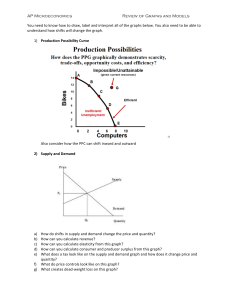
ECON 2100 Ch 10 Prac..
advertisement
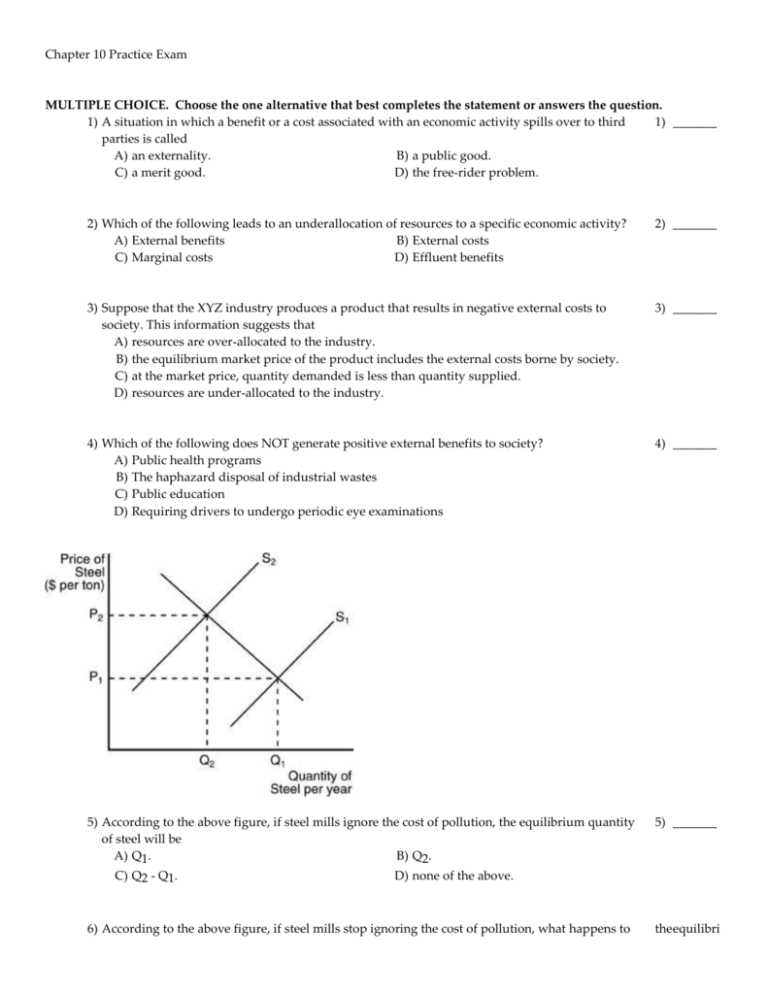
Chapter 10 Practice Exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A situation in which a benefit or a cost associated with an economic activity spills over to third 1) _______ parties is called A) an externality. B) a public good. C) a merit good. D) the free-rider problem. 2) Which of the following leads to an underallocation of resources to a specific economic activity? A) External benefits B) External costs C) Marginal costs D) Effluent benefits 2) _______ 3) Suppose that the XYZ industry produces a product that results in negative external costs to society. This information suggests that A) resources are over-allocated to the industry. B) the equilibrium market price of the product includes the external costs borne by society. C) at the market price, quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied. D) resources are under-allocated to the industry. 3) _______ 4) Which of the following does NOT generate positive external benefits to society? A) Public health programs B) The haphazard disposal of industrial wastes C) Public education D) Requiring drivers to undergo periodic eye examinations 4) _______ 5) According to the above figure, if steel mills ignore the cost of pollution, the equilibrium quantity of steel will be A) Q1. B) Q2. 5) _______ C) Q2 - Q1. D) none of the above. 6) According to the above figure, if steel mills stop ignoring the cost of pollution, what happens to the equilibri um price 6) and equilibri um quantity? __ __ __ _ A) The equilibrium price increases from P1 and P2, but the equilibrium quantity is unchanged. B) They change from P1 and Q1 to P2 and Q2. C) They change from P2 and Q2 to P1 and Q1. D) They are unchanged. 7) The Do-Good Company produces goods that provide benefits to society-at-large. If consumers of Do-Good's products fail to take external benefits into account, A) the demand curve will be too far to the left. B) the supply curve will be too far to the right. C) the demand curve will be too far to the right. D) the supply curve will be too far to the left. 7) _______ 8) To correct for the underproduction of products with positive externalities, the government must A) fine the industry. B) increase taxes on the industry. C) provide tougher regulations on the industry. D) provide the incentives for the private sector to produce the good. 8) _______ 9) Assume the production of a good gives rise to external benefits. The government may increase efficiency by A) imposing taxes on the good. B) subsidizing production of the good. C) regulating production of the good. D) requiring all producers of the good to be licensed. 9) _______ 10) A government subsidy is typically used A) to reduce inflation. B) to correct a market that generates a negative externality. C) to provide a demerit good. D) to encourage production of a good that generates a positive externality. 10) ______ 11) Society is likely to over-allocate resources to produce goods that A) generate positive externalities. B) are merit goods. C) generate negative externalities. D) are public goods. 11) ______ 12) Which of the following often involves positive external benefits? A) Inoculation programs for contagious diseases B) Water pollution C) Drunken driving D) Tobacco smoking 12) ______ 1) A 2) A 3) A 4) B 5) A 6) B 7) A 8) D 9) B 10) D 11) C 12) A