LECTURE #9: MICROECONOMICS CHAPTER 10
advertisement

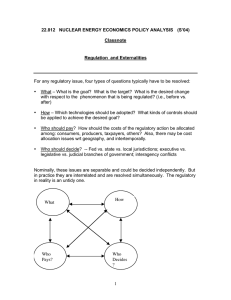
LECTURE #9: MICROECONOMICS CHAPTER 10 Market Externalities Solutions to Problems Caused by Externalities Market Externalities Uncompensated impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander Positive Externalities = consumers or producers benefit Education Research activity Negative Externalities = consumers or producers do not benefit Pollution Loss of Patent Protection Increases in Cost – Less Quantity at every price level Market Externalities Market Failure Decision maker - fails to account for externalities Government intervention: protect the interests of bystanders Impact on Welfare Economics Increase in cost of goods, decrease in revenue to producers Taxes imposed to repair effects of externalities Reduced consumer and producer surpluses Are reductions in surplus offset by economic value of increased welfare Pollution and the Social Optimum Price of Aluminum External Cost Social cost (private cost and external cost) Supply (private cost) Optimum Equilibrium Demand (private value) 0 QOPTIMUM QMARKET Quantity of Aluminum In the presence of a negative externality, such as pollution, the social cost of the good exceeds the private cost. The optimal quantity, QOPTIMUM, is therefore smaller than the equilibrium quantity, QMARKET. 4 Education and the Social Optimum Price of Aluminum Optimum Supply (private cost) External Benefit Equilibrium Social value (private value and external benefit) Demand (private value) 0 QMARKET QOPTIMUM Quantity of Aluminum In the presence of a positive externality, the social value of the good exceeds the private value. The optimal quantity, QOPTIMUM, is therefore larger than the equilibrium quantity, QMARKET. 5 Solutions To Problems Caused By Externalities Private Market Solutions Moral codes Social sanctions Coase Theorem private parties bargain on costs Private solution to externality [problem] Provide incentives Corrective taxes and subsidies Violation carries a price Conformance obtains a [tax] benefit Solutions To Problems Caused By Externalities Public (Government) Solutions Regulation Making certain behaviors either required or forbidden Cannot eradicate pollution Taxation and Subsidies Tradable [Pollution] Permits Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Develop and enforce regulations protecting the environment Dictates maximum level of pollution Requires that firms adopt a particular technology to reduce emissions Homework Questions for Review: 3, 4, 6 (4, 5, 6 4th Ed) Problems and Applications: 1, 6, 12