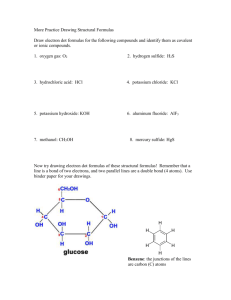
05-Nomenclature
advertisement

Drill: Determine the atomic mass of the following element that exist as: • 10.00 % Px-399 • 65.00 % Px-400 • 20.00 % Px-401 • 5.00 % Px-402 Review Drill, Grade HW & Collect Both CHM II HW • Review PP 5 • No written homework over the holiday weekend CHM II HW • Review PP 5 • Work the attached assignment & turn it in tomorrow. Nomenclature Naming Compounds Naming Binary Ionic Compounds •Name positive element first with its normal name •Name negative element last & change its ending to -ide KCl CrO2 CaCl2 Mn2O5 Al2O3 H2S Na2O etc Name Each: FeCl2 FeCl3 If the Positive element is not from columns I or II •its ox # must be determined and written in roman numerals Determining the Charge 1) Add up the oxidation numbers of all the negative elements 2) The positive portion must balance out the negative portion 3) Divide the positive portion by the metal subscript Name Each: CaCl2 K2O TiF2 LiF Deriving Formulas • Write the symbol for each element • Determine each element’s charge & apply subscripts to balance charge Derive Formulas • Magnesium chloride • Lead(II)sulfide • Iron(III)carbide BaO AlCl3 Cr2S3 SnO2 Derive Formulas • Potassium chloride • Chromium(III)phosphide • Lead(II)iodide • Tungsten(IV)arsenide Drill: Name Each: CaO BiCl3 Al2S3 TiO2 Review Drill & HW CHM II HW • Review PP 5 • Complete the attached assignment & turn it in tomorrow. Show Metals & Nonmetals on the Periodic Table. Ionic Compounds •Large EN difference •Metals bound to nonmetals Covalent Compounds •Small EN difference •Nonmetals bound to each other Naming Molecules or Covalent Compounds •Same rules as ionic compounds except: •use geometric prefixes to determine the # of each atom Geometric Prefixes 1-mono 2-di 3-tri 4-tetra 5-penta 6-hexa 7-hepta etc Name Each: CO S2O3 N2H4 SO3 Write formulas for: •Sodium sulfide •Lead (II) iodide •Diphosphorus pentoxide Write formulas for: •Chromium(III) oxide •Aluminum carbide Polyatomic Ion •A group of atoms chemically combined that together has a charge •Most are oxoanions -3 -2 •PO4 SO4 •A root element bound to oxygen Drill: Name each CuCl2 PCl5 Mn2O7 KBr MgO S2O3 Naming Polyatomic Ions • Learn the polyatomic table on page 54 • Learn how to use the periodic table to determine polyatomic ions •Name the root element •Change the ending to -ate -3 •PO4 = phosphate •Some are unusual -1 CN -1 OH C2H3O2 -2 C2O4 -1 +1 O H2O H3 +1 NH3 NH4 Polyatomic Ion Endings •Maximum O = -ate •1 less than max O = -ite -2 •SO4 = sulfate -2 •SO3 = sulfite Naming Ternary Compounds • Follow ionic rules for naming the compound • Name the polyatomic ion as the positive or negative portion Name Each: CaCO3 K2SO4 Write Formulas For: •Lead (II) nitrate •Aluminum sulfate •Potassium chromate •Ammonium phosphite Name: Ti(NO3)2 CaSO3 MnSO4 Write Formulas For: •Magnesium nitrate •Aluminum phosphate •Potassium nitrite •Ammonium chloride Drill: Name: Pb(NO3)2 MgSO3 S2O4 Review Drill & HW CHM II HW • Review PP 1 – 5 • Work the attached assignment & turn it in tomorrow. • Lab: Thursday Name the Following: BaSO4 CuNO3 SO2 (NH4)3PO4 Column 7 Dilemma for Polyatomic Ions • There are 2 polyatomic names (-ate & -ite) for each root element. • Polyatomic ions from column 7 have 4 possibilities 4 examples from Column 7 -1 ClO4 -1 ClO3 -1 ClO2 -1 ClO 4 examples from Column 7 -1 ClO4 perchlorate -1 ClO3 chlorate -1 ClO2 chlorite -1 ClO hypochlorite Also true for others IO4 periodate -1 IO3 iodate -1 IO2 iodite -1 IO hypoiodite -1 Naming Acids • ___ ide ions become: • hydro ___ ic acids • ___ ate ions become: • ___ ic acids • ___ ite ions become: • ___ ous acids Name or Give Formulas For: •HBr(aq) H2SO4(aq) •NaNO3 (NH4)3PO3 •Phosphoric acid •Nitric acid •Chloric acid Derive formulas for each: • Cesium oxide • Barium chloride • Calcium phosphide • Aluminum sulfide Drill: Name Each •Fe2(SO4)3 •H2CrO4 •SF6 Review & Collect Drill & HW Did Anyone Miss Lab Yesterday? CHM II HW •Review for a Test on Monday covering PPs 1 - 5 % Composition • Determine the mass of each element in the compound. • Determine the total mass of the compound • Divide each portion by the total & multiply by 100 % Determine the % composition each element in: Fe2O3 C3H6O3 BaCl2*2H2O Test 1 Review Classify types of matter •Dirt •Sodium •Glucose •Vodka Classify properties •Color •Shape •Ability to burn Convert the following: •2.1 mg to mg •3.2 km to cm •4.8 Gm/Ms to mm/ns Name each of the following: KCl SO2 NaNO3 H2CO3(aq) MnSO4 HI(aq) HClO NH4BrO4 Name each of the following: NH4Cl KC2H3O2 KNO3 Li2CO3 BaSO4 K2HPO3 CuBrO MgC2O4 Derive formulas for each: • Silicon dioxide • phosphorus trichloride • Sulfur hexafluoride • Iodine trifluoride Derive formulas for each: • Potassium sulfate • Lead(II)chromate • Aluminum hydroxide • Ammonium cyanide Name each of the following: •SeO •NO2 •N2O4 CS2 Cl2O PCl3 Drill: Determine % Comp for Each: C2 H 6 O Name each of the following: •SO4 -3 •PO4 -1 •ClO4 -1 •ClO2 -2 -2 SO3 -1 NO3 -1 ClO3 -1 ClO Derive formulas for each: Chromate Arsenate Arsenite Bromite Sulfate Nitrate Cyanide Acetate Drill: Name each: •KBr •BaF2 •K2O •Al2O3 MgS K3P LiH H2S Name each of the following: HCl H2S HNO3 H2CO3 H2SO4 H3PO3 HBrO HBrO4 Derive formulas for each: •Chromic acid •Hydroiodic acid •Sulfurous acid •Bromic acid Name each of the following: •CuO •PbO2 •CrCl2 •CrCl3 MnS Cu2O MnF2 SnCl4 Name each of the following: FeO Fe2O3 Derive formulas for each: • Lead(IV)oxide • Copper(II)sulfide • Manganese(VII)oxide • Nickel(II)fluoride Name each of the following: • BaCO3 • KNO2 • CuClO3 • Al2(SO4)3 Name each of the following: • Cl2O • N2O3 • CO2 • SO3 SO2 P2O5 CO N2H4 Name each of the following: NaCl S2O3 Na2CO3 HNO3(aq) MnSO4 HBr(aq) HClO NH4IO4 Chapter 3 General •Define all the Key Terms on page 74 Nomenclature •Work problems 43 – 56 •On Pages 51 & 52