The Cell Cycle Notes
advertisement

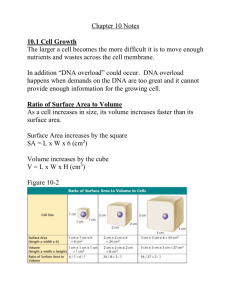
The Cell Cycle Sections 5.1-5.2 The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication, and cell division. Four Main Stages • The cell cycle has four main stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Gap 1 (G1) Synthesis (S) Gap 2 (G2) Mitosis (M) • • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Interphase First Stage: Gap 1 (G1) – Cell carries out normal functions • Ex: skeletal muscle cell contracts to move joints – Cells also continue to grow during this stage. – Cells spend most of their time in this stage. • Length of this stage depends on the type of the cell Second Stage: DNA synthesis (S) • DNA is copied • At the end of the synthesis stage, the cell nucleus contains two complete sets of DNA. Third Stage: Gap 2 (G2) •Cells continue to carry out their normal functions •Additional growth occurs Fourth Stage: Mitosis (M) • Includes two processes: – Mitosis • division of the cell and its contents • During mitosis, the nuclear membrane dissolves, the duplicated DNA condenses around proteins and separates, and two nuclei form. – Cytokinesis • Process that divides the cell cytoplasm • Result is two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the original cell. • Mitosis occurs only if the cell is large enough and the DNA undamaged. • Cells divide at different rates. –The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. –Some cells are unlikely to divide (G0). • Cell size is limited. –Volume increases faster than surface area. • Surface area must allow for adequate exchange of materials. –Cell growth is coordinated with division. –Cells that must be large have unique shapes. Chromosomes • DNA plus proteins is called chromatin. • One half of a duplicated chromosome is a chromatid. • Sister chromatids are held together at the centromere. • Telomeres protect DNA and do not include genes. • Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. chromatid telomere centromere telomere Condensed, duplicated chromosome • Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. • Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter cells. – Interphase (G1, S, G2) prepares the cell to divide. – During interphase, the with DNA is duplicated. nucleus DNA Parent cell centrioles spindle fibers centrioles 4 Phases of Mitosis 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase • PMAT Remember this… Please Make A Taco Prophase • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes (consisting of two identical sister chromatids). • Nuclear envelope breaks down • Nucleolus disappears • Centrosomes and centrioles begin to move to opposite sides of the cell • Spindle fibers form from the centrioles Interphase -> Prophase Metaphase • Spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome. • Chromosomes align along the cell equater • Meta=Middle Prophase -> Metaphase Anaphase • Sister chromatids separate from each other. • Spindle fibers begin to shorten, which pulls the sister chromatids away from each other and toward opposite sides of the cell. Metaphase -> Anaphase Telophase • Complete set of identical chromosomes is positioned at each pole of the cell. • Nuclear membranes start to form • Chromosomes begin to uncoil • Spindle fibers fall apart Anaphase -> Telophase Cytokinesis • Divides the cytoplasm into two daughter cells, each with a genetically identical nucleus • Completion of one full stage of the cell cycle • Differs in animal and plant cells – In animal cells, cleavage furrow forms pinching the membrane closed. – In plant cells, a cell plate forms. • Cells enter interphase and the cylces begins again Telophase -> Cytokinesis Formation of New Cells… • Critical in both multicellular and single-celled organisms • Single-celled organisms use cell division to reproduce • Multicellular organisms use it for growth, development, and repair. Cell Cycle Book Directions • Title Page: Your name • Interphase: picture, description, label…nucleus, chromatin, centrioles, and spindle fibers • Mitosis: definition • Prophase: picture, description, label…nuclear membrane, chromosomes, centrioles, and spindle fibers Cell Cycle Book Directions • Metaphase: picture, description, label… chromosomes, centrioles, and spindle fibers • Anaphase: picture, description, label…chromatid, centrioles, and spindle fibers • Telophase: picture, description, label…nuclear membrane, chromatid, centrioles, and spindle fibers • Cytokinesis: picture, description, label…nucleus, chromatin, and centrioles