location of cell bodies Enter spinal nerve Substancia Gelatinosa at the posterior horn of grey matter Enter cranial nerve Brain stem Fibers of 2nd order neuron Concious tracts Always cross to contralateral side Always relay on thalamus Unconcious tracts Never cross to contralateral side If crossed, crosses back to ipsilateral side Never reaches the thalamus 3rd order neuron Absent in unconcious tract Cell bodies on the VentroPostero-Lateral (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus Subdivisions Concious Sensation Tracts o o o o Stimuli from external environment Extroceptive impulses Sends concious sensations Pain Temperature Touch Consist of 3 order neurons 1st order neuron Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (AST) Senses o Pressure o Light touch Location o Ventral white column Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (LST) o o Dorsal Column/ Fasciculus Dorsalis Senses Vibration Fine touch Sense of position and movement Location o Fasciculus Gracilis Medial aspect of white dorsal column o Fasciculus Cuneatus Lateral aspect of white dorsal column Stimuli from within the body o Interoceptive/ proprioceptive impulses Sends unconcious sensations o State of muscle contraction o Position of joints Consist of 2 order neurons 2nd order neuron o o Senses o Pain o Temperature Location o Lateral white column Fasciculus Gracilis o o o Pseudounipolar in nature Proximal part of fiber synapse with 2nd order neuron at the Substantia Gelatinosa Unconcious Sensation Tracts Sensation of o Lower limbs o Lower part of thorax Fasciculus Cuneatus Sensation of o Upper limbs o Upper part of the thorax Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract Senses** o Uconcious proprioceptive impulses from Muscle spindle Golgi Tendon Organ Location** Lateral white column Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract ** Pseudounipolar in nature Enter spinal cord and directly ascend upward without o Synapse to 2nd order neuron o Crossing to other side Synapse to the 2nd order neuron at the lower part of medulla Pseudounipolar in nature Proximal part of fiber synapse with 2nd order neuron at the Substantia Gelatinosa Cell bodies located at the Subtantia Gelatinosa Fiber crosses to the contralateral side LST - In front of the central canal AST – further in front of central canal Reaches AST – ventral white column LST - lateral white column Turns upward to the thalamus Fibers end at the VPL nuclei in the thalamus Nuclei located at the lower part of medulla Fasciculus gracilis synapse at the Nucleus gracilis Fasciculus cuneatus synapse at the Nucleus cuneatus Fibers o Curved upward to form Internal Arcuate Fiber o This fiber will cross to the contralateral side o Crossing of fibers produced the Sensory Decussation Fibers ascend upward to the VPL as Medial Lemniscus Cell bodies located at the Nucleus Dorsalis (Clarke’s column) Crosses to the contralateral side Ascends immediately at the anterior part of the lateral white column Enter the Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Can be either o Terminated at the contralateral hemisphere of cerebellum Cross back though the Middle Cerebellar Peduncle t the contralateral hemisphere of Cerebellum Cell bodies located at the Nucleus Dorsalis (Clarke’s column) Ascends immediately at the posterior part of lateral white column Passes through the Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Reaches the same side of Cerebellar hemisphere 3rd order neuron N/A N/A Cell bodies located at the VPL nuclei of thalamus Projects fibers to the Primary Sensory cortex (Area 3,1,2) at the Precentral gyrus Cell bodies located at the VPL nuclei of thalamus Projects fibers to the Primary Sensory cortex (Area 3,1,2) at the Precentral gyrus Descending Tracts Types of Tracts Pyramidal Tracts Consists of (90%) o 1st order neuron Upper motor neuron o 2nd order neuron Interneuron/ Internuncial neuron o 3rd order neuron Lower motor neuron The rest 10%, upper motor neuron directly synapse with lower motor neuron Functions Influence the motor neurons for o Voluntary movement o Rapid skilled movements Modulate the function of ascending system Subdivisions 1st order neuron Ventral Corticospinal Tract Lateral Corticonuclear/ Corticobulbar Tract 1st order neuron is called the Pyramidal/Betz cells Cell bodies located at the 5th layer of cortical cell layers of cerebrum Locations o Infero-lateral part of cereberal cortex Neurons concern with Head Neck o Supero-medial part Neurons concern with Upper limbs Lower limbs Fibers o Converge into the Conrona Radiata to the Posterior Limb of the Internal Capsule o Upon reaching the midbrain, passes thorugh the 3/5th of the Cerebral Peduncle o After reaching the Pons Fibers located at the ventral part Separated into small bundles/ fasciculi by Nuclei Pontis o Then at the Medulla, fibers again converge and descends through the Pyramid 1/3 of Medulla, it can be either 85% cross to the contralateral part – Lateral Corticospinal Tract o Descends thought the posterior part of the lateral white column 15% descends directly without crossing to other part – Ventral Corticospinal Tract o Descends through the ventral white column 1st order neuron arised from the Betz cells of the cerebral cortex Coverged downward through the Corona Radiata to the Genu of the Internal Capsule Reaching the Pons will pass through the 3/5 th of Cerebral Peduncle Upon reaching to the brainstem, will synapse to respective 2nd order neuron of respective cranial nerves 2nd order neuron Interneuron at the dorsal grey matter 1st order neuron needs to cross to the contralateral part of dorsal grey mater Located at the respective level Interneuron at the dorsal grey matter 1st order neuron directly synapse to the 3rd order neuron at the same side Located at the respective level Located at the brainstem in the respective cranial nuclei 3rd order neuron Cell bodies are located at the ventral grey horn of the respective level Most of 1st order neuron crosses to the other side and synpase with the 3rd lower motor neuron of respective cranial nuclei