Theories - UHS-CD3
advertisement

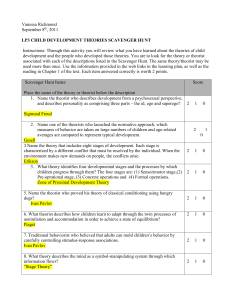
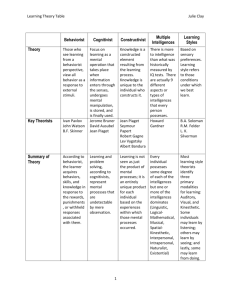
Theories and Theorists Jamie Clem and Shelby King Psychodynamic Theory • • • Psychodynamic theory is about personality development and emotional problems. Psychodynamic theories look at development in terms of internal drives that are often unconscious. These motives are the underlying forces that influence human behavior and provide the foundation for universal stages of development. Psychodynamic Theorist: Sigmund Freud • • • • • • May 6 1856-September 23 1939 Austrian Sigmund Freud began his career as a medical doctor. Became known as the founding father of psychoanalysis According to Freud, people possess three basic drives: the sexual drive, survival instincts, and a drive for destructiveness. Believed that all people have an ID, ego, and superego o Id-The personality component made up of unconscious psychic energy that works to satisfy basic urges, needs, and desires. o Ego- The organized, realistic part that mediates between the Id and the ego o Superego- Plays the critical moralizing role; can control your urges that you receive from your id Psychodynamic Theorist: Erik Erikson • • • • Born June 15, 1902 German born American developmental psychologist He proposes 8 stages of psychosocial development. The stages are: 1) The newborn- Trust vs. Mistrust; 2) Toddlers- Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt; 3) Childhood- Initiative vs. Guilt; 4) School- Competence vs. Inferiority; 5) Adolescence- Search for Identity vs. Role Confusion; 6) Young adulthood- Intimacy vs. Isolation; 7) Grown-Ups- Generativity vs. Stagnation; 8) Old age- Integrity vs. Despair A key point of Erikson’s theory is balance. Balancing a child's wishes and the demands of the environment with a mentally healthy dose of each emotion is essential for personality strength. Behaviorist Theory • • • • • An approach to psychology that combines elements of philosophy, methodology and theory The most pragmatic and functional of the modern psychological ideologies Developed during the 1920’s and is continually modified According to behaviorists three types of learning occur o Classical Conditioning o Operant Conditioning o Observational Learning Learning is mostly a developmental habit Behaviorist Theorist: Ivan Pavlov • • • • • September 26 1849-February 27 1936 Russian psychologist Main focus of study was animals Used the experiment of “Pavlov’s dogs to found classical conditioning o Classical Conditioning- A learning process that occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired, a response that is at first elicited by the second stimulus is eventually elicited by the first stimulus alone This became a cornerstone of behaviorist theory Behaviorist Theorist: John B. Watson • • • • • January 8 1878- September 25 1958 American theorist who studied Pavlov’s animal experiments Converted Ivan Pavlov’s ideas into human terms One of his ideas was to discourage emotional ties between parents and their children because they interfered with the child’s direct learning from the environment He gave scientific validity to the idea that teachers should set conditions for learning and reward proper responses Behaviorist Theorist: Edward L. Thorndike • • • • • August 31, 1874- August 9, 1949 Studied the conditions of learning. Known as the “godfather of standardized testing” Helped to develop scales to measure student achievement and usher the era of standardized educational testing Set forth the famous “stimulus-response” technique. A stimulus will recall a response in a person; this forms learned habits Attention should be focused on the consequences of behavior and the various kinds of reinforcement Behaviorist Theorist: B. F. Skinner • • • • Born March 20, 1904 Took the idea of “tabula rasa” one step further to create the doctrine of the “empty organism”. That is, a person is like a vessel to be filled by carefully designed experiences Skinner maintained that there is no behavior that cannot be modified Some people argue that Skinnerian concepts tend to depersonalize the learning process and treat people as puppets. Others say that behaviorist psychology has made us develop new ways to help people learn and cope effectively with the world Behaviorist Theorist: Albert Bandura • • • • Born December 4, 1925 Developed another type of learning theory, called social learning As behaviorists began to accept that what people said about their feelings and internal state was valid, they looked at how children became socialized Socialization is the process of learning to conform to social rules. Sociallearning theorists watch how children learn these rules and use them in groups. They study the patterns of reinforcement and reward in socially appropriate and unacceptable behavior Cognitive Theory • • • The cognitive theory describes the structure and development of human thought processes and how those processes affect the way a person understands and perceives the world. Studies how children learn to think and what to think about Jean Jacques Piaget’s theory forms the cornerstone of early childhood educational concepts Cognitive Theorist: Jean Jacques Piaget • • • • • • • • 1896-1980 Studied thought processes and how they change with age While recording children’s abilities to answer questions correctly, he became fascinated with children’s incorrect responses. He noticed that children tended to give similar kinds of wrong answers at certain ages Developed the psychiatric method of question and response Piaget did not believe the development of thinking was either intrinsic or extrinsic Regardless of their age, all people develop schemas We use three basic processes to think: these are known as the adaptive processes of assimilation and accommodation and the balancing process of equilibration He identified four major stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor stage, preoperational stage, concrete operational stage, formal operational stage Constructivist Theory • • • • • Developed from the cognitive theory. Concerns the best method of teaching children Based on experiential learning through real life experience to construct and conditionalize knowledge It is problem based, adaptive learning, that challenges faulty schema, integrates new knowledge with existing knowledge, and allows for creation of original work or innovative procedures Constructivism is a theory of learning which states that individuals learn through adaptation Sociocultural Theory • • • The sociocultural theory focuses on the child as a while and incorporates ideas of culture and values into child development, particularly the areas of language and self-identity In this view, children’s development is more than just a response to personal experience . Rather, children are influenced by their family, community, and socioeconomic status Culture plays a deep role in learning Sociocultural Theorist: Lev Vygotsky • • • • November 17 1896-June 1934 Graduated from Moscow university with a degree in literature in 1917 Vygotsky focused on how how values, beliefs, skills and traditions are transmitted to the next generation Believed in the connection between culture and development • o Particularly the connection between the child and other important people Considered the child as a whole o Taking a humanistic- more quantitative approach to studying children Ecological Theory • • • • Based on the premise that development is greatly influenced by the forces outside the child Bronfenbrenner’s model describes four systems that influence human development; these four are the settings in in which a child spends a significant period of time, the relationships of those settings, the societal structures, and then the larger contexts in which these systems operate The values of the community can influence social conditions Everything in the environment of the child’s life indirectly or directly affects the child Multiple Intelligences Theory: Howard Gardner • • • • Born in Pennsylvania His theory of multiple intelligences asserts that there is strong evidence, both from the brain-based research and from the study of genius, that there are at least eight basic intelligences Intelligence becomes the ability to solve a problem or to create a product that is in a culture The intelligences are musical intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, linguistic intelligence, spatial intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, and naturalist intelligence Maturation Theory: Arnold Gesell • • • • • • Maturation is the process of physical and mental growth that is determined by heredity The maturation sequence occurs in relatively stable and orderly ways Maturation theory holds that much growth is genetically determined from conception Maturation and growth are interrelated Arnold Gessell was a physician intrigued with the notion that children’s internal clock governed their growth and behavior Gessell established norms for several areas of growth and behaviors that accompany such development Humanistic Theory • • • • The humanist theory has a place in early childhood education because it attempts to explain how people are motivated Centered on people’s needs, goals, and successes This was a change from the study of mental illness Self-actualization is what gives a person satisfaction in life