Classification and Taxonomy

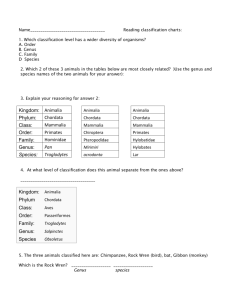
Warm-Up
In each of the following groups, which organism does not belong?
A.Horse, fish, dog, human
B.Canary, parrot, penguin, snail
C. Fish, shark, dolphin, eel
D.Snake, turtle, rabbit, iguana
Warm-Up
In the previous examples, was there always only one right way to group and classify the organisms?
Why or why not?
wikimedia.org
Taxonomy &
Classification
Wake County
Biology Curriculum
Essential Standard
3.5.1 Explain the historical development and changing nature of classification systems.
3.5.2 Analyze the classification of organisms according to their evolutionary relationships
(including dichotomous keys and
How do we classify organisms? How do we figure out what is related to what?
• The world is filled with millions of different organisms…
• To study how they relate to one another, we need to name them and organize them into groups
• Organisms used to be sorted by
physical similarities…
But, close relationships are not always evident using physical appearance.
You would think that the American
Vulture is closely related to the
African Vulture.
wikimedia.org
But it’s not! The
American vulture is more closely related to the stork.
Weird, right?
Evolutionary
:
Classification
Phylogeny
• Now that we know and understand DNA, we have been able to compare species and identify organisms that are closely related by using DNA, and not just by physical similarities.
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that shows how species are related to each other through common ancestors.
Dr. Jessica Theodor
The first phylogenetic trees were based on body shape and structure...
…but they have changed due to our understanding of DNA and evolutionary relationships.
Dr. Jessica Theodor
artsci.wustl.edu
BABOON
Most closely related
More closely related
More closely related
Least relationship
biology.unm.edu
Phylogenetic
‘Tree of Life’
Cladograms
• A cladogram is a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms and their derived characters
• (It looks like a phylogenetic tree, but it has physical characteristics attached to it).
Cladograms
• Derived characters are traits that show up later in the cladogram
• Cladistics: tracing the derived characters that are shared amongst organisms
Where would placentas the derived characteristic appear?
schoolworkhelper.net
Where would placentas the derived characteristic appear?
schoolworkhelper.net
Where would
“live
At which point on birth” or placentas appear?
schoolworkhelper.net
Where would
“live
At which point on birth” or placentas appear?
schoolworkhelper.net
Point at which whale ancestors become aquatic again.
www.classhelp.info
What’s another derived character that we could add to this cladogram?
www.answersingenesis.org
For example, in historic
Homo sapiens cladograms,
Neanderthals have been both ancestors and cousins
www.answers.com
New info can change the cladogram: more recent cladograms & phylogenetic studies show
Neanderthal as a cousin
wikimedia.org
Taxonomy &
Classification
Wake County
Biology Curriculum
How do you identify relationships?
wikipedia.org
wikipedia.org
Mountain Lion Lion wikipedia.org
Leopard
Which two are more closely related?
Which are the least related?
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Puma
Species - concolor
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Panthera
Species - leo
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Panthera
Species - pardus
How do you identify relationships?
wikipedia.org
wikipedia.org
Mountain Lion Lion wikipedia.org
Leopard
Which two are more closely related?
Which are the least related?
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Puma
Species - concolor
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Panthera
Species - leo
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Panthera
Species - pardus
How do we identify different or unknown related organisms?
• A tool known as a
dichotomous key is used to identify different species of related organisms.
Dichotomous
Key
Dichotomous
Key
• Each step gives you
new choices to help identify the organism
What tree is this?
www.statesymbolsusa.org
www.schools.utah.gov
www.statesymbolsusa.org
www.schools.utah.gov
www.statesymbolsusa.org
www.schools.utah.gov
www.statesymbolsusa.org
www.schools.utah.gov
Blue Spruce
www.statesymbolsusa.org
wikimedia.org
Taxonomy &
Classification
Wake County
Biology Curriculum
wikipedia.org
Warm –Up
wikipedia.org
Grizzly Bear Panda Bear wikipedia.org
Polar Bear
Which two are more closely related?
Which is the least related?
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Ursidae
Genus - Ursus
Species - arctos
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Ursidae
Genus - Ailuropoda
Species - melanoleuca
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Ursidae
Genus - Ursus
Species - maritimus
Essential Standard
3.5.1 Explain the historical development and changing nature of classification systems.
3.5.2 Analyze the classification of organisms according to their evolutionary relationships
(including dichotomous keys and
Taxonomy & Classification
• The world is filled with millions of different organisms…
• To study how they interact and how they are related, we need to name them and organize them into groups
• This grouping and naming process is called taxonomy or classification
How do we classify living things?
• The first recorded attempt at classification was by Aristotle, who attempted to classify all the kinds of animals in his History of Animals ( Historia
Animalium in Latin).
• He grouped the types of creatures according to their similarities: animals with blood/animals without blood, and animals that live in water and animals that live on land
Classification of Living things
• Think back to the grouping activities that we’ve done recently: is there more than one way to sort or classify a group of living things?
Early Attempts of Classification
Using Common Names
• A big problem was that some organisms had different names depending on the region:
• A puma, mountain lion, cougar, and a panther are all the same species, but they have different names depending on the region
• In the UK, “buzzard” means “hawk”. In the US,
“buzzard” means “vulture”
Classification of Living things
• Aristotle came up with another innovation: a binomial naming system
• "Binomial" means "two names," and according to this system each kind of organism can be defined by the two names of its "genus and difference.”
• His system wasn’t perfect, however…
Carolus Linnaeus
• (1707 – 1778)
• Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist
• Laid the foundations for the modern scheme of binomial nomenclature
• Known as the father of modern taxonomy www.entomologia.org
Carolus
Linnaeus
&
Binomial
Nomenclature
Two-word naming system
First word is Capitalized,
the second isn’t
Always written in italics
Genus, then species
Example: white oak is
Quercus alba employees.csbsju.edu
Carolus Linnaeus
• Taxon: a group or level of organization
• Linnaeus came up with a 7 taxon system that contained all organisms…
Kingdom, Phylum , Class , Order ,
Family
,
Genus
,
Species
Biggest/Broadest Smallest/Specific www.goldiesroom.org
How will I remember that?
Kingdom = Kings = __________
Phylum =
Class =
Order =
Family =
Play
Chess
On
Fridays
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
Genus = Generally = __________
Species = Speaking = __________
More KPCOFGS acronyms…
• King Phillip Came Over From Great Spain
• King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup/Good Spaghetti
• Kings Play Chess on Fine Gold Sets
• Kids Playing Chicken on Freeways Get Smashed
• Keep Pots Clean or Family Gets Sick
• Kids Prefer Cheese Over Fried Green Spinach
• You can also make up your own!
How will I remember that?
Kingdom = King = __________
Phylum = Phillip
Class = Came
Order = Over
Family = From
Genus = Great
Species = Spain
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
Kingdoms
There are six kingdoms:
A grizzly bear belongs to the
Kingdom
Animalia www.cartage.org.lb
Phylum
Each Kingdom is divided into groups called Phyla
Grizzly bears are in the phylum Chordata which means it has a backbone .
Class
Each Phylum is divided into groups called Classes
Grizzly bears are in the class Mammalia, which means mammal
www.missmaggie.org
Order
Each Class is divided into groups called Orders.
Grizzly bears belong to the Order Carnivora, which means carnivores
Family
Each Order is divided into groups called Families.
Grizzly bears are in the family Ursidae, which means “bear-like” animals
bioweb.uwlax.edu
Genus
Each Family is divided into groups called Genera
(plural for genus)
Grizzly bears belong to the Genus Ursus, which means “true bear”
Species
The Genus is divided into all the individual species
– this is the most specific taxon.
Grizzly bears belong to the species arctos
Therefore, the binomial nomenclature for the grizzly bear is Ursus arctos
Ursus arctos – Grizzly bear www.hickerphoto.com
History of the Kingdoms…
1700’s – two kingdoms: Plant and Animal
Late 1800’s – three kingdoms: Plant,
Animal, Protists
1950’s – Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plant, and Animal
1990’s – Eubacteria, Archaebacteria,
Protista, Fungi, Plant, and Animal
…6
KINGDOMS!
Kingdom #1: Archaebacteria
Unicellular prokaryotes
The simplest life form, the smallest genome
Can live in the most extreme environments
Some are thermophiles --- why scientists now believe that life first evolved at deep ocean volcanic vents.
Cell walls do not have peptidoglycan
Kingdom #2: Eubacteria
Unicellular prokaryotes
Live in ecologically diverse environments
Can be free-living in natural surroundings
Some can be deadly or cause disease
Some photosynthesize
Some need oxygen, others are killed by it
Thick, rigid cell walls that have peptidoglycan
Kingdom #3: Protista
Eukaryotes
Most diverse kingdom
Mostly unicellular but some are multicellular
Some photosynthesize but some are heterotrophic, some are plant-like and some are animal-like.
Ex. algae, amoebas, slime molds, protists, blue-green algae, paramecium
Kingdom #4 Fungi
Eukaryotes
Decomposers - most feed on dead or decaying organic matter
Secrete digestive enzymes into their food source and then absorb the nutrients
Cell walls with chitin
Can be parasitic (ex. athlete’s foot)
Multicellular (ex. mushrooms) and singlecelled (ex. yeasts)
Kingdom #5 Plantae:
Eukaryotes
Multicellular
Photosynthetic autotrophs
Chlorophyll
Cell walls contain cellulose
Ex. mosses, ferns, flowers, trees
Kingdom #6 Animalia
Eukaryotes
Multicellular
Heterotrophs
No cell walls
Many are motile
Ex. sponges, worms, insects, vertebrates
Domains –
Larger than
Kingdoms
!
1. Eukarya
– Kingdoms Animalia, Fungi,
Plantae, Protista
2. Bacteria
– Kingdom Eubacteria
3. Archea
– Kingdom Archaebacteria
How will I remember that NOW?
Domain = Dorky = __________
Kingdom = Kings
Phylum = Play
= __________
= __________
Class = Chess
Order = On
Family = Fridays
Genus = Generally
Species = Speaking
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
= __________
Today’s Three Domain System:
Eukarya – contains protists, fungi, plants, and animals
Bacteria – contains cyanobacteria
(which can photosynthesize) and heterotrophic bacteria
Archae – contains archaebacteria, the most primitive, including thermophiles
(heat loving) and halophiles (salt loving); live in extreme environments