Atoms and Molecules
advertisement

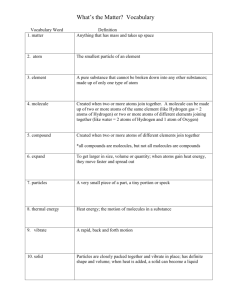
Atoms and Molecules Basic units of EVERYTHING! Which of these is true? 1. “Atom” and “molecule” mean the same thing. 2. Atoms are made of molecules. 3. Molecules are made of atoms. 82% 15% 3% 1 2 3 What is the smallest structure in this list that can be seen with an ordinary desk microscope? 1. 2. 3. 4. Cells. Cell nucleus. Atoms. Chain molecules, such as proteins. 35% 38% 18% 10% 1 2 3 4 Atoms In our model of scale, remember that the BB represented an atom. Electrons Hydrogen Helium Neutrons Protons As a class, identify the atoms represented here and label the sub-atomic particles. Carbon Oxygen Phosphorous Calcium What elements are represented here? Use the Periodic Table on the wall to identify these atoms. What does the term “valence shell” mean? Label the valence shell on each of these. Ions Loss or gain of an electron makes an atom into an ion. - + Gaining an electron makes a positive or negative ion? - Losing an electron makes a positive or negative ion? Isotopes Atoms that gain or lose a neutron become isotopes. Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for imaging (such as PET scanners). Why is this important? • Each element has distinct properties: color, melting point, reactivity, etc. • The basic atomic structure of each element determines that element’s properties. Change the structure, and you have an entirely different element. Which of these is found in the nucleus of an atom? 78% 1. 2. 3. 4. Protons Electrons DNA Depends on the atom 11% 6% 1 2 3 6% 4 An ion is an atom that has lost or gained: 83% 1. 2. 3. 4. An electron A proton A neutron Any sub-atomic particle 6% 1 2 11% 0% 3 4 T or F: An atomic nucleus and a cell nucleus are about the same size. 33% 33% 33% 1. True 2. False 3. Depends on which cell and which atom. 1 2 3 Atoms bond together • Molecules are made up of atoms bonded together. • The structure of an individual atom determines: • Whether the atom can form bonds. • How many other atoms it can bond to. In our model of scale, remember that the marble represented a small molecule, such as glucose. How many atoms can each of these atoms bond with? How do we know? 1 4 3 2 5 2 Fill in the blank column with number of covalent bonds formed by each atom. Ionic Bonding Ionic substances tend to form crystaline lattices rather than distinct molecules. Covalent Bonding Co = together valent = valence shells The hydrogen atom. How many bonds can it form? Covalent bonding A hydrogen molecule. How many hydrogen atoms are involved? Can there be more? Why or why not? W O R K • Describe in your own words the difference between ionic and covalent bonding. T O G E T H E R Covalent Bonding Polar bonding between atoms produces a polar molecule, which has areas with slightly positive or slightly negative charges. W O R K • Describe in your own words the difference between nonpolar and polar covalent bonding T O G E T H E R When atoms bond together, they make: 20% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 20% 20% 2 3 20% 20% Cells Molecules More atoms Ions Isotopes 1 4 5 Which of these is true? 1. Molecules and cells are about the same size. 2. Molecules are much smaller than cells. 3. Cells are much smaller than molecules. 4. “Cell” and “molecule” mean the same thing. 94% 6% 0% 1 2 3 0% 4 Which kind of bond between atoms creates a distinct molecule? 44% 1. Ionic bonding 2. Covalent bonding 3. Both ionic and covalent bonding. 39% 17% 1 2 3 Which is true about polar covalent bonding? 1. An electron is shared equally between two atoms. 2. An electron is shared unequally between two atoms. 3. An electron leaves one atoms and becomes part of another. 94% 6% 1 0% 2 3 True or false? The atomic “shell” is a cell membrane. 88% 1. True 2. False 13% 1 2 Why is polarity so important? Salt dissolves in water. Oil does not. Why? What will oil dissolve in? Why? • Is a water molecule in the gas phase larger than, smaller than, or the same size as a water molecule in the solid phase? • Describe what happens to water molecules as liquid water evaporates. W O R K T O G E T H E R Molecules bond together Weak attractive forces between molecules are called hydrogen bonds. Here, sugar (a polar substance) is in solution with water (also polar). Mark where the hydrogen bonds will form. Hydrogen bonding occurs: 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. Between atoms. 2. Between molecules. 3. Between cells 4. Between any particles. 1 2 3 4 Hydrogen bonding is: 1. Strong and difficult to break, like polar covalent bonding. 2. A strong attraction between charged ions, like ionic bonding. 3. A weak attraction between polar molecules. 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 Properties of Water • Water is: • Cohesive • Adhesive • A “universal solvent” • Water also has: • A high specific heat • A high heat of vaporization pH is a ratio between H+ and OH- ions in solution. • One unusual property of water is that it is less dense in the solid stage than in the liquid stage, which causes ice to float. Why does water become less dense as it freezes? Use what you learned about hydrogen bonding between molecules. W O R K T O G E T H E R Recap 1. What is the difference between atoms and molecules? 2. What is the difference between ionic bonding and polar covalent bonding? 3. How is polarity related to pH?