Careers in Exercise Physiology - University of Miami
advertisement

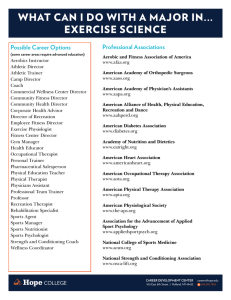
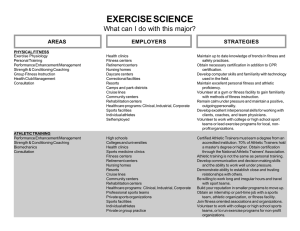
Careers in Kinesiology and Sport Sciences Because of high visibility gained from our student presentations and the advanced multidisciplinary research, our graduates have consistently enjoyed success in a variety of different job settings: Personal Trainer A personal trainer typically works one-on-one with an individual to improve their fitness level and general health. A personal trainer should have a strong background in anatomy and kinesiology, as a large part of this job deals with improving muscular strength and cardiovascular endurance. Certified Clinical Exercise Specialist Cardiopulmonary Specialist These clinicians are typically responsible for providing exercise testing, training and education regarding disease management. Clinical settings include hospitals, outpatient clinics, and medically supervised fitness centers. Group Exercise Instructor A group exercise instructor leads exercise sessions for a group of participants. Examples of group exercise instruction include land- or water-based general classes, dance/step aerobics, chair aerobics, and cycling. Group exercise instructors can be employed in a variety of settings including commercial fitness centers, employee fitness programs, and hospitals. Employee fitness Director Employee fitness programs are common in the workplace, especially in the corporate, commercial, and hospital setting. Along with conducting exercise programs and supervising all fitness staff, the employee fitness director may also be trained as a wellness specialist to provide broad-based health promotion and wellness education programs. Strength (Sport) and Conditioning Coach Sport teams employ strength and conditioning coaches to enhance their athletes’ agility, strength, endurance, flexibility, and power. Positions usually require a Master’s degree and certification by the National Strength and Conditioning Association. Athletic Trainer Athletic trainers are health care professionals that specialize in the emergency care and treatment of sportrelated illness and athletic injuries. One must successfully pass the NATA certification examination. Athletic trainers work with patients and clients in high school, college or professional sports, sports medicine and rehabilitation clinics, physician offices, hospitals, military, performing arts, and commercial enterprises. Dietician/Sports Nutritionist Dietetics is the study of nutrient intake and how foods are digested and metabolized in order to provide the necessary energy to fuel muscular activity. Dieticians also study dietary patterns in order to maximize performance, prevent disease and improve general health. Sports nutritionists specialize in nutritional recommendations for active individuals and competitive and recreational athletes. Occupational Physiologist Occupational physiologists work with many different professionals to improve the performance of workers by enhancing their health and occupational abilities, preventing or rehabilitating workplace injuries, and redesigning the work environment to fit the worker. They may also develop and administer pre-employment physical capacity tests to determine if the worker is physically able to perform the job. Physical/Occupational Therapist The physical therapist helps people recover from injuries or diseases of the muscles, joints, nerves, or bones. The occupational therapist works more with fine motor skills and dexterity and both therapists use various physical modalities and exercise, to improve movement function. Medical Doctor A medical doctor is highly trained in the art and science of diagnosis and treatment of diseases and the maintenance of health. Medical schools require a minimum of four years after a basic college degree. Beyond medical school, there are many specialties to choose from in order to be part of a sports medicine or exercise science team, including primary care sports medicine, orthopedic surgery, or cardiology. Biomechanics Specialist Biomechanics is the study and explanation of the laws of physics applied to physical activity, exercise, and sport. Biomechanics can be used to explain how muscles, bones, and joints are injured under certain conditions, and how to improve performance using motion analysis techniques. Researcher Researchers conduct studies from either a basic or applied scientist’s perspective. Basic researchers usually conduct studies on the cellular and molecular levels, examining how organ systems work, adapt, or respond to various factors. Applied researchers usually conduct studies with a more practical focus, addressing questions that are more applicable for immediate use, such as how to improve general health, quality of life, and performance in various sports. Sport Administrator Sport administrator’s role in an organization is to handle all things from reception work to human resources, and from marketing to managing a club or sport organization. They are equipped with resources to ensure the smooth operation of all major activities and events in an organization. Duties may include promotion of a sport organization’s or club’s visibility, its services, its fundraising, or its public relations efforts. Sports Medicine Clinic Director The clinical director is usually a trained health care professional with managerial experience. The director ensures appropriate assessment, evaluation, treatment and follow-up of all patients participating in his/her clinic. Chiropractor Chiropractors are also known as doctors of chiropractic medicine or chiropractic physicians. They diagnose and treat patients with health issues involving the musculoskeletal system and treat the effects of those problems on the nervous system and on general health. Many chiropractic treatments deal specifically with the spine and the manipulation of the spine as it enhances painfree physical activity and movement. Physician Assistant Physician assistants (PAs) practice medicine under the supervision of physicians and surgeons. PAs are formally trained to provide diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive healthcare services, as delegated by physicians. Working as members of a healthcare team, they take medical histories, examine and treat patients, order and interpret laboratory tests and x-rays, and make diagnoses. Professor College and university faculty instruct students in a wide variety of academic and vocational subjects. In addition to teaching, professors, particularly those at 4-year colleges and universities, perform a significant amount of research in their areas of expertise. They must also deliver oral presentations, keep current in their field, and often consult with government, business, nonprofit, and community organizations. References Modified from Careers section of American Kinesiology Association website (www.AmericanKinesiology.org) Bureau of Labor Statistics Website (www.bls.gov) Google (www.google.com) Google Images (www.google.com/imghp) Sample Job Descriptions (www.samplejobdescriptions.org) University of Miami School of Education Website (http://www.education.miami.edu/Program/Programs.a sp?Program_ID=38)