Cells
advertisement

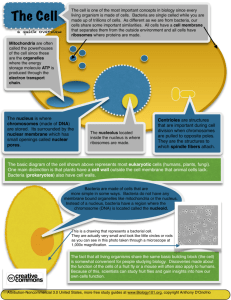
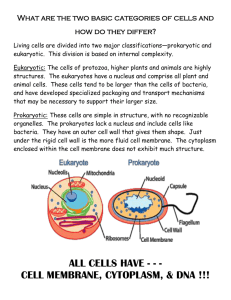
Chapter 3: Cells and cell structure Cells • A cell is the smallest unit of life. • Each cell is alive and has all of the characteristics of life. • Cytology is the study of cells. • Scientists began learning about cells after the development of the microscope Robert Hooke - 1665 Hooke was the 1st person to see cells. Hooke coined the word “cell” after viewing cork cells with a microscope Late 1600s Leeuwenhoek’s microscope Anton von Leeuwenhoek Was the 1st to observe living cells. He saw unicellular living organisms (“wee beasties”) and other living cells. What did Leeuwenhoek see? Algae Vorticella, a protist Bacteria Schleiden & Schwann • Mattias Schleiden observed that all plants were made up of cells. • Theodor Schwann observed that all animals were made up of cells. The Cell Theory • All living things are made of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic building blocks of organisms. • All cells come from from existing cells by the process of cell reproduction. Virchow History of Cells 5 min All cells come from preexisting cells Microscopes have: Magnification Resolution making an a measure of image appear the clarity of larger an image Microscopes 1. Compound Light Microscope 2. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) 3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Compound Light Microscope Up to about 1000x Elodea leaf at 40x Elodea leaf at 400x Answer this! A student wants to view cells under the compound microscope at a total magnification of 400X. If the eyepiece is 10X, which objective lens should be used? Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Highly magnified, 2-dimensional images Plant cell Transmission electron micrograph Liver cell more Transmission Electron Micrographs A mitochondrion A nucleus in a cell Even more TEMs Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) 3-dimensional images Tsetse fly head Scanning Electron Micrographs Human hair in a knot Human hair with dandruff More SEMs Human hair with split ends Human hair emerging from skin More SEMs Dog tongue More SEMs A daphnia (water flea) More SEMs Scotch tape More SEMs Paper towel Why are cells so small? All substances must pass through the cell membrane. Thus, the surface area of the cell membrane must be sufficient for the volume of a cell. All Cells Have: 1) Cell membrane - the outer boundary. It separates the inside from the outside & controls what enters & leaves the cell. 2) Cytoplasm – everything inside the cell except for the nucleus. 3) Ribosomes - the place on which proteins are made 4) Genetic material (DNA) - instructions for the cell. In eukaryotes, it is kept in the nucleus. It is often called the “brain” of the cell. Types of Cells Pro & Euk 1 min Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes • Prokaryotes are single cells that lack a true nucleus. Prokaryotes are bacteria. • Eukaryotes are cells that have a true nucleus and membrane-bound internal organelles. • An organelle is a structure surrounded by a membrane, found only in eukaryotic cells. Relative Sizes of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Prokaryotes are Bacteria • Bacteria are found in all environments on earth. • Bacteria are hypothesized to have been the first life on earth. The first bacteria “ate” organic molecules. Later, bacteria evolved that could do photosynthesis, getting energy from the sun. Oxygen was released into the atmosphere and other cells could develop, and eventually multicellular organisms appeared. Prokaryote Video 2 min Archaebacteria Many are Extremophiles, living in extreme environments such as hot springs and acid pools. Eubacteria, common bacteria E. coli are found in your intestines Bacterial Cell Structure of a Prokaryote: • Cell wall – provides structure & protection. • Pili – helps bacteria stick to surfaces • Flagella – allows bacteria to move Yet another bacterial cell Bacillus: Rod-shaped bacteria Coccus: Round-shaped Bacteria Spirilla: Spiral-shaped Bacteria Many bacteria are beneficial • Food • Some antibiotics • Decomposers (saprobes) • Nitrogen fixation – converts nitrogen gas in the air to a form that plants can use. • Photosynthesis (cyanobacteria) • Environmental cleanup Cyanobacteria: Photosynthetic bacteria Bacteria that caused bubonic plague Y. pestis Some bacteria are pathogens Pathogen: a diseasecausing agent Pathogenic Bacteria Bacteria that are pathogenic secrete a toxin (poison) Antibiotic – a chemical that kills bacteria Bacteria that cause anthrax Bacteria that cause botulism Some other bacterial diseases Cholera Dental cavities Lyme disease Tuberculosis Typhus Strep throat Botulism (a type of food poisoning) A Eukaryote Eukaryotes • All cells except bacteria are eukaryotic. • Early bacteria released oxygen into the air through photosynthesis. Oxygen is necessary for eukaryotic cells to make energy. So, eukaryotic cells could develop. This is called the “oxygen revolution”. Eukaryotic Animal Cell Eukaryotic Plant Cell Cell Membrane: controls what enters & leaves the cell Plasma (cell) Membrane Cell Wall •Found only in plant cells •Gives plant cells structure •Makes up the bark of trees Cell Wall Video 35 sec Nucleus Contains DNA, so the nucleus is called the “brain” of the cell. It controls all cell activities. Nucleus DNA Nucleolus & Ribosomes • Nucleolus is found within the nucleus. • It makes ribosomes, which will then leave the nucleus and go into the cytoplasm. • Ribosomes: the place where proteins are made. Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) •Passageways in the cell for transportation of molecules •Rough ER has ribosomes •Smooth ER does not have ribosomes ER 1 min Golgi Apparatus Golgi apparatus •Repackages proteins and lipids. •It exports molecules through structures called vesicles. Lysozomes Lysosomes •Digestion of worn-out cell parts •The lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. Mitochondria Mitochondria • The “mighty mitochondria” provides energy for the cell. • It is referred to as the “powerhouse” of the cell. The mitochondria is folded! • The mitochondrion has an inner membrane and an outer membrane. The inner membrane has many folds. Energy (ATP) is made along these folds. • The folds allow for high surface area, which means that a lot of energy can be made in a small space. Chloroplast • This green structure is found only in plant cells. • Photosynthesis occurs here. • Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose (sugar) and oxygen. Chloroplasts Cytoskeleton A series of protein fibers and microtubules that provide structure and movement of organelles inside of the cell. Cilia and flagella are structures that help a cell to move. Cilia Flagella Cilia & Flagella 40 sec Plant vs Animal Cells • All cells (prokaryotic & eukaryotic) have 4 structures in common – remember them? • Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells. • Some animal cells have cilia and flagella. • Plant cells have: – chloroplasts (for photosynthesis) – cell wall – large central vacuole Organization of Organisms Organization of Cells in a Multicellular Organism • Multicellular: made up of many cells • Multicellular organisms can be large because cells specialize and do different functions. • Specialized cell: a cell programmed by its DNA to perform one primary job for the organism. Organization of Cells in a Multicellular Organism • Cell • Tissue – a group of cells with similar structure & function. • Organ – a group of tissues which have formed a specialized structure with a specific function. • Organ system – group of organs which carry out a major body function • Organism