Descartes - Psychology
advertisement

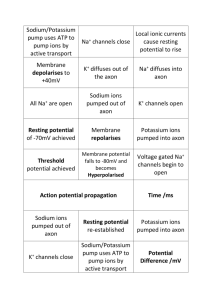
Descartes View K&W 4-1 Luigi Galvani (1737-1798) Electrified Frogs • Luigi Galvani • Frog legs attached to wire in market • Electrical storm made legs move • Early idea of electrical properties of nervous system Electrical Stimulation K&W 4-2 Neural Communication The journey of nerve message As message passes along the nerve, Electrode indicates a shift from negative to positive and then back to negative again K&W 4-4 Neural Communication Cell body end of axon Direction of neural impulse: toward axon terminals Hodgkin and Huxley Two Cambridge profs and a squid get together (1939) Squid and axon K&W 4-5 Microelectrodes KW 4-7 Recording from an axon K&W 4-6 Reversal of charges K&W 4-15 Ions Ions on the move Concentration gradient: move from area of higher concentration to area of lower concentration K&W 4-8 Ions meet a barrier No pores = No movement of ions With pores, ions can move. Charge develops Electrical Gradient: opposite charges attract (+ --) like charges repel (+ +) K&W 4-9 Ions of the axon KW 4-10 Resting Cell Recording KW 4-10 Resting Cell Charges KW 4-10 Depolarization A Graded Potential KW 4-11 Hyperpolarization KW 4-11 A Graded Potential Axons get polarized K&W 4-11 When an action potential occurs, Na+ and K+ work together KW 4-13 Fig. 2-17, p. 43 Phases of the action potential K&W 4-14 Fig. 2-15, p. 39 Neural Communication Reversal of Charges Cell body end of axon Direction of neural impulse: toward axon terminals Falling dominos K&W p. 131 Ion flow K&W 4-15 Properties of Action Potentials • • • • • All or none: fires completely or not at all Self-propagates: recreates itself Does not degrade: doesn’t lose power Full strength to the end of axon Axon can be any length Analogies for Action Potentials • Band of Fire moving down tube • Ring sliding down a string • Doing “the wave” in stadium End of segment one Naked Neurons • Neurons without myelin sheath • Slower • Shorter • Can’t carry messages long distances • What does myelin sheath provide? Louis-Antoine Ranvier • French physician discoverer of the myelin sheath. • 1835-1922 • In 1878 he discovered myelin and the famous nodes which received his name Nodes of Ranvier K&W 4-16 Saltatory conduction K&W 4-17 Multiple Sclerosis • • • • Jacqueline Du Pre 1945-1987 MS diagnosis in 1971 Hilary and Jackie (1998 movie) Neuronal Integration • To fire or not to fire, that is the question • All or none principle: all or nothing at all • Why important? Firing Line Threshold Sherrington • Sir Charles Scott Sherrington • (1857-1952) • Withdrawal reflex • Principle of summation • Nobel prize in medicine 1932 Withdrawal Reflex in Dogs • One mild pinch between toes no response • Two pinches quickly in same spot withdraw paw • Temporal Summation • Temporal = over time Paw reflex: part 2 • One mild pinch in one location no response • Two pinches in different locations withdraw paw • Spatial Summation • Spatial = over space Temporal: one location Postsynaptic cell Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential Presynaptic cell KW 4-19 synapse Temporal EPSP KW 4-19 top Spatial: more than one location K&W 4-20 Spatial EPSP KW 4-19 Importance of EPSP • • • • Excite cells Bring about activity Sensation felt Muscle moved Excitation must be balanced • Nervous system can’t run on just excitation • Sometimes better not to respond • Role on inhibition • Calm down the nervous system Role of Inhibition • Provides break for the nervous system • Lowers activity levels • Keeps the brain from over-excitation, as in epilepsy EPSP vs IPSP Temporal IPSP KW 4-19 Temporal Combos Spatial Combos A cell decides to fire Democracy of Cells K&W 4-21 Emotional Arousal Autonomic nervous system controls physiological arousal Sympathetic division (arousing) Parasympathetic division (calming) Pupils dilate EYES Pupils contract Decreases SALIVATION Increases Perspires SKIN Dries Increases RESPIRATION Decreases Accelerates HEART Slows Inhibits DIGESTION Activates Secrete stress hormones ADRENAL GLANDS Decreases secretion of stress hormones Control over heart • Sympathetic excites • Parasympathetic inhibits • Work together to control heart