Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology - Mrs. Jackson
advertisement

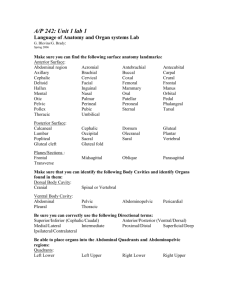
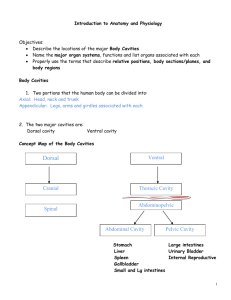
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 History of Anatomy & Physiology Important Individuals: • William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who was the first to describe correctly and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the body by the heart. • Henry Gray (1827–1861) was an English anatomist and surgeon most notable for publishing the book Gray's Anatomy the leading reference text on structures. (Still in print today!) Historical Examples of Medical Care • • • • • • • • I. History of Anatomy and Physiology 1775 - Period Practices: Mortified o Mortification occurs when the wounded area no longer receives enough blood or air in order for the tissue to sustain itself. The most common term for mortification is gangrene. o Gangrene (tissue death) is the rotting and decay of the flesh or body parts caused by infection or thrombosis or lack of blood flow. Typical sign of mortification is the stench of dead flesh, a blackening of the skin and painful swelling. o The most common form of gangrene involving gunshot wounds or amputation was gas gangrene. Today we know it is caused by the clostridium perfringens bacteria. It spreads quickly and is still often fatal. Removing leg; Used wine and brandy to disinfect; Difficulty stopping bleeding; Wiped wounded soldiers with water (American Revolutionary Times) 1861-1865 - Poultice (Civil War Medicine) II. Body Barriers- Defenses we have against disease and infection. A. Anatomic Barriers 1.intact skin 2.mucous lining of respiratory tract B. Physiological Barriers 1. gastric acid (HCL) of the stomach 2. immune factors in blood (serums, antibodies) and white blood cells C. Unknown Factors: which could be genetic and/or chemical in nature II. Body Cavities A. Axial portion - head B. Appendicular portion - arms and legs C. Dorsal cavity: fairly small and well protected 1. Cranial - brain 2. Spinal - spinal cord D. Ventral cavity - large and partially protected 1. Thoracic cavity - three parts, mediastinum separates into 3 areas 2. Abdominopelvic cavity - contains small pelvic cavity in bottom cavity cavities II. Body Membranes A. Abdomen - peritoneum 1. Parietal peritoneum - lines body wall 2. Visceral - lines surface of organs B. Thorax - 2 varieties of membranes 1. Pleura - always found in lung areas a) Parietal pleura - covers wall of thorax b) Visceral pleura - on surface of lungs 2. Pericardium - on heart a) Parietal pericardium - forms a sac around the heart b) Visceral pericardium - on surface of heart Chart of Membranes Abdomen Heart Thorax peritoneum pericardium pleura Visceral = on an organ Parietal = on an outside of an organ or surrounds an organ Regions and Cavities