Elements, Atoms, and Ions
advertisement

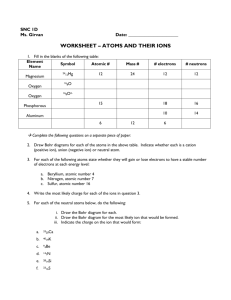
Elements, Atoms, and Ions Elements 88 occur naturally Table 4.1 -18 most abundant elements in Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere Table 4.2 - Abundance of elements in the human body Symbols -one, two, or three letters -first letter is capitalized, others are not -some come from English names -some come from Latin names Dalton’s atomic theory 1. 2. 3. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Atoms are simply rearranged. Formulas of compounds Compound - distinct substance that is composed of the atoms of two or more elements and always contains exactly the same relative masses of those elements. Chemical formula -atoms are indicated by element symbols -number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript *if there is no number after the chemical symbol, there is only one atom of that element Atomic Structure J.J. Thomson - atoms contained negative particles, which are now called electrons Rutherford - atoms have a dense center of positive charge *proton - positive charge in nucleus *neutron - neutral particle in nucleus Atoms differ in: number of protons number and arrangement of electrons - electrons determine the chemical behavior of atoms Isotopes Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons Atomic number - # protons Mass number - # of protons and neutrons - X = symbol of element - A = mass number - Z = atomic number A - Z = number of neutrons Natural states of elements Noble elements - gold, silver, platinum relatively unreactive Diatomic molecules - molecules made up of two atoms HON F ClIBr Ions Atoms are neutral - zero net charge Ions are atoms with a charge *cation - positive ion, produced when electrons are lost *anion - negative ion, produced when electrons are gained Ion charge can be predicted using the periodic table Group 1 ----1+ (lose one electron) Group 2 ----2+ (lose two electrons) Group 13 ----3+ (lose three electrons) Group 14 ----4+ (lose four electrons) Group 15 ----3- (gain three electrons) Group 16 ----2- (gain two electrons) Group 17 ----1- (gain one electron) Group 18 ---- no charge Compounds that contain ions Ionic compounds: *Often have very high melting points, and conduct electric current when melted or dissolved in water. *Composed of a metal (cation) and a nonmetal (anion) *Have a net charge of zero (positive charge = negative charge)