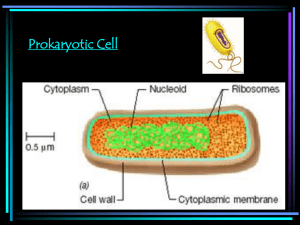
Taxonomy

Taxonomy
Classification
Classification - the grouping of objects or information based on similarities.
Used to better understand and study the enormous variety of living things.
Taxonomy
Taxonomy
-The branch of biology that groups and names organisms based on studies of their different characteristics.
Classification
Based on a system developed by Carolus
Linnaeus .
He established a system of groups called
Taxa (Taxons)
He ranked taxa from the largest , most general groups to the smallest , most specific groups.
Classifying Living Organisms
Organisms are grouped into taxon
King-
Philip-
Came-
Over -
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
For -
Good-
Family
Genus
SpaghettiSpecies
Classifying Living Organisms
At each level, organisms that share the most characteristics are grouped.
Species is the most s pecific. (members of the same species can produce offspring.)
Kingdom - is the most general.
NOTE: THE PLANT KINGDOM IS DIVIDED INTO DIVISIONS
INSTEAD OF PHYLA.
Linnaeus’s System
Carolus Linnaeus’ classification system: in 18th century
Divided organisms into 2 groups: plants
& animals
Placed plants & animals into groups based on similarities of form (shape, structure)
Linnaeus’s System
Has groups within larger groups within still larger groups
Uses unique (one-of-a-kind), descriptive
Latin names as scientific names for each organism
• Bats fly like birds, but have hair and produce milk
Therefore bats are mammals and not birds
Binomial Nomenclature
Crawdad, Crayfish, Mudbug
What is the difference?
Scientists need a universal name for every organism.
He proposed a system of naming using 2 names ; this system is called
Binomial nomenclature
The 2 names for each organism are:
Genus - always first and capitalized; can be abbreviated to 1 letter.
species - second and lowercase
**** Both are underlined or italicized***
HumansHomo sapiens
HomoGenus sapiens“Wise”
1.
2.
3.
Archae
Eubacteria
Eukarya
Domain
Six Kingdom Taxonomy System
How evolutionary relationships are determined:
Today the most generally accepted classification system contains six kingdoms :
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Protists
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Six Kingdoms
These kingdoms are then broken down into smaller categories.
Characteristics that scientists use to classify the relationships of organisms include:
structural similarities
breeding behavior geographical distribution chromosome comparison biochemistry
Dichotomous Key
Dichotomous Key: made of sets of numbered statements; each set deals with 1 trait of the organism; follow the numbered sets until the key reveals the name of the organism.
Classification Models
Phylogeny- The evolutionary history of a species.
Also shows evolutionary relationships of species
Cladistics
Cladistics: system of classification based on phylogeny (evolutionary history of a species)
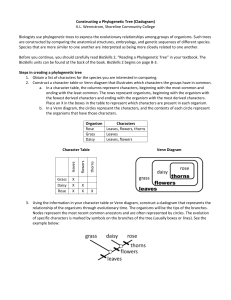
Cladogram
Cladogram: branching diagram that models the phylogeny of a species, resembles a pedigree or family tree showing proposed ancestry of the species.
Cladogram Example
1. What five probable ancestors of the modern bird (robin) are shown on the cladogram?
Answer to #1
• Archaeopteryx
• Velociraptor
• Sinornis
• Allosaurus
• Theropods
2. Which dinosaur is probably the most recent common ancestor of Velociraptor and Archaeopteryx ?
Answer to #2:
Sinornis
3. Which traits shown on the cladogram are shared by Archaeopteryx and modern birds?
Answer to #3
Light bones, 3-toed foot, Wishbone, down feathers, and feathers with shaft, veins, and barbs
Phylogenetic Diagram
Fan-like model can show time organism became extinct, or the relative number of species in a group (evolutionary history)
1. How does the fanlike diagram differ from a cladogram?
Answer to #1
Cladograms provide phylogenetic relationships among species.
Fanlike diagrams communicate the time organisms became extinct or the relative number of species in a group.
2. To which group are sea stars more closely related, arthropods or jellyfishes?
Answer to #2 arthropods
3. Which group of animals includes the fewest species?
Answer to #3
Sea Stars
(Echinoderms)
Question
As scientists began to learn more about geologic time, they incorporated their findings in their systems of classification.
The new system that accounted for an organism’s evolutionary history is called-
A. Binomial nomenclature
B. Phylogeny
C. Taxonomy
D. None of the above
B. phylogeny
Question
What does a fanlike diagram show that a cladogram does not?
A. Phylogenetic relationships
B. Relative number of species in each group
C. Anatomical features of each species
D. Mode of extinction
B. Relative number of species in each group