up11_educue_ch20 - University of Manchester
advertisement

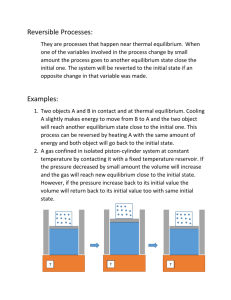
Q20.1 Which statement about these two thermodynamic processes is correct? 1. both processes are reversible 2. both processes are irreversible 3. process #1 is reversible and process #2 is irreversible 4. process #1 is irreversible and process #2 is reversible A20.1 Which statement about these two thermodynamic processes is correct? 1. both processes are reversible 2. both processes are irreversible 3. process #1 is reversible and process #2 is irreversible 4. process #1 is irreversible and process #2 is reversible Q20.2 During one cycle, an automobile engine takes in 12,000 J of heat and discards 9000 J of heat. What is the efficiency of this engine? 1. 400% 2. 133% 3. 75% 4. 33% 5. 25% A20.2 During one cycle, an automobile engine takes in 12,000 J of heat and discards 9000 J of heat. What is the efficiency of this engine? 1. 400% 2. 133% 3. 75% 4. 33% 5. 25% Q20.3 During one cycle, an automobile engine with an efficiency of 20% takes in 10,000 J of heat. How much work does the engine do per cycle? 1. 8000 J 2. 6400 J 3. 2000 J 4. 1600 J 5. 400 J A20.3 During one cycle, an automobile engine with an efficiency of 20% takes in 10,000 J of heat. How much work does the engine do per cycle? 1. 8000 J 2. 6400 J 3. 2000 J 4. 1600 J 5. 400 J Q20.4 A copper pot at room temperature is filled with roomtemperature water. Imagine a process whereby the water spontaneously freezes and the pot becomes hot. Why is such a process impossible? 1. it violates the first law of thermodynamics 2. it violates the second law of thermodynamics 3. it violates both the first and second laws of thermodynamics 4. none of the above A20.4 A copper pot at room temperature is filled with roomtemperature water. Imagine a process whereby the water spontaneously freezes and the pot becomes hot. Why is such a process impossible? 1. it violates the first law of thermodynamics 2. it violates the second law of thermodynamics 3. it violates both the first and second laws of thermodynamics 4. none of the above Q20.5 A Carnot engine takes heat in from a reservoir at 400 K and discards heat to a reservoir at 300 K. If the engine does 12,000 J of work per cycle, how much heat does it take in per cycle? 1. 48,000 J 2. 24,000 J 3. 16,000 J 4. 9000 J 5. none of the above A20.5 A Carnot engine takes heat in from a reservoir at 400 K and discards heat to a reservoir at 300 K. If the engine does 12,000 J of work per cycle, how much heat does it take in per cycle? 1. 48,000 J 2. 24,000 J 3. 16,000 J 4. 9000 J 5. none of the above Q20.6 If you put an ice cube at 0°C inside a large metal box at 70°C, the entropy of the ice increases. In addition, 1. the entropy of the metal box is unchanged and the total entropy increases 2. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy decreases 3. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy remains the same 4. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy increases 5. none of the above A20.6 If you put an ice cube at 0°C inside a large metal box at 70°C, the entropy of the ice increases. In addition, 1. the entropy of the metal box is unchanged and the total entropy increases 2. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy decreases 3. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy remains the same 4. the entropy of the metal box decreases and the total entropy increases 5. none of the above