Schizophrenia & Schizoaffective (PowerPoint)
advertisement

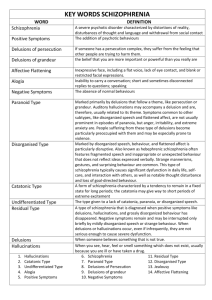
Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder DSM-IV-TRTM American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision. Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association, 2000 Russell L. Smith, M.S., LPA, HSP-PA, CCBT, MAC, FABFCE, NCP In Schizophrenia, “Psychotic” refers to delusions, any prominent hallucinations, disorganized speech, or disorganized or catatonic behavior. Subtypes 295.30 295.10 295.20 295.90 295.60 Paranoid Disorganized Catatonic Undifferentiated Residual Course Specifiers Episodic With Interepisode Residual Symptoms Episodic With No Interepisode Residual Symptoms Continuous Single Episode in Partial Remission* Single Episode in Full Remission* Other Or Unspecified Pattern *With Prominent Negative Symptoms can be added ... Range of Emotional & Cognitive Dysfunction* Perception Inferential thinking Language & communication Behavioral monitoring Affect Fluency & productivity of thought & speech Hedonic capacity Volition & drive Attention * Associated with impaired occupational or social functioning Positive Symptoms Reflect an excess or distortion of normal functions “psychotic dimension ” Thought content Perception “disorganization dimension ” Language & thought processes Self-monitoring of behavior Negative Symptoms A decrease or loss of normal functions Range & intensity of emotional expression Fluency & productivity of thought and speech Initiation of goal-directed behavior Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion A A. Characteristic symptoms: two or more ... for significant portion of 1-month (or less if successfully treated): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech (e.g., frequent derailment or incoherence) Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative symptoms, i.e., affective flattening, alogia, or avolition Note: Only one Criterion A symptom is required if delusions are bizarre or hallucinations consist of a voice keeping up a running commentary on the person’s behavior or thoughts, or two or more voices conversing with each other. Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion B B. Social/Occupational Dysfunction ... • ... for a significant portion of time since onset ... • one or more major areas of functioning such as work, interpersonal relations, or self-care ... markedly below level prior to onset • If onset in childhood or adolescence ... failure to achieve expected level of interpersonal, academic, or occupational achievement Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion C C. Duration • Continuous signs persist for at least 6 months at least one month meet Criterion A (less than month if effectively treated) may include prodromal or residual symptoms • may be manifested by only negative symptoms or two or more symptoms listed in Criterion A presented in an attenuated form (e.g., odd beliefs, unusual perceptual experiences). Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion D D. Schizoaffective and Mood Disorder have been ruled out because either • there has been no Major Depressive, Manic, or Mixed Episodes, or • if mood episodes have occurred during the active-phase symptoms, their total duration has been brief relative to the duration of the active and residual periods. Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion E E. Substance/general medical condition exclusion: • The disturbance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) • The disturbance is not due to a general medical condition. Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criterion F F. Relationship to Pervasive Developmental Disorder • If there is a history of Autism Disorder or another Pervasive Developmental Disorder ... the additional diagnosis of Schizophrenia is made only if prominent delusions or hallucinations are also present ... for at least one month (or less if successfully treated). 295.30 Paranoid Type Preoccupation with one or more delusions or frequent auditory hallucinations. None of the following is prominent: • disorganized speech • disorganized or catatonic behavior • flat or inappropriate affect. 295.10 Disorganized Type All of the following are prominent: disorganized speech disorganized behavior flat or inappropriate affect. The criteria are not met for Catatonic Type. 295.20 Catatonic Type At least two of the following: motoric immobility as evidenced by catalepsy (including waxy flexibility) or stupor excessive motor activity (purposeless and not influenced by external stimuli) extreme negativism or mutism peculiarities of voluntary movement as evidenced by posturing, stereotyped movements, prominent mannerisms, or prominent grimacing echolalia or echopraxia 295.90 Undifferentiated Type ... the presence of symptoms that meet Criterion A of Schizophrenia but that do not meet criteria for the Paranoid, Disorganized, or Catatonic Type. 295.60 Residual Type Absence of prominent delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, and grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior. There is continuing evidence of the disturbance ... presence of negative symptoms, or two or more of the symptoms listed in Criterion A but in an attenuated form (e.g., odd beliefs, unusual perceptual experiences). Schizophrenia: Features Cultural & Socioeconomic Beliefs & Religion Language, Emotional Expression & Nonverbal style Industrial vs Developing Men: Onset 18-25 years ... more negative symptoms (flat affect, avolition, social withdrawal) Women: Onset 25 to mid-30s (3% to 10% onset after 40) ... better permorbid functioning, more affective symptoms, paranoid delusions, and hallucinations 295.70 Schizoaffective Disorder A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which, at least some time, there is either a Major Depressive Episode, a Manic Episode, or a Mixed Episode concurrent with symptoms that meet Criterion A for Schizophrenia. B. During the same period of illness, there have been delusions or hallucinations for at least 2 weeks in the absence of prominent mood symptoms. 295.70 Schizoaffective Disorder C. Symptoms that meet criteria for a mood episode are present for a substantial portion of the total duration of the active and residual periods of the illness. D. Not due to drug of abuse, medication or a general medical condition. Specify Type: Bipolar Type: ... if Manic or Mixed Episodes (or Manic or Mixed and Major Depressive Episodes) Depressive Type: Major Depressive Episodes TO BE OR NOT MALADAPTIVE (B-) ADAPTIVE (B+) R+ of BR- of BP+ of B+ P- of B+ R+ of not B+ R- of not B+ P+ of not BP- of not B- R+ of B+ R- of B+ P+ of BP- of BR+ of not BR- of not BP+ of not B+ P- of not B+ R+ of B+ P+ of not B+ R- of B+ R- of not B- P- of B- R+ of not B- YOU P+ of B- P- of not B+