ppt
advertisement

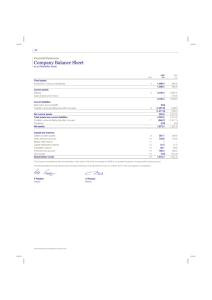
ACCOUNTING BASIC TERMS ASSETS These are economic resources of an enterprise that can be usefully expressed in monetary terms. Assets are things of value used by the business in its operations. Fixed Assets Current Assets ASSETS continue… Fixed Assets are assets which have been purchased by the enterprise for long-term use and not for resale in the ordinary course of business. e.g. Land, Building, Machinery, Plant, Furniture and Fixtures, goodwill, patent, copyright. ASSETS continue… Current Assets are assets held on a short-term basis and can be easily converted into cash. e.g. Debtors, Bills receivable, Stock(Inventory), Cash and Bank balances, etc. LIABILITIES These are obligations or debts that the enterprise must pay in money or services at some time in the future. • Long-term liabilities • Short-term liabilities LIABILITIES continue.. Long-term liabilities are those that are usually payable after a period of one year. e.g. A term loan from a financial institution, debentures (bonds) issued by a company. LIABILITIES continue.. Short-term liabilities are obligations that are payable within a period of one year. e.g. Creditors, bills payable, overdraft from a bank for a short period. CAPITAL Investment by the owner for use in the firm is known as capital. Owner’s equity is the ownership claim on total assets. It is equal to total assets minus total liabilities. REVENUES These are the amounts the business earns by selling its products or providing services to customers. Other titles and sources of revenue common to many businesses are: sales, fees, commission, interest, dividends, royalties, rent received, etc. EXPENSES These are costs incurred by a business in the process of earning revenue. Generally, expenses are measured by the cost of assets consumed or services used during an accounting period. The usual titles of expenses are: depreciation, rent, wages, salaries, interest, costs of heat, light and water, telephone, etc. PURCHASES Purchases are total amount of goods procured by a business on credit and for cash, for use or sale. In a trading concern, purchases are made of merchandise for resale with or without processing. In a manufacturing concern, raw materials are purchased, processed further into finished goods and then sold. Purchases may be cash purchase or credit purchase. SALES Sales are total revenues from goods or services sold or provided to customers. Sales may be cash sales or credit sales. STOCK Stock (Inventory) is a measure of something on hand – goods, spares and other items – in a business. It is called stock on hand. STOCK: continue… In a trading concern, the stock on hand is the amount of goods which have not been sold on the date on which the balance sheet is prepared. This is also called closing stock. STOCK continue… In a manufacturing concern, closing stock comprises raw materials, semi-finished goods and finished goods on hand on the closing date. Similarly, opening stock is the amount of stock at the beginning of the accounting year. DEBTORS Debtors are persons and/or other entities who owe to an enterprise an amount for receiving goods and services on credit. The total amount standing against such persons and/or entities on the closing date, is shown in the Balance Sheet as Sundry Debtors on the asset side. CREDITORS Creditors are persons and/or other entities who have to be paid by an enterprise an amount for providing the enterprise goods and services on credit. The total amount standing to the favour of such persons and/or entities on the closing date, is shown in the Balance Sheet as Sundry Creditors on the liability side.