Website Research: School Violence
advertisement

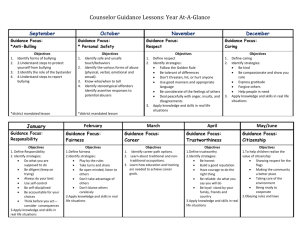
Christina Savage Coun 511, Spring 2010 csavage@holyfamily.edu http://hfweb428.angelfire.com/ Click Here Summary of Findings My research has shown that school violence is very prevalent within the school systems. Each year thousands of children are affected leaving many to feel helpless and alone. The good news is that there seems to be an overwhelming amount of research and anti-violence programs that are very active in the fight against school violence. My research has also revealed that there are also numerous counseling curriculums and training programs which counselors can implement in their schools to help combat these violent behaviors. Lastly, from a more general approach these findings show that there is an abundance of information and help for parents and community leaders to get informed on this topic and help them handle this behavior SCHOOL COUNSELING SITES - OVERALL RATINGS 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 OVERALL RATING Reccomended School Counseling Site Ratings 10 Teens Health Schoolcounselor.com 9 Safe Schools Coalition National Centre Against Bullying Nt'l Mental Health Info Center Bullying Awareness Week 8 Workshop Express ASCA Bullying.org 7 Bullies to Buddies Stophazing.org Dr. Spock 6 National Youth Violence Prevention Int'l Bullying Prevention Assoc Hank Nuwer Stanford Prison Experiment 5 Bullying Statistics & Web Resources About.com: GBLT Teens NoBully 4 3 Site’s Design / Feel / Appearance Ease of Using the Site Usefulness of the Material Detailed Findings These findings delve into a variety of topics and resources surrounding school violence. Some the websites below will cover just general information on the topic of school violence while other sites will highlight more specific areas of interest such as bullying, hazing and school prevention. These sites also appeal to a wide variety of individuals. Some of the sites are geared towards school counselors, teachers and school administrators yet others are more general and can be useful to a broader population. There are also a few sites which help explain why today’s youth is actively engaging in this type of negative behavior. Bullying.org www.bullying.org The purpose of this website is to reduce the occurrence of bullying in society through education and awareness. The site offers a wealth of information and resources with the goal of being proactive in the fight against bullying. Among its many resources the site offers online courses and online video presentations that deal with all the various forms of bullying. It also provides links to other helpful resources such as www.cyberbullying.org. National Youth Violence Prevention Resource Center http://www.safeyouth.org/scripts/topics/bullying.asp This website provides a wide range of useful statistics and resources regarding violence and youth. It also provide school prevention programs as well as health care practitioners and community organizations that are active in bullying prevention. The cite would be usefule to recommend to everyoen from teachers and counselors to parents and students. There are the bullying prevention curriculums that would be beneficial for a school counselor but then there are also several articles and resources that discuss bullyin in general which would be useful for a concerned parent. The cite is also a wonderful resource to have in general because it does not just deal with bullying. It also covers alcohol abuse, dating violence, depression and other related topics in great depth. External Resources · Addressing the Problem of Juvenile Bullying (PDF 43 KB) This fact sheet defines bullying, noting that it can take three forms: physical, verbal, and psychological. It also describes a recently published report by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and summarizes the report's findings on the long- and short-term effects of bullying. Federal Partner: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, U.S. Department of Justice · The ABCs of Bullying: Addressing, Blocking, and Curbing School Aggression This online course from the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention examines the causes and effects of bullying, prevention techniques and programs, screening, treatment options, and legal/ethical issues surrounding bullying. Bullying Stastics and Web Resouces http://www.highlands.k12.fl.us/~msdp/BullyingStatsResources.htm This website is very straightforward and plain visually but would be very beneficial for someone looking for quick statistics and facts on the topic of violence in schools. The website direct yet informative approach provides helpful information a school counselor could reference when stressing the serious implications of school violence. For example, the following information can be found on this website: In a 1993 survey of 720 school districts nationwide, 82% reported an increase in violence in their school over the past five years. (Harvard School of Public Health) In a 1993 survey of students grades 6-12, 79% said that violence was caused by "stupid things like bumping into someone." Other causes of violence included: boyfriend-girlfriend disputes, outsiders, racism, and gangs. (National School Safety Center) Bullying Awareness Week www.bullyingawarenessweek.org Started by Canadian educator, Bill Belsey, over a decade ago, Bulllying Awareness Week has become a widespread movement throughout many countries to bring awareness to the dangers of bullying and to encourage people to get invovled in preventing bullying in the communities. Below is a more detailed explaination that the website provides explaining this week of bully prevention: The vision behind Bullying Awareness Week: Bullying Awareness Week is about working at preventing bullying through education and awareness Bullying is a community issue. Schools are a critically important part of the solution, but bullying should not be defined solely as a "school problem". Addressing bullying is best done with a wholistic, community approach because bullying is a community health and wellness issue. Bullies to Buddies http://www.bullies2buddies.com/ Out of all my research this website proved to be one of the more unique and especially useful resources for school counselor. This website takes a psychological approach to explaining and preventing bullying and is geared towards those in the mental health profession. The website provides free manuals and well as several indepth articles that deal with various aspects of bullying, such as: Has your school’s anti-bully policy turned you from an educator into a warden? Why do students keep on bullying each other no matter how hard you try to make them stop? Examples of a Curriculum: Lesson 1 - KNOW WHY YOU ARE TEASED Lesson 2 - CHANGE YOUR ATTITUDE Lesson 3 - THREE WARNINGS Lesson 4 - HOW TO HANDLE RUMORS Lesson 5 - HOW TO HANDLE PHYSICAL BULLYING Lesson 6 - GETTING REVENGE Lesson 7 - HOW TO STOP PEOPLE FROM HATING YOU Lesson 8 - HAVE A SENSE OF HUMOR Lesson 9 - LOSE YOUR FEAR Lesson 10 - DEALING WITH BROTHERS AND SISTERS Bonus Lesson - HAVE MORE FRIENDS No Bully http://www.nobully.com/counselors.htm This website covers all the general aspects of bullying including the definition of bullying and the emotional and physical costs of bullying. This cite is unique in that it provides resources directed towards specific groups such as administors, parents and counselors: Resources • Administrators • Teachers • Parents • Counselors • Survivors National Centre Against Bullying (Australia) http://www.ncab.org.au/ This website, like many of the others, provides several facts and explainations surrounding bullying. However, the unique aspect surrouding this site is that it was commissioned by the Australian government and therefore brings a cultrally diverse view point to the discussion of bullying. This site is also resourceful because it describes 5 clear and concise types of bullying which could be useful for many different reasons. Bullying can take a number of different forms. 1. Physical bullying This is when a person (or group of people) uses physical actions to bully, such as hitting, poking, tripping or pushing. Repeatedly and intentionally damaging someone's belongings is also physical bullying. 2. Verbal bullying Using negative words, repeatedly and intentionally to upset someone, is also a form of bullying. Examples of verbal bullying includes name calling, insults, homophobic or racists remarks, and verbal abuse. 3. Social bullying Lying, spreading rumours, playing a nasty joke are all examples of social bullying. Repeatedly mimicking someone and deliberately excluding someone is also social bullying behaviour. 4. Psychological bullying Psychological bullying is when someone (or a group of people) repeatedly and intentionally use words or actions which cause you psychological harm. Intimidating someone, manipulating people and stalking a person are all examples of psychological bullying. 5. Cyberbullying Cyberbullying is when someone (or a group of people) uses technology to verbally, socially or psychologically bully. Cyberbullying can happen in chat rooms, through social networking sites, emails or mobile phones. International Bullying Prevention Association http://www.stopbullyingworld.org/Research_W365.cf m Among the numerous services that the IBPA provides, the International Bullying Prevention Association presents annual conferences throughout the United States that provides information and professional development opportunities for those involved in bullying prevention. Like several of the other sites, this website also provides excellent resources and research in regards to bullying but the confrences and training opportunities that the association provides truely make this an invaluable site to have for individuals working in a school or community setting. IBPA ANNUAL CONFERENCES 2009: PITTSBURGH 2008: INDIANAPOLIS 2007: HOLLYWOOD/FT. LAUDERDALE 2006: ATLANTA 2005: ATLANTA MEMBERS CAN DOWNLOAD MATERIALS FROM THE 2007 AND 2009 CONFERENCES IN OUR MEMBERS AREA. WE ARE HOPING TO MAKE AN ANNOUNCEMENT SOON REGARDING OUR CONFERENCE PLANS FOR 2010. PLEASE CALL US AT 800-293-9071 OR EMAIL US HERE IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS Teens Health http://teenshealth.org/teen/ This website is just an overall great resource for counselors to refer their students too. Teens Health gives advice and information on several serious topics facing adolescents such as sexual health, food & fitness, dugs & alcohol and infections. It provides teenagers with advise on how to take care of their body with tips covering everything from skin care to safe sex. The sight also has links for parents who may have questions regarding something their child is going through like bullying. Your Body/Your Mind Sexual Health Food & Fitness Recipes Drugs & Alcohol Diseases & Conditions Infections Staying Safe En Español The Stanford Prison Experiment http://www.prisonexp.org/ In 1971 a famous psychological experiment took place at Standord University. Lead by Dr. Phillip Zimbardo, the Standford Prison Experiment involved college aged students simulating a prison environment but having half the participants playing prisoners and the other half portraying the prison guards. The results of the experiment were shocking but very revealing about human nature. Zimbardo and his associates found that individuals are capable of very evil and sadistic behaviors when placed in a power of position. I found that this website was helpful in explaining why students may be lead to commit violent acts against their fellow students: The guards were given no specific training on how to be guards. Instead they were free, within limits, to do whatever they thought was necessary to maintain law and order in the prison and to command the respect of the prisoners. The guards made up their own set of rules, which they then carried into effect under the supervision of Warden David Jaffe, an undergraduate from Stanford University. They were warned, however, of the potential seriousness of their mission and of the possible dangers in the situation they were about to enter, as, of course, are real guards who voluntarily take such a dangerous job. As with real prisoners, our prisoners expected some harassment, to have their privacy and some of their other civil rights violated while they were in prison, and to get a minimally adequate diet -- all part of their informed consent agreement when they volunteered. About.com:GLBT -Interview with Rebecca Haskell on GLBT Bullying http://gayteens.about.com/od/sexuality/a/bully-study.htm This interview discusses the lack of attention that the GLBT community receives in regards to bullying in harassment. Haskell explains that 59% of schools still don't include gay, lesbian or bisexual students in their harassment or non-discrimination policies. The article goes on to explain the unique issues and problems facing this community in regards to school violence and bullying. Haskell has researched this topic thoroughly and was able to provide some unique insight that many counselors would find helpful: "As a high school student I often heard the words ‘gay’, ‘queer’, and ‘homo’ used as insults towards others or objects. These comments made it very difficult for me to openly explore and come to terms with my sexuality, and I knew there were others who must have been affected in the same way. I became disappointed in classmates when I was the lone voice of dissent in classes where others framed homosexuality as a sin or deviant lifestyle.” American School Counselor Association http://www.schoolcounselor.org/content.asp?contentid=240 As a general overall resource, this website is essential to have access to as a school counselor. It keeps counselors informed on everything from the role of the counselor to state certification requirements. When working in schools as a counselor its just a great tool to have to ensure that you are up-to-date on the association’s guidelines, protocol and ethics. PENNSYLVANIA STATE REQUIREMENTS Educational Requirements: Completion of an approved program in school counseling; Required Coursework: Supervised counseling practicum experiences, prior to and separate from the field experience, providing direct service with individuals and groups (60 clock hours) Experience Requirements: A minimum of an additional 300 clock hours of internship/supervised field experiences to include instructional experience and a minimum of 70 hours (elementary) OR 75 hours (secondary) of direct service with individual and group clients. Examination: Must score 173 on Praxis Mathematics, 172 on Praxis Reading, and 173 on Praxis Writing. Also must score a minimum of 590 on the Praxis II School Guidance and Counseling. Institution Recommendation Required?: Yes, required for certification Certification: (1) Elementary - grades K-6; OR (2) Secondary - grades 7-12 Reciprocity: No, but Pennsylvania has signed an Interstate Agreement with 45 other states/jurisdictions based upon the mutually agreed-upon conditions of that contract. It should be noted, however, that in all cases, candidates for Pennsylvania certification must complete the Praxis tests required by Pennsylvania. Background Check: Yes, for employment. AND have integrity and ethical behavior, professional conduct as stated in Pennsylvania’s Code of Professional Practice and Conduct for Educators School Counselor.com http://www.schoolcounselor.com/macomb/all-sites.asp This website is obviously is geared towards school counselors, making it a great resource for all those in this profession. It provides information on training, lesson plans and various other resources. The only problem with this site is that it does not provide the actual curriculums themselves, just the titles and a brief description of these lesson plans. Below is an example: Addressing CyberBullying in Schools CATEGORY1: ADAPTABLE RESOURCES CATEGORY2: ALL LEVEL: ADAPTABLE DESC: An Article for The TechEdge: The Journal of the Texas Computer Education Association. The digital environment increasingly provides a window into face to face (F2F) as well as virtual interactions between people. Bullying, which sadly seems to be a timeless activity, has moved into virtual environments as more students have gained access to and knowledge about the Internet. While some educational leaders may prefer to metaphorically “paint over” these windows in schools to hide these negative interactions from public view, schools need to take a more proactive stance than merely banning social networking websites to adequately address issues like cyberbullying. On November 1, 2006, a panel of educators addressed issues of bullying and cyberbullying at the Oklahoma “Safe and Healthy Schools” conference sponsored by the Oklahoma State Department of Education. The following are ten specific suggestions for educators and school district leaders to effectively address bullying and cyberbullying which emerged as a result of this panel discussion. Safe Schools Coalition http://www.safeschoolscoalition.org/safe.html The Safe Schools Coalition is an organziation that works with schools with the goal of creating a safer environment for GLBT youth in their schools and their community. The SSC has a very strong prescence in Washington intervening on the behalf of GLBT youth and campaigning for laws that protect the safety of these adolescents. For example: 1. Intervening and advocating on behalf of individual students, educators and families experiencing sexual orientation/identity-based harassment and violence. 2. Holding legislators, school boards and school administrators accountable for making schools safe and free of bias-based bullying and violence, through community organizing and principled activism. This website provides a wealth of information surrounding the safety of GLBT youth and it also provides volunteer opportunities. It also lists when SSC meetings will be held which cover everything from new legistlation, volunteer opportunites and ideas to improve your schools safety. SAMHSA's Mental Health Information Center This website is excellent for those counseling in schools and communities because it provides numerous violence prevention programs and bullying counseling groups: Programs/Curriculums A Model Bullying Prevention Program (Olweus Program) What Can Schools Do? 15+ Brochure: Take Action Against Bullying How to Intervene to Stop Bullying: Tips for On-the-Spot Intervention at School Documenting Bullying at Your School: Tips for School Administrators Steps to Address Bullying at Your School: Tips for School Administrators School Health Guidelines to Prevent Unintentional Injuries and Violence Providing Support to Children Who Are Bullied: Tips for School Personnel (and Other Adults) Workshop Express http://www.workshopsexpress.com/child-abuse- workshop-new-york-state.php This website provides applications for online training programs and workshops geared towards child abuse and school violence. The programs offered also fulfill state requirements that many working professionals, such as physicians, social workers and schools counselors, need to complete in order to work in the state of New York. Even if you do not need to complete these tests for state requirements, they are very informational and helpful. Another benefit is that they can be taken at your own pace since you go through the workshops on your computer. Its important to note however, that there is a few to purchase these workshops which varies from around $35 to $75. Florida Department of Education http://www.fldoe.org/workforce/programs/cd_lesson.asp Of all the resources, I found this website to be the most beneficial and resourceful for school counselors. Not only is the site designed in a clear and easy to use format but it provides invaluable counseling curriculums for grades K-12. Also, all curriculums are provided in either a PDF or word format. Although, there is no specific curriculum for bullying there are several lessons plans that could be incorporated into an anti-bullying counseling curriculum. Such as: 5. Self-Management and Responsible Behavior 5.2 Demonstrate appropriate attitudes and behaviors. "What's Up With Your Attitude?“ 7. Interpersonal and Communication Skills 7.4 Demonstrate effective skills for interacting with peers and adults. "Cooperation" 7.5 Identify sources and effects of peer pressure. "Peer Pressure" Dr Spock © http://www.drspock.com/article/0,1510,9600,00.html This is another website that gives tips and helpful information for teachers and counselors to help combat bullying in their schools. The site addressed questions such as “Knowing your school’s policy on bullying,” and “Ways to halt intimidation”. It also offers advise such as: Increase supervision. Bullying takes place in areas that are shielded from direct adult view, such as bathrooms, unsupervised hallways, and hidden corners of the playground. One way to discourage bullying is to eliminate these areas--for example, by fencing off areas of the playground that can't be seen easily or by placing adult monitors in the bathrooms and halls. Teach children to take a stand, not stand by. Bullies play to their audience of frightened, possibly impressed classmates; they count on other children to remain silent. Through classroom discussions, children can come to see that it's not OK to simply be a bystander when another child is being bullied. Instead, children learn that when they stick up for each other, they all are safer. Hank Nuwer’s Author Page http://www.hanknuwer.com/hs2 Hank Nuwer is a published author known for his works and research on the topic of hazing. One of the key points that Nuwer stresses is that hazing is not something that is isolated to college campuses. According to his research, hazing is occurring throughout high schools and is spreading rapidly among the adolescent population. This website offers numerous sites on current events surrounding hazing. There is also a special section of the site designated towards current events and research involving hazing in high school. For example: High School Hazing Page: Chronology of Selected High School Incidents. California hit with hazing cases: August 28, 2009 (Fontana Miller High School incident latest) Wilson High School case against two coaches was dismissed on July 6. Texas bill proposes to end hazing amnesty for those reporting hazing A second high school student in New Mexico accepts guilty plea in violent physical hazing case South Africa schools for boys report rampant, vicious hazing Taft coach and employees cleared after investigation and back at work. Robertson High School football player convicted and sentenced in hazing cases. Robertson High School expels three football players and Wilson High sees serious charges lightened by prosecutor Stop Hazing http://www.stophazing.org There is a large misconception that hazing only occurs at universities within sport teams and greek life. Most fail to realize that hazing is actually very prevalent within the secondary education school systems. This website strives to inform the public about the realities of hazing occuring among today's adolescents. Spearheaded by the research of Hank Nuwer, the website explains how hazing can involve everything from silly and embarrassing pranks to dangerous and harmful dares. The site also provides definitions of hazing as well as laws regarding hazing. Considering the fact that many people are unaware of the full dangers involved with hazing this type of information would be very helpful. Hazing Defined Hazing refers to any activity expected of someone joining a group (or to maintain full status in a group) that humiliates, degrades or risks emotional and/or physical harm, regardless of the person's willingness to participate. In years past, hazing practices were typically considered harmless pranks or comical antics associated with young men in college fraternities. Today we know that hazing extends far beyond college fraternities and is experienced by boys/men and girls/women in school groups, university organizations, athletic teams, the military, and other social and professional organizations. Hazing activities are generally considered to be: physically abusive, hazardous, and/or sexually violating. The specific behaviors or activities within these categories vary widely among participants, groups and settings. While alcohol use is common in many types of hazing, other examples of typical hazing practices include: personal servitude; sleep deprivation and restrictions on personal hygiene; yelling, swearing and insulting new members/rookies; being forced to wear embarrassing or humiliating attire in public; consumption of vile substances or smearing of such on one's skin; brandings; physical beatings; binge drinking and drinking games; sexual simulation and sexual assault. Conclusion School violence is a serious issue but it is one that thankfully is not being ignored. From my website research, it is clear that everyone from psychologists, journalists and members of office are coming together to help fight these acts of violence. This research shows that they are an overwhelming amount of general sites open to parents, students and school administrators to help find answers as to why bullying occurs and how to counteract this behavior. There is also a surprising amount of site that offer either school counseling curriculums or training programs for school administrators that deal with bullying and school violence. Lastly, through this research by utilizing websites such as the Stanford Prison studies experiments, I was able to get a clear explanation for why seemingly normal people would engage in such hateful behavior. References Internet Address Book IAB Research Excerpts IAB Research Report