Yr.8 Mid-Term Revision weather and climate 2015
advertisement

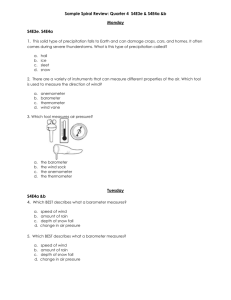
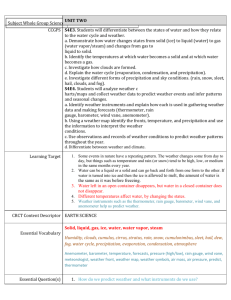
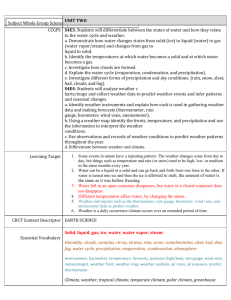
What is the meaning of weather and climate? Copy the definition for: Weather = the state of the atmosphere around us (changes every day) Climate = the average weather over a period of time (many years) The 4 main parts of the weather Precipitation (How much it has rained / snowed and how wet it is) Visibility (How much we can see Is it foggy / dusty?) Temperature (How hot or cold it is) Wind (How fast it is and which direction it will travel) Final Task – Build a sentence Level 3/C The word weather means… The word climate means. Describe what the weather it is like today. Level 4/B The word weather means. The word climate means. The weather today is… (use specific examples like wind, visibility, precipitation) Level 5/A The difference between weather and climate is… The weather today is… (use examples like wind, visibility, precipitation) The weather in the UK is… (use examples like wind, visibility, precipitation) It is important for humans to know the weather because… Important words Condensation Water vapour (con/den/sa/tion) Ice Evaporation (e/vap/or/ation) Water turns from gas to a liquid Liquid water Water turns from a liquid into a gas Solid water Plain H2O Water gas The Water Cycle The Water Cycle in more detail Places get warm because of the _______. It heats up the ________, and the ______. The warm air ________, so ______ air ________ in to replace it. This cold air is ______. The water from the oceans __________ to become a gas ( _________ __________). As warm air rises it ________ down. The water vapour ____________. That’s why we get ________. When the clouds become too _________, it rains. Sometimes when the weather is very ________ the water droplets may fall as __________, hailstone or sleet. Clouds causes rises rising cold raining sun evaporates ocean snow condenses cold evaporation flows condensation heavy wind water vapour cools Earth Places get warm because of the s_______. It heats up the E________ and the o______. The warm air r________, so c______ air f________ in to replace it. This cold air is w______. The water from the oceans r__________ to become a gas ( w_________ v__________). As warm air rises high it c________ down. The water vapour c____________. The tiny droplets form c________. When the clouds become too h_________, it rains. Sometimes when the weather is very c________ the water droplets may fall as s__________, hailstone or sleet. Clouds causes rises rising cold raining sun evaporates ocean snow condenses cold evaporation flows condensation heavy wind water vapour cools Earth Type of weather Instrument How it works Units it measures in Temperature Anemometer The arm points in the same direction that the wind is travelling in Degrees celcius (ºC) Wind speed Thermometer The person recording looks at how much of the sky is covered in cloud, they divide the sky into 8ths Kilometres per hour (kph) Wind direction Rain gauge The metal cups rotate in the wind. The stronger the wind, the faster the cups turn. Precipitation Barometer This records the force of the air on the surface of the earth Air pressure Eyes Cloud cover Weather vane A container is placed in a stationary position and records how much rain/sleet/snow/hail falls. The liquid (mercury or spirit) in the bulb at the bottom expands as it gets warm and rises up a tube. You can then read off the value. Compass direction (NSEW) Millimeters (mm) Millibars (mB) Oktas (8ths) Type of weather Instrument Units it measures in Temperature Thermometer Degrees celcius (ºC) Wind speed Anemometer Kilometres per hour (kph) Wind direction Weather vane Compass direction (NSEW) Precipitation Rain gauge Millimeters (mm) Air pressure Barometer Millibars (mB) Cloud cover Eyes Oktas (8ths) Temperature Temperature is a measure of how warm or cool it is. The units of temperature are degrees Celsius °C or degrees Fahrenheit °F. (Like MPH and KMPH) How is temperature measured? Temperature is measured using a thermometer. Most thermometers are made so liquid (mercury or spirit) in the bulb at the bottom expands as it gets warm and rises up a tube. Temperatures are measured in the shade, so the sun’s rays do not heat up the instrument being used. Air pressure The force exerted on the Earth by the air above. Air pressure is measured using a barometer. It records it in millibars (mB) Air pressure changes with height, the higher up we go, the more air pressure. Wind Direction: • A Weather vane records the direction the wind is blowing in. • It spins and points towards the direction. • A compass direction can be calculated: – North – South – East – West Wind speed Wind is simply moving air. Wind speed is a measure of how fast the air is moving. It is measured using an anemometer An anemometer has metal cups that rotate in the wind. The stronger the wind, the faster the cups turn. Precipitation: Rainfall Rain is a type of precipitation, Snow, sleet, hail, dew and fog are also types of precipitation. Precipitation occurs when water vapour in the air cools and condenses into water droplets. Rainfall is measured using a rain gauge. Rainfall is usually measured in millimetres (mm). Cloud Cover • Your eyes are the most useful tools to measure the weather • You can look at the sky and see how much is covered in cloud • We record this in Oktas • 1 Okta is ⅛th • A full sky of cloud would be 8 Oktas Beaufort scale How is wind speed estimated without an anemometer? The Beaufort scale measures wind intensity using the effects of wind to estimate its speed. It uses a scale from 0 to 12. 0 on the scale means there is no wind. 12 indicates hurricane conditions. Type of weather Instrument How it works Units it measures in Temperature Thermometer The liquid (mercury or spirit) in the bulb at the bottom expands as it gets warm and rises up a tube. You can then read off the value. Degrees celcius (ºC) Wind speed Anemometer The metal cups rotate in the wind. The stronger the wind, the faster the cups turn. Kilometres per hour (kph) Wind direction Weather vane The arm points in the same direction that the wind is travelling in Compass direction (NSEW) Precipitation Rain gauge A container is placed in a stationary position and records how much rain/sleet/snow/hail falls. Millimeters (mm) Air pressure Barometer This records the force of the air on the surface of the earth. Millibars (mB) Cloud cover Eyes The person recording looks at how much of the sky is covered in cloud, they divide the sky into 8ths Oktas (8ths) Picture 1.Rain gauge a) A rain gauge is used to measure: The amount of rain that has fallen. Rain is a type of precipitation b) The rain gauge is: A container which gathers the rainfall. c) The unit of measurement used is: Millimeters (mm) 2.Anemometer a) An anemometer is used to measure: b) The anemometer is: c) The unit of measurement used is: 2.Anemometer a) An anemometer is used to measure: The speed of the wind. b) The anemometer is: made of metal cups which catch wind and spin. The faster the wind, the more they spin. C) The unit of measurement used is: Killometers per hour (KPH) 3.Barometer a) A barometer is used to measure: b) The barometer is: A gauge (like a clock) which measures the pressure the sky exerts (puts) on the Earth. C) The unit of measurement used is: 4.Eyes a) Eyes are used to measure: b) The eyes are: A part of the body which we use to see things. We measure the amount of sky that is covered with clouds by dividing it in to 8 parts and check how many parts are covered. C) The unit of measurement used: Quick Fire Activity Name 5 extreme weather events beginning with the following letters: H____________________ H____________________ M____________________ S____________________ F____________________ Why is climate so different in different places, and in different months? EARTHS TILT LATITUDE WIND DIRECTION/ SPEED DISTANCE FROM THE COAST HEIGHT ABOVE SEA LEVEL OR ALTITUDE Factors that influence climate OCEAN TEMPERATURE 1.Use page 84 and 85 to add drawings to your spider diagram 2. Explain a. latitude b. altitude c. wind direction Climate data for London The climate generally gives us average temperature and precipitation As geographers we can represent this in an excellent and interesting way!! A way that will allow us to compare them both visually…….. A climate graph. Here is your data…… Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Average temperature (˚C) 8 8 11 14 17 21 23 23 19 15 11 8 Precipitation (mm) 55 40 41 43 49 44 44 49 49 68 59 55 Climates around the world Type Climate Countries Desert Very dry and hot all year round, especially in summer, with cooler winters Very cold all year. Many parts covered in snow and ice. Saudi Arabia Egypt Australia Canada Serbia Polar Mountain High up and cold. Lots of rain and snow. Maritime Tropical Switzerland China Very wet. Warm summers and UK cool winters. France Holland Rainy and hot most of the year Brazil with a dry season Madagascar India Picture • Key words and definitions • Altitude: How high a place is, above sea level • Atmosphere: The air or climate around us / a layer of gas around the Earth. Frontal rainfall: A warm front (warm air) meets a cold front, causing it to condense and rain. High pressure This weather type bring clear skies with no clouds. Hurricane: A severe depression, with very strong winds. • Climate change: How the Earth and its climate are changing due to the Earth getting warmer. • Climate: The average weather conditions of an area usually measured over 30 years Low pressure: This weather type of weather brings wind and rain. • Compass: An instrument used to show direction, with a magnetic needle that points North. Meteorologist: This is a person who studies the weather • Condensation: When water vapour (gas) cools to form water droplets (liquid). This process produces clouds, mist and fog • Convectional rainfall: The sun heats the Earth, convection currents of warm air rise, water vapour condenses and rain falls. • Depression: A low pressure weather system that brings wet and windy weather. • Earths tilt: The angle the earth rotates around the sun • Equator: An imaginary circle around the centre of the Earth, dividing it into two parts. Weather Forecast: A prediction of what the weather will be like. • Evaporation When rain (liquid) or ice or snow (solid) is heated up to change to water vapour (gas). Weather: The state of the atmosphere at one place at one time (can change daily). • Latitude: How far a place is North or South of the equator. Meteorology: This is the study of weather Microclimate: Where variations in the weather conditions occur over a small area. Ocean current: how warm or cold the sea is. Relief rainfall: When warm air is forced to rise above a mountain, in to a higher, cooler place causing it to condense and rain. Water vapour: The liquid water, in its Gas form. LATITUDE This means the distance from the Equator. It is one of the main factors that affects climate. The Earth is tilted so some of the suns rays which hit the middle (equator area) are the hottest and those that hit the top (UK) and bottom of Earth are spread out so they are not so hot. EARTH’S TILT The Earth is tilted as it orbits (travels around) the Sun. One full orbit takes one year. The tilt is the reasons we get different seasons. When our country is tilted towards the Earth it is hotter (Summer), when it is tilted away it is colder (Winter). WIND DIRECTION/SPEED When air travels from colder regions then it brings cold wind with it. If the wind comes across the ocean then it will bring water vapour with it. When water vapour cools down with the cold wind it becomes rain! ALTITUDE (HEIGHT ABOVE SEA LEVEL) The higher you are the cooler it becomes. The temperature can drop 1*C for every 100 metres you go up. That’s why its so cold on top of mountains.