Kitakyushu
advertisement

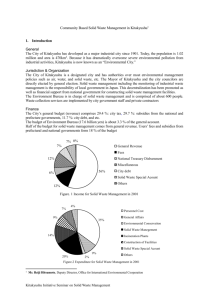
Kitakyushu’s Challenge to Promote the Development of Green Industry Kenji Kitahashi Mayor, City of Kitakyushu, Japan Today’s Points 1 Pillars of Kitakyushu’s environmental policies 2 Action taken on behalf of Kitakyushu’s environment (1)Overcoming severe environmental pollution (2)Development of eco-industries (3)International cooperation with cities overseas (4)New challenges for city’s “Green Growth” strategy Compatibility of environment and economy Development of an Industrial City Supporting the Modernization of Japan Major businesses in the Kitakyushu area Japan NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION Kitakyushu Four major Industrial areas TOTO Population: 975,000 (Oct 2011) Area: 487.89km2 (Oct 2010) GDP: 3.52 trillion yen (2008) YASKAWA Electric Mainstay of Kitakyushu’s Environmental Policies Paving the way for economic development through environmental action Living together, creating together Kitakyushu’s Basic Concept & Plan Objective of city development Encouraging the city’s people and culture to create an environmentally- and technology-rich city hand-in-hand with the world Create city brand Enhance the city’s sustainability Eco-Model City Approved July 2008 Based on the principle of a resource-based society Creation of low carbon society CO2 reduction target (2050) World Capital of Sustainable Development Technology Capital of Asia Citywide: 50% 150% decrease in Asia Overcoming Severe Pollution: Kitakyushu’s Experience 1960s Kitakyushu, the site of Japan’s most deplorable air pollution, saw nearby elementary schools close down due to the pollution “Dokai Bay, the Sea of Death” Water pollution in the bay disintegrated screws on ships and even E. coli could not be detected. Overcoming Severe Pollution: Kitakyushu’s Experience Today 1960s Key Factors: Partnerships among Multi-Stakeholders Residents Residents observing a private company Study session on air pollution measures with university professors Partnership Environmental supervision & environmental infrastructure Local Government Cleaner Production & pollution control equipment Private Enterprises 5 Compatibility of Environmental Improvement and Economic Growth Environmental pollution (Sulfur oxide) Environmental Pollution 2/day) (mg-SO 3/100cm (mg-SO3/100c ㎡/day) 2 1968 1968 1.5 Achieving economic development together with environmental improvement 1969 1970 1967 1 1963 1962 1966 1965 1961 1964 1972 1971 1973 1974 1960 1960 0.5 1976 1977 1978 1980 1980 1979 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Economic Development Economic Development (Value of shipments: 100 billion yen) (Value of Shipments: 100Billiom Yen) Source: World Bank, MEIP Report, 1993 30 Taking on the Challenge of a Resource Recycling Society Kitakyushu Eco-Town Project Japan’s Largest Eco-Town Approved 1997, Started operations 1998 No. business facilities: 29 No. research facilities: 16 Automobile recycling R&D on recycling technologies for solar power systems ・Investment ・Employees ・Visitors Collection/treatment of rare metals ~66 billion yen ~1,300 ~940,000 (1998-March 2011) Fluorescent lighting recycling Low-Carbon Technologies in Kitakyushu Mitsubishi Chemical Mitsubishi Materials Nippon Coke & Engineering 15 types of waste treatment and recycling, such as metal waste and sludge CDQ (Coke Dry Quenching Process) Processable organic photovoltaics Next-generation flexible and Supply power and steam to lightweight photovoltaic modules neighboring factories Power generation capacity: 27,900kW Eco-Techno Western Japan’s largest eco-technology expo that displays the latest ecotechnologies, products and information Yaskawa Electric Energy saving, inverters Kitakyushu Eco-Premium Creating a low-carbon economy through eco-products and services (Select eco-premium goods) in electric arc furnaces using Eco-friendly sanitary ceramic Next-generation lighting CCFL Long-lasting (similar to LED). Energy products (with tank) steel scrap Reduces amount of water flushed to savings of 20-40% compared with Thick boards manufactured 75% reduction in CO2 emissions 4.8 liters fluorescent lights. Outline started in 2004 Technologies and products (eco-products), as well as services (eco-services) within the city that reduce impacts on the environment are selected as “Eco-Premiums,” which then promote the environmental activities of local industries through their expansion and penetration into various markets. Focal points: Resource conservation, energy saving, long-lasting, simple maintenance, leasing, reusing, etc. Continuous “Collection of Knowledge” ~Kitakyushu Science and Research Park~ Graduate School, Waseda University Open in April 2001 Promoting local industries and academic institutions, such as universities that apply “knowledge” Graduate School, Fukuoka University Graduate School of Engineering Core science and research focal point in Asia Create new industries, advance technology Graduate School of Information, Production and Systems Information, Production and Systems Research Center University of Kitakyushu Kyushu Institute of Technology Graduate School of Life Science and System Engineering Center for Human Quality of Life Through IT Environment & Information Faculty of Environmental Engineering Graduate School of Environmental Engineering International Cooperation with Cities Overseas Contributing to the improvement of the global environment with the experience and know-how acquired in the process of environmental improvement Trainees: 6,207 persons, 138 countries Experts sent overseas: 160+ persons Kitakyushu International Technocooperative Association (KITA) Japan International Cooperation Agency Kyushu International Center (JICA Kyushu) Environmental Cooperation (China) Japan-China Recycling Society Cooperation Project (Eco-Town) Cooperation for actions to create resourcerecycling cities in China, using Kitakyushu’s Eco-Town Project as reference 2007-08 Qingdao 2008-09 Tianjin 2009-10 Dalian At the Prime Minister’s official residence (May 2008) Environmental Improvement Project in Dalian 1994 2000 ※Dalian received the Global 500 award in 2001 Leading Figures from China Visiting Kitakyushu Kitakyushu’s actions attract attention from international society Xi Jinping (Vice-President of PRC) made a formal visit to Kitakyushu on Dec 16, 2009 The People’s Daily (Dec 17, 2009) reported that Kitakyushu’s rich experiences in environmental protection and development of advanced technologies deserve to be used as a model for application to China today. International Environmental Cooperation (Indonesia) Environmental improvement in Surabaya, Indonesia’s 2nd largest city Spread of organic waste composting techniques from Kitakyushu to over 20,000 households in Surabaya 30% reduction of waste Koji Takakura of JPEC teaching about the composting technique City in 2001 Streets overrun by garbage Surabaya’s streets today Increased greenery in parks and along roads using compost International Environmental Cooperation (Indonesia) A joint statement was made in March 2011 on a strategic environmental partnership between Surabaya and Kitakyushu. (Left: The Honorable Tri Rismaharini, Mayor, City of Surabaya) International Environmental Cooperation (Cambodia) Since cooperation began in 1999, there has been rapid improvement in Phnom Penh’s water supply Kitakyushu staff providing on-site technological guidance October 2011 (1996⇒2006) Water supply diffusion rate: 25%=>90% Water supply time: 10h => 24h %of non-revenue water: 72% => 8% A friendship award was granted to staff involved in cooperation activities by the Government of Cambodia to commemorate the many years of cooperation. Water Business with Hai Phong, Viet Nam Development of new water-based business in Hai Phong April 2009 October 2011 MoU with Hai Phong for exchange and cooperation A comprehensive MoU on water projects was concluded between the two cities based on past exchange and cooperative agreements Achievements of agreement Carrying out cooperation, such as enhancing support for businesses, implementing governmental exchange activities, and developing human resources (L: Deputy Chair, Hai Phong Diet Affairs Committee) (L: Mr. Trinh Quang Huy, Chairman of the People’s Committee Hai Phong) Hai Phong authorized the introduction of the water block system adopted by Kitakyushu and is targeting improvement within five years New Challenges① Water Plaza (Water recycling demo plant) ①Sewage membrane treatment area ②UF/RO membrane system area (2F: Observation Bldg.) Water Plaza Product water from sewage: 1,000m3/day Product water from seawater: 400m3/day ③Test bed Started operations in April 2011 Water Plaza: The Water Plaza is a demo plant for recycling water, integrating the processes of sewage membrane treatment (sewage reuse system) and seawater desalination. (Capacity: 1,400m3/day) ・Development/testing of world class technology ・Showroom disseminating info ・Used for on-site training for overseas trainees Seawater intake Sewage discharge Sea 100m New Challenges② Kitakyushu Smart Community Development Project Creating a new lifestyle with locally produced and locally consumed energy Selected as one of four bases in Japan in April 2010 Hydrogen network Hydrogen by-products Fuel cells Smart buildings Power grid Next-generation SS IT grid 新エネルギー等 Smart housing Solar panels Installing a large quantity of smart meters Local power conservation center Wind power Natural gas co-generation New Challenges③ Development of Eco-Business in Asia Establishment of “Kitakyushu Asian Center for Low Carbon Society” (Asia Green Camp), the country’s first, in June 2010 with an objective to promote low-carbon societies and create environmental business in Asia. Environmental impact control business Energy business Promote in Asia! Hiroshi Komiyama, President (Former President, Tokyo University) Recycling business Water business Aims of Asian Center for Low Carbon Society Needs of newly emerging economies: Not only the simple export of technology, but going beyond to create green cities Collective strength as a top eco-city (Kitakyushu) Experience in overcoming pollution + Leading social system (Eco-Town, other) + Standout ecotechnologies Respond to the diverse needs of Asian cities and businesses “Eco-cities” and “Smart Communities,” other Order-made system City (area) export GHG reduction Bilateral credit Asian region’s Focal point for demonstrations and development of human resources Focal point for environmental business in the Asian region Projects Aiming Towards Bilateral Mechanisms Yaskawa Electric (World’s largest share in industrial robots, inverters) METI project promoting wider use of technologies to counter global warming (October 2010) This project tested the potential for energy savings and reducing GHG emissions, based on the data collected from past trials and research, in three factories in Beijing where existing equipment had been updated with highly efficient motor systems and inverters. TOTO (Global leader in home equipment and fixtures) MOEJ feasibility study on new mechanisms (July 2011) ○Creation of measuring technique to reduce CO2 emissions from water use ○Intercity/bilateral credit system ○Examine introduction of measures to expand use of water saving equipment ・Low-interest financing ・Introduction of certification system for water saving equipment, other MoU with UNIDO (L : Dr. Kandeh Yumkella, Director General of UNIDO ) Conclusion of MoU with the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) on mutual collaboration for the realization of a low-carbon society in June 2010 MoU with China Beijing Environment Exchange (August 2011) Asian Center for Low-Carbon Society Beijing Environment Exchange Creation of information platform as a channel for both Japan and China Promoting eco-business between companies in China and Japan Fostering Environmental Power in Residents Tree planting (NGO “Green Corridor with Birds Singing”) Certified as a regional centre of expertise for ESD by UNU Hibiki Biotope: Formally open in fall 2012 Environment Museum (Focal point for environmental education and learning) Kitakyushu: Eco-City of the Future Concept Creating a city in which the brilliant light of its people lead to a prosperous, peaceful and energy-filled city ~Harnessing the city’s experience overcoming pollution and its unceasing innovation~ Environment ●Formation/expansion of low-carbon areas implementing local energy management system ・Smart Community project ●City Forest Project ~Creating a city symbiotic with nature~ ・Planting 1 million trees (city greening) ・Multi-generational farming exchange activities on idle land Other Response to unprecedented aging society ●Maintaining/improving health through local connections ・Prevention of lifestyle-related diseases and serious illnesses ・Local “GO!GO! Health” project (local community health project) ・Int’l eco-business ・Reconstruction support, risk reduction ●Asian Center for Low Carbon Society ・Smart Community project, overseas development of Eco-Towns ●Exporting water infrasructure overseas Water Plaza ●Educational plan for children’s futures ・Providing school helpers ・Promoting school education linking with the business community, other ●Supporting reconstruction of disaster-affected areas ・Expanding output from smart community project to Kamaishi city (reconstruction support) Selected as OECD Green Growth Model City The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) selected Kitakyushu as a green growth model city in July 2011, having been evaluated for its activities and achievements in international environmental cooperation and the city’s Eco-Town project. L: Ms. Yoshie Nakatani (Director, OECD Tokyo) Other cities selected include Paris, Chicago, Stockholm Creation of a WIN-WIN Relationship Kitakyushu’s environmental technology making the world a better place